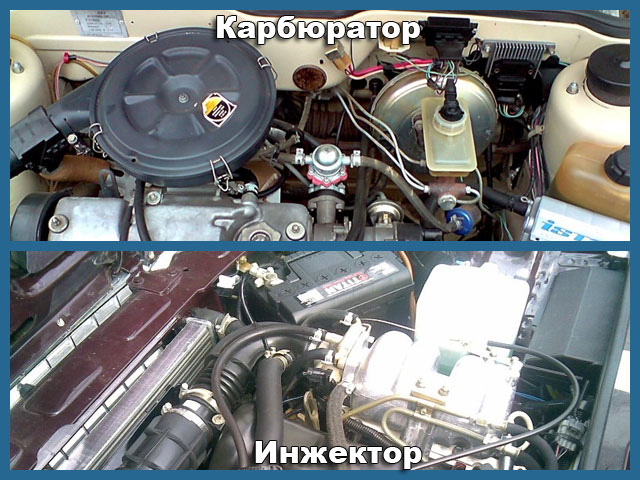
What is the difference between an injector and a carburetor
Content
There are different ways to fill the working volume of the cylinders of an internal combustion engine with a combustible mixture. According to the principle of mixing gasoline with air, they can be conditionally divided into carburetor and injection. There are fundamental differences between them, although the result of the work is approximately the same, but there are also quantitative differences in dosing accuracy.
We will consider in more detail about the advantages and disadvantages of a gasoline engine power system below.
The principle of operation of the carburetor engine
In order to create conditions for combustion in the cylinder, gasoline must be mixed with air. The composition of the atmosphere contains oxygen, which is necessary for the oxidation of gasoline hydrocarbons with the release of a large amount of heat.
Hot gases have a much larger volume than the original mixture, tending to expand, they increase the pressure on the piston, which pushes the crankshaft crankshaft and makes it rotate. Thus, the chemical energy of the fuel is converted into mechanical energy that drives the car.
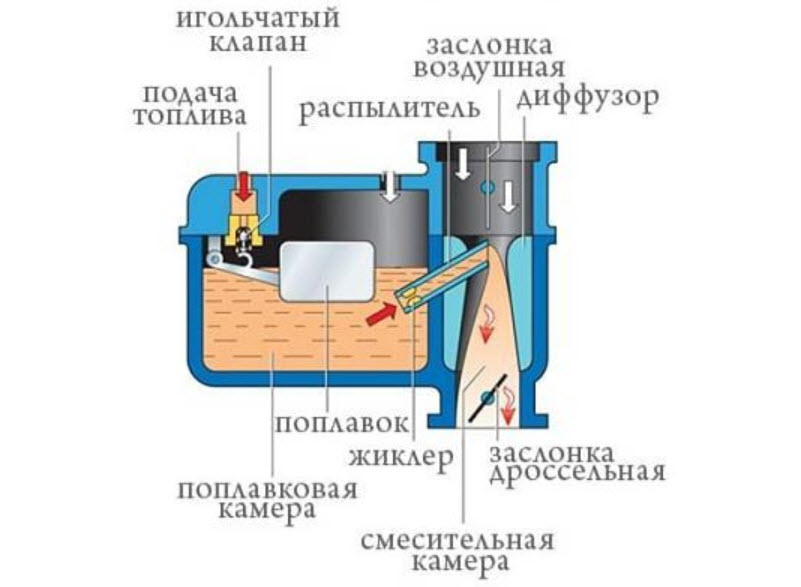
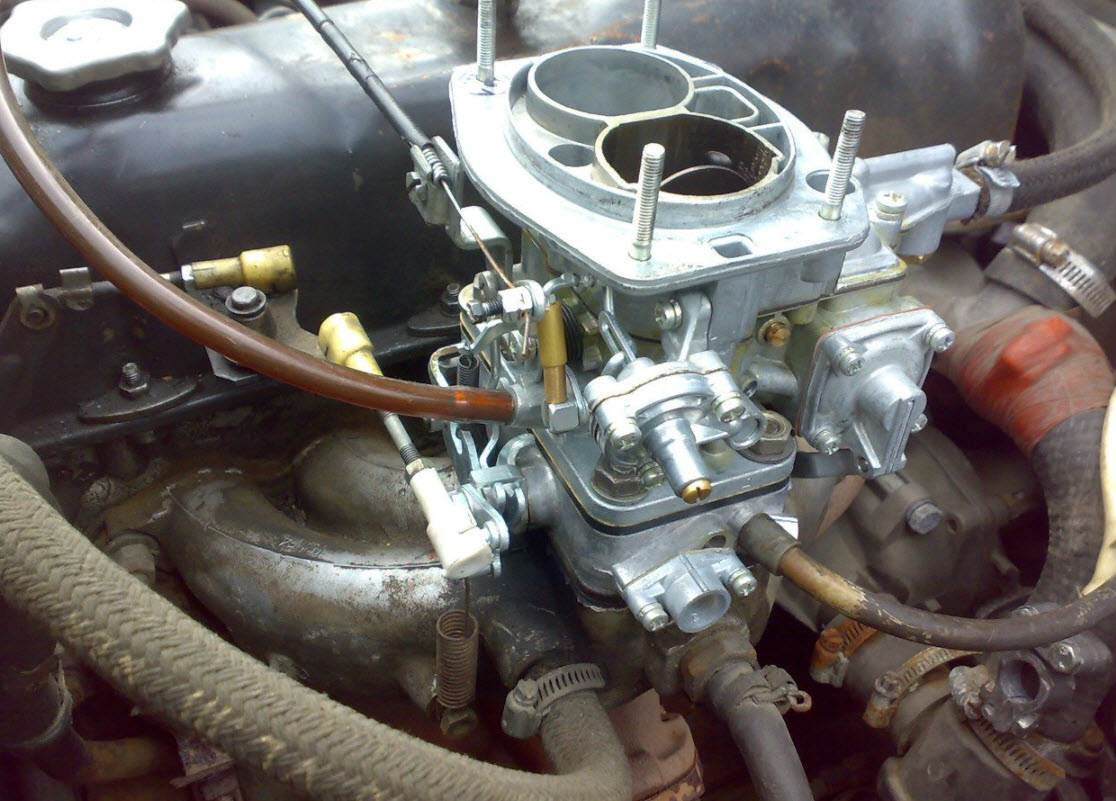
The carburetor is needed for fine atomization of gasoline and mixing it with the air entering the cylinder. At the same time, the composition is dosed, since for normal ignition and combustion, a fairly strict mass composition is needed.
To do this, in addition to the sprayers themselves, the carburetors have several dosing systems, each of which is responsible for a certain mode of engine operation:
- main dosing;
- idle system;
- a starting device that enriches the mixture on a cold engine;
- an accelerator pump that adds gasoline during acceleration;
- econostat of power modes;
- level controller with float chamber;
- transition systems of multi-chamber carburetors;
- various economizers that regulate and limit harmful emissions.
The more complex the carburetor, the more of these systems it has, usually they are hydraulically or pneumatically controlled, although in recent years, electronic devices have become used.
But the basic principle has been preserved - the fuel emulsion formed by the joint work of the air and fuel jets is drawn into the air flow sucked in by the pistons through the atomizers in accordance with Bernoulli's law.
Features of the injection system
The main difference between injectors, or more precisely, fuel injection systems, was the supply of gasoline under pressure.
The role of the fuel pump is no longer limited to filling the float chamber, as it was in the carburetor, but has become the basis for dosing the amount of gasoline supplied through the nozzles to the intake manifold or even directly to the combustion chambers.
