What is a shock absorber and how does it work
Content
- What is a shock absorber
- Shock absorber history
- Shock absorber design
- Why shock absorbers are needed
- Types and types of automobile shock absorbers
- Which shock absorbers are better
- How to check shock absorber struts
- How to replace shock absorbers
- Video - how shock absorbers work
- Video - how to tell a bad shock absorber from a good one
- Video "How to adjust the shock absorber"
- Questions and answers:
A shock absorber is a key element of the car's suspension designed to compensate for the loads on the chassis when driving on rough roads. Consider what a shock absorber is, how it works, what types there are and how to make a replacement.
What is a shock absorber
A modern shock absorber is a complex mechanism that dampens vibrations, absorbs shocks and ensures constant contact of the wheels with the road surface when driving a car. It is installed next to the wheel. With the help of a lever system, mechanical loads (shocks and vibrations) are transmitted from the rotating wheel to the mechanism.

This part is equipped with a spring, which provides a quick return of the stem after compression when hitting a bump. If this process does not occur quickly, then on the roads the car will become uncontrollable.
Shock absorber history
As the transport evolved, the designers came to the conclusion that in addition to a powerful and efficient power unit with a solid body, the car needs a good suspension that would soften the shocks from bumps on the road. The first shock absorbers had an unpleasant effect - during the ride, they strongly swayed the vehicle, which greatly affected the control.
Spring shock absorbers partially damped body vibrations due to the friction force between the sheets, but this effect was not completely eliminated, especially with an impressive load of transport. This prompted the designers to design two separate elements. One was responsible for softening the impacts from the wheel on the body, and the other restored the contact patch of the wheel, springing it, quickly bringing the damper element to its original position.
At the beginning of the last century, a separate suspension damping element was developed. It was a dry friction shock absorber, which included friction discs. The first piston oil telescopic shock absorbers appeared in the 50s of the last century. Their operation was based on the principle of fluid friction.
The design of these shock absorbers was borrowed from the design of the aircraft chassis. This type of shock absorber design is still used today.
Shock absorber design
Most shock absorbers consist of such nodes:
- Steel hollow tube (cylinder). On the one hand it is muffled. An eye is welded to this part, which allows you to fix the rack on the wheel hub. The tank is filled with liquid (a mixture of gas and liquid or only gas), providing load compensation during compression of the piston. On the open side, a stem seal is installed to prevent leakage of fluid from the cavity.
- Shock Absorber This is a steel bar, the cross section of which depends on the model of the mechanism. It is placed in the tank. On the one hand, the rod is attached to the thrust bearing, and on the other, a piston is attached to it, placed inside the cylinder.
- Piston. This element moves inside the cylinder, creating pressure on the liquid or gas inside the tube.
- Bypass valve. Mounted on the piston, and has several holes with spring-loaded valves. When the piston moves, one group of valves is activated, which ensures flow from the cavity under the piston to the part above it. The smoothness of the course is ensured by resistance due to small holes (the liquid does not have time to quickly move between the cavities). A similar process occurs during the recoil (when the piston rises), only in this case the valves of another group are triggered.

The device of modern damper mechanisms is constantly being improved, which increases their efficiency and reliability. The design of the shock absorbers may vary significantly depending on the modification of the mechanism. However, the principle of operation remains unchanged. When pushing, the rod moves the piston inside the cylinder, in which liquid or gas is compressed.
Sometimes shock absorbers are confused with gas springs that are installed on the boot luggage or on the hood. Although they are similar in appearance, each of them performs its function. Dampers dampen shocks, and gas springs provide smooth opening and holding in this position of heavy covers.

What is the difference between shock absorbers and struts
The shock absorber and the strut are attached differently. The strut design eliminates the need for an overhead ball joint and arm. It is attached to the lever and ball only at the bottom, and at the top it is installed in the support bearing.
The shock absorber itself is attached with silent blocks without a thrust bearing. The rod has a large diameter at the strut, while the shock absorber has a small one. Thanks to this method of fastening, the strut is able to perceive multidirectional loads, and the shock absorber - only along its axis. The shock absorber can be part of the strut.
Why shock absorbers are needed
When creating vehicles, the first developers faced a serious problem. While driving on the road, the driver experienced terrible discomfort from constant shaking. In addition, due to the load, the parts of the chassis quickly failed.
To eliminate the problem, rubber hoses extended along the wheels began to be put on. Then came the springs that damped the bumps, but the transport lacked stability. on bumps the car swayed a lot.

The first shock absorbers appeared in 1903, and were made in the form of springs fixed to levers near each wheel. Basically, they were installed on sports cars, as horse-drawn vehicles did not need such a system due to low speeds. Over the years, this development has been improved, and friction shock absorbers are replaced by hydraulic counterparts.
When driving on bumps, the wheels of the machine must be in constant contact with the coating. Vehicle handling will also depend on the quality of the shock absorber.

When the car accelerates, the body leans back. Because of this, the front of the car is unloaded, which reduces the adhesion of the front wheels to the road. During braking, the reverse process occurs - the body leans forward, and now the contact of the rear wheels with the ground is broken. When turning, the load moves to the opposite side of the car.
The task of shock absorbers is not only to dampen shocks, providing maximum comfort for the driver, but also to maintain the car body in a stable horizontal position, preventing it from swinging (as it was in cars with a spring suspension), which increases the controllability of the vehicle.

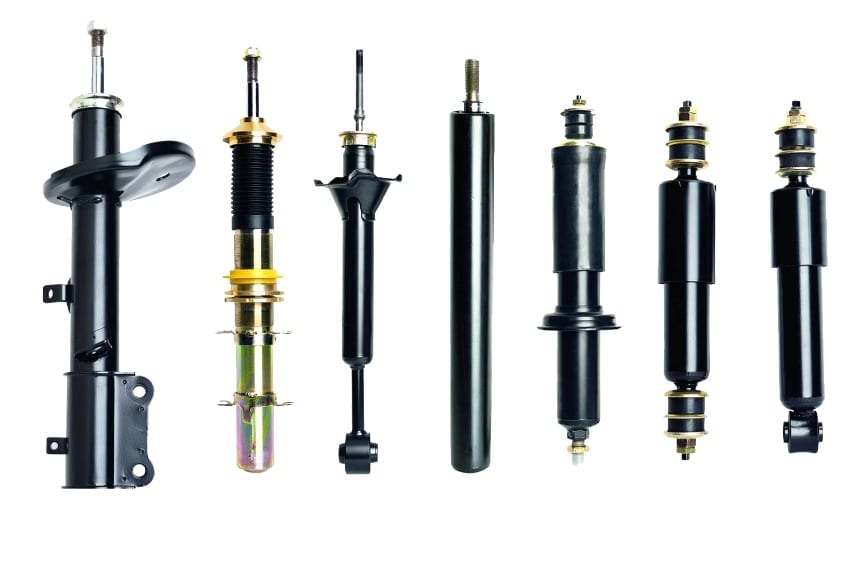
Types and types of automobile shock absorbers
All shock absorbers are divided into three types:
- Hydraulic. There is oil in the reservoir, which, under the action of the piston, flows from one plane of the reservoir to another.
- Gas-hydraulic (or gas-oil). In their design, the compensation chamber is filled with gas, which reduces the likelihood of breakdown of the bottom due to excessive load.
- Gas. In this modification, the gas used in the working cylinder under pressure is used as a damper.

In addition, damper mechanisms are divided into:
- single tube;
- two-pipe;
- adjustable.
Each modification has its own design and principle of operation.
Monotube (monotube) shock absorbers

Single-tube modifications are a new generation of damping mechanisms. They have a simple design, and consist of:
- a flask partially filled with oil and gas (among single-tube models, there are completely gas ones);
- a rod that moves the main piston inside the cylinder;
- the piston mounted on the rod is equipped with bypass valves through which oil flows from one cavity to another;
- a separation piston separating the oil chamber from the gas one (in the case of gas-filled models, this element is absent).