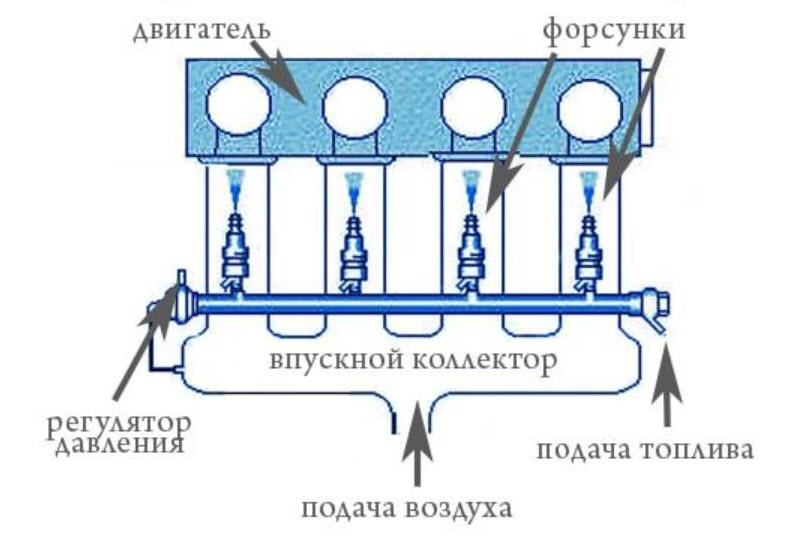
There are mechanical, electronic and mixed injection systems, but they have the same principle - the amount of fuel per operation cycle is calculated and strictly measured, that is, there is no direct connection between the air flow rate and the cycle consumption of gasoline.
Now only electronic injection systems are used, where all the calculations are done by a microcomputer that has several sensors and continuously regulates the injection time. The pump pressure is maintained stable, so the composition of the mixture is uniquely dependent on the opening time of the solenoid valves of the injectors.
Advantages of a carburetor
The advantage of a carburetor is its simplicity. Even the most primitive designs on old motorcycles and cars regularly performed their role in powering the engines.
A chamber with a float to stabilize the pressure on the fuel jet, an air channel of the emulsifier with an air jet, an atomizer in the diffuser and that's it. As the requirements for motors increased, the design became more complicated.
However, the fundamental primitiveness gave such an important advantage that carburetors are still preserved in some places, on the same motorcycles or off-road vehicles. This is reliability and maintainability. There is nothing to break there, clogging can become the only problem, but you can disassemble and clean the carburetor in any conditions, no spare parts are required.

Injector advantages
But a number of shortcomings of such atomizers gradually led to the appearance of injectors. It all started with a problem that arises in aviation, when the carburetors refused to work normally when the aircraft rolled over or even deep banks. After all, their way of maintaining a given pressure on the jets is based on gravity, and this force is always directed downwards. The pressure of the fuel pump of the injection system does not depend on the spatial orientation.
The second important property of the injector was the high accuracy of dosing the composition of the mixture in any mode. The carburetor is not capable of this, no matter how complicated it is, and the environmental requirements grew every year, the mixture had to burn out completely and as efficiently as possible, which was also required by efficiency.
Accuracy gained particular importance with the advent of catalytic converters, which serve to burn off harmful substances in the exhaust, when poor-quality fuel regulation leads to their failure.

The high complexity and associated decrease in the reliability of the system was offset by the stability and durability of electronic components that do not contain wear parts, and modern technologies make it possible to create sufficiently reliable pumps and nozzles.
How to distinguish an injection car from a carburetor
In the cabin, one can immediately note the presence of a control knob for the carburetor starting system, also called suction, although there are also automatic starters where this knob is absent.
The mono injection unit is very easy to confuse with a carburetor, outwardly they are very similar. The difference is the location of the fuel pump, at the carburetor it is located on the engine, and at the injector it is quenched in the gas tank, but single injections are no longer used.
Traditional multipoint fuel injection is defined by the absence of a common fuel supply module, there is only an air receiver that supplies air from the filter to the intake manifold, and on the manifold itself there are electromagnetic nozzles, one per cylinder.
Approximately similarly, direct fuel injection is arranged, only there the nozzles are on the head of the block, like spark plugs, and the fuel is supplied through an additional high-pressure pump. Very similar to the power system of diesel engines.
For the driver, the injection power system is an undoubted boon. There is no need to additionally manipulate the starting system and the gas pedal, the electronic brain is responsible for the mixture in any conditions and does it accurately.
For the rest, the environmental friendliness of the injector is important, practically only relatively harmless carbon dioxide and water vapor are released from the exhaust system into the environment, so carburetors on cars are irretrievably a thing of the past.