Such modifications work according to the following principle. During oil squeezing, the piston valves open in the reservoir. The pressure at the bottom of the cylinder is reduced by fluid flowing through small holes in the piston. The rod gradually lowers, compensating for shocks during the movement of the car.
The gas cavity is filled with nitrogen. Due to the high pressure (over 20 atm.), The piston does not reach the bottom of the cylinder, which reduces the likelihood of penetration of the shock absorber on large bumps.
Two-pipe types of shock absorbers
Today it is the most common category of shock absorbers. They consist of the following elements:
- The case, inside which is placed another flask. In the space between the walls of the vessels there is a gas and compensation cavity.
- The flask (or slave cylinder) is completely filled with shock absorbing fluid. Inlet and outlet valves are made at the bottom.
- The rod pushing the piston is the same as in the single-tube version.
- Piston equipped with check valves. Some open when the piston moves down, and others when it comes back up.

Such mechanisms work according to the following principle. The rod presses on the piston, due to which oil flows into the upper part of the working cylinder. If the pressure increases sharply (the car runs over a bump - a strong push occurs), then the bottom valves of the working flask are activated.
Leaked oil in the compensation cavity (the space between the walls of the working cylinder and the housing) compresses the air located in the upper part of the chamber. Stabilization of rebound forces occurs due to the operation of piston and bottom valves, through which oil moves back to the working chamber.
Combined (gas oil) shock absorbers

This type of shock absorber replaced the previous type. The design of the mechanisms is identical to the hydraulic modifications. Their only difference is that in the combined damper struts the gas is under a pressure of 4-20 atmospheres, and in hydraulic ones - under normal atmospheric pressure.
This is called gas backwater. This modernization allows automakers to improve the controllability of cars. The gas support serves as an additional compensator, increasing the efficiency of the rack. For front and rear damper struts, different gas pressures in the compensation cavity may be required.
Adjustable shock absorbers

This type of shock absorbers is installed on expensive cars equipped with the function of choosing the road surface. Such mechanisms are identical to the two-pipe modifications, only they have an additional reservoir. It can be next to the rack, or made in the form of another tube placed inside the housing (forms an additional bump cavity).

Such shock absorbers are paired with a pump station, which changes the pressure in the gas cavity, giving the suspension the desired characteristics. Parameters are monitored by electronics. Adjustment is made from the inside of the machine using the appropriate control knobs. Here are the most common types of settings:
- Standard. The shock absorber is operating normally. Suspension at this setting is soft, which gives the ride increased comfort. In this case, the stroke of the shock absorbers is much larger than with other settings. Pits on the road in the cabin are practically not felt.
- Comfort. The gas pressure in the compensation chamber increases slightly, providing an increase in rebound stiffness. Most drivers use this particular function. It is considered the “golden mean” between ride comfort and handling.

- Highway. The stroke in this mode becomes even shorter. It is included for riding on flat roads. At this setting, there are flaws in the clarity of the steering (if any). The machine will behave softer with significant load.
- Sports. If you drive on normal roads in this mode, then the driver may soon need a chiropractor. The body of the car accurately transmits every hillock of the road, as if the car had no suspension at all. However, the presence of this mode allows you to check how high-quality cars are made. The responsiveness of the steering is felt. Thanks to the minimal rocking of the body provides maximum traction.
Such shock absorbers are equipped with expensive car models. They are also used for professional tuning. With the help of such a suspension, you can not only change the stiffness of the rebound, but also change the clearance of the machine.

More primitive adjustable shock absorbers look like a regular two-pipe combination. A thread is cut on the rack housing, on which a spring support is wound. This modification is called a coilover. Adjustment is carried out manually using a wrench (turning the support nut, moving it either up or down).
Watch also a video about the device and classification of shock absorbers:
Which shock absorbers are better
Each type of shock absorber has its own advantages and disadvantages. The ideal option is to select the struts and springs in accordance with the recommendations of the machine manufacturer. "Soft" models will provide increased comfort during the trip, but at the same time reduce the grip of the wheels with the road. With the “hard” ones, the opposite effect is observed - the stability of the machine is improved by lowering comfort for the driver and passengers.
1. Monotube. The advantage of such damping racks is:
- High precision machine control. They do not allow the car to swing and reduce roll in corners.
- They can be installed upside down. The gas pressure and oil do not mix due to the floating piston.
- The cooling of the working cylinder is more effective, because air blows directly through its walls. Due to the absence of a housing, the size of the piston and reservoir are increased, due to which the range of operation of the shock absorber is expanded in comparison with two-pipe counterparts.


Among the shortcomings, the following can be distinguished:
- Vulnerability to Damage. Since they are not equipped with a shell, even slight deformation of the bulb leads to failure of the entire mechanism - the piston can no longer move freely inside the tank. The only solution to this problem is to replace the rack.
- High sensitivity to changes in ambient temperature. The warmer it is outside, the higher the gas pressure, which increases the stiffness of the suspension.
2. Two-pipe. The advantages of this modification are:
- Simple design, making it cheaper than previous counterparts.
- The slave cylinder is protected from external damage. The rack body serves as a buffer.
- Belong to the category of "soft" shock absorbers.


The disadvantages include such factors:
- High aeration of oil. The air in the gas cavity is under atmospheric pressure, so liquids are easier to mix with. The problem persists even when replacing normal air with nitrogen.
- Bad cooling. The working cylinder, in fact, has a double shell, due to which the oil heats up during friction of the piston, its fluidity increases, and the shock absorber becomes even softer.
3. Combined. Since gas-oil shock absorbers are an improved version of conventional two-pipe, the advantages and disadvantages are the same. Their main difference is the lack of aeration due to the high pressure in the gas backwater.


4. Adjustable. This category of dampers is the next step in the evolution of the adaptive suspension of the machine. Their advantages:
- Adjustment of the damper to the appropriate road surface. This will allow you to choose the optimal position between the stability of the car and ride comfort.
- Low-cost coilovers are easy to adjust - just turn the retaining nut to compress or loosen the spring. More expensive automatic models provide fine-tuning the suspension stiffness. In this case, it is enough to move the regulator to the appropriate position. Some models allow you to separately adjust the front and rear racks.


If the car was not equipped with an adaptive suspension from the factory, its installation can damage the mounting position of the rack. Changing the factory characteristics of the car can improve the performance of the car, but at the same time, significantly reduce the working life of different parts of the suspension and chassis.


When choosing between the oil and gas filled type of shock absorbers, you should pay attention to:
- cost - gas more expensive than oil;
- comfort and durability - the gas version is tougher than the oil one, therefore it is not suitable for trips on country roads, however they last longer than liquid ones;
- controllability of the car - the gas-filled version is ideal for sports driving, as it ensures stability of the car on bends and small climbs, as well as reduces braking distances. Oil-filled models are designed for measured driving, since at high speed due to buildup and roll, road adhesion deteriorates.
Here's another video to help determine which shock absorber is better:


Watch this video on YouTube
How to check shock absorber struts
To determine the malfunction of the racks, you must perform a simple procedure. At speeds between 20-30 km / h. sharply press a brake. If the shock absorbers have worked out their life, then the car will “bite” forward, or the rear part will noticeably jump.
You can also check the suspension on a bumpy and winding road. If the machine began to sway more than usual, then the service life of the racks has expired, and they must be replaced.


Another way to check shock absorbers is on a vibration stand. Such a procedure will help determine the state of the mechanisms and how urgently they need to be changed.
The need for replacement appears as a result of the natural wear of parts, as well as due to excessive loads on the damper mechanism (frequent overloads and fast driving along bumps).
Shock absorbers resource
Every part of a car or motorcycle has its own working resource. This is especially true of mechanisms that are regularly exposed to heavy loads. The service life of shock absorbers directly depends on the driver's accuracy (he goes around bumps or rushes along them at high speed), the condition of the roads and the weight of the car.
An average car operating on the territory of the CIS needs to be replaced with shock absorbers after about 60-70 thousand kilometers. In this case, it is recommended to carry out diagnostics every 20 thousand.
Faults and how to identify them?
Visually, a shock absorber malfunction can be identified by the nature of the damping while driving. If the car begins to sway unnaturally when driving on uneven roads, then the shock absorbers should be diagnosed. To do this, first of all, you need to inspect the condition of the shock absorbers and their anthers.
A failed damper will be smeared with oil (the working fluid has drained out of the container). Oil leaks on the housing or anthers are the reason for replacing the shock absorber. The performance of this part is checked by an attempt to swing the car body in a vertical direction (press and release several times, trying to increase the amplitude of the vibration, applying more effort each time). A serviceable shock absorber will not allow the car to swing, but will stop the swing almost immediately.
How to replace shock absorbers


Shock absorbers are replaced in the following sequence.
- Raise the machine on the lift. If it is lifted by means of jacks, then changing the front shock absorbers, the machine must be put on the handbrake, and when installing the rear ones, the gear must be engaged (in rear-wheel drive cars, the front wheels must be blocked in another way, for example, using wheel chocks).
- Unfasten mount on steering knuckle.
- When replacing the front struts, the steering tip is removed.
- Unscrew the rod mount on the support bearing.
Rack installation is carried out in the reverse order.
The example of VAZ 2111 shows how the procedure is performed:


Watch this video on YouTube
Recommendations from professionals:
- Before installing a new rack (for a two-pipe modification), the shock absorber must be pumped so that the air leaves the working cylinder. If this is not done, then during the ride “dips” of the piston will appear. Pumping is carried out as follows: the shock absorber, turned upside down, gently squeeze, fix for 2-3 seconds, in this state it is turned over and after 3-5 seconds. smoothly let go. Then the stand is turned upside down, wait a couple of seconds, and repeat the procedure three to four times. After pumping, the shock absorber should be stored in an upright position, as it will be installed on the car.
- Do not use a pneumatic wrench to tighten the rod mount. Because of this, the stem can turn over and damage the oil seal. If this does not happen, excessive tightening will create tension in the shock absorber rod, because of which it may break on the big bump.
- It is strictly forbidden to fix the rod with pliers and other clamping tools. This will damage the rod mirror. To fix it, use a special key.
- Before final tightening of the stem nut, the vehicle must be lowered from the hoist or jack. So the rod will be twisted smoothly and during the ride will not break or break silent block.


Regarding the comprehensive replacement of shock absorbers, motorists disagree. Some people think that everything needs to be changed immediately, while others are sure that replacing a damaged part is enough.
Although each motorist decides for himself how to repair his car, experts insist on a pair replacement - even if one is out of order, then change both on the side (either front or rear). Due to fatigue wear, old parts in conjunction with new ones can significantly reduce the efficiency of the entire assembly. In any case, it should be remembered: one defective part can adversely affect other important components of the suspension or chassis.
When to change


Here in what cases it is definitely necessary to change racks:
- as a result of visual inspection on the body, traces of fluid leakage were identified;
- deformation of the rack body;
- increased stiffness of the suspension - tangible blows to the body occur at the pits;
- the car sank noticeably (more often one shock absorber fails, so the car will sag on the corresponding side).
The following video shows one of the options how to diagnose the suspension malfunction yourself:


Watch this video on YouTube
If there is a knock in the suspension, you must immediately contact the service station. Such changes in the car cannot be ignored, because the safety of not only the owner of the damaged car, but also other road users depends on them.
Video - how shock absorbers work
Here is a short video on how modern shock absorbers work, as well as their design:


Watch this video on YouTube
Video - how to tell a bad shock absorber from a good one
The following video shows how you can independently determine whether the shock absorbers are still good in the car or are already bad, and they need to be replaced:


Watch this video on YouTube
Video "How to adjust the shock absorber"
Some vehicles have adjustable shock absorbers. Here's how they can be adjusted (using the example of the CITYCOCO air / oil shock absorber for the Skyboard electric scooter):


Watch this video on YouTube
Questions and answers:
What is a shock absorber in a car? This is a thick pipe, sealed on one side, and on the other side a metal piston is inserted into it. The cavity in the pipe is filled with a substance that softens the impact from the wheel, which is transmitted to the body.
What types of shock absorbers are there? There are three main modifications: oil, gas and gas-oil. The experimental option is the magnetic option. The part can consist of one or two pipes. There can also be a remote reservoir.
How to determine if a shock absorber is defective? A defective shock absorber is detected by vibration damping. It is necessary to press on the corresponding part of the body - with a working shock absorber, the car will not swing.