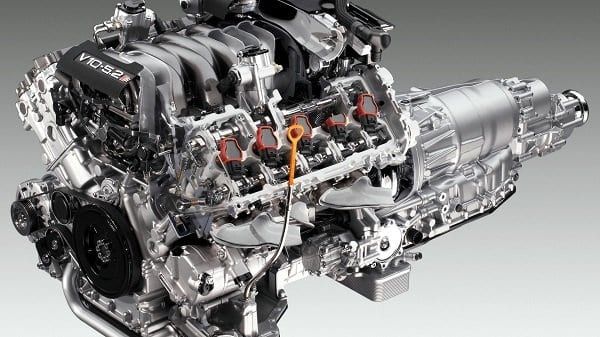
Gasoline engine: device, principle of operation, advantages and disadvantages
Content
In order for the car to be able to move independently, it must be equipped with a power unit that will generate torque and transfer this force to the drive wheels. For this purpose, the creators of mechanical devices have developed an internal combustion engine or internal combustion engine.
The principle of operation of the unit is that a mixture of fuel and air is combusted in its design. The motor is designed to use the energy released in this process to rotate the wheels.

A gasoline, diesel or electric power unit can be installed under the hood of a modern car. In this review, we will focus on the gasoline modification: on what principle does the unit work, what device it has and some practical recommendations on how to extend the resource of the internal combustion engine.
What is a gasoline car engine
Let's start with the terminology. A gasoline engine is a piston power unit that works by burning a mixture of air and gasoline in specially designated cavities. The car can be filled with fuel with different octane numbers (A92, A95, A98, etc.). For more information on what the octane number is, see in another article... It also explains why different types of fuel can be relied on for different engines, even if it is gasoline.
Depending on what goal the automaker pursues, vehicles coming off the assembly line can be equipped with different types of power units. The list of reasons and marketing of the company (every new car should receive some kind of update, and buyers often pay attention to the type of powertrain), as well as the needs of the main audience.
So, the same model of the car, but with different gasoline engines, may leave the factory of an automobile brand. For example, it might be the economical version that is more likely to be noticed by low-income buyers. Alternatively, the manufacturer may offer more dynamic modifications that satisfy the needs of fast-driving enthusiasts.

Also, some cars must be able to carry decent loads, such as pickups (what is the peculiarity of this body type, read separately). A different type of motor is also required for these vehicles. Typically, such a machine will have an impressive working volume of the unit (how this parameter is calculated is separate review).
So, gasoline engines enable auto brands to create models of cars with different technical characteristics in order to adapt them to different needs, ranging from small city cars to large trucks.
Types of gasoline engines
A lot of different data is indicated in the brochures for new car models. Among them, the type of power unit is described. If in the first cars it was enough to indicate the type of fuel used (diesel or gasoline), then today there is a wide variety of some gasoline modifications.
There are several categories by which such power units are classified:
- Number of cylinders. In the classic version, the machine is equipped with a four-cylinder motor. More productive, and at the same time more voracious, have 6, 8 or even 18 cylinders. However, there are also units with a small number of pots. For example, Toyota Aygo is equipped with a 1.0-liter gasoline engine with 3 cylinders. The Peugeot 107 received a similar unit. Some small cars can even be equipped with a two-cylinder petrol unit.

- The structure of the cylinder block. In the classic version (4-cylinder modification), the engine has an in-line arrangement of cylinders. Mostly they are installed vertically, but sometimes tilted counterparts are also found. The next design, which has won the trust of many motorists, is the V-cylinder unit. In such a modification, there is always a paired number of pots, which are located at a certain angle relative to each other. Often this design is used to save space in the engine compartment, especially if it is a large engine (for example, it has 8 cylinders, but it takes up space like a 4-cylinder analogue).
 Some manufacturers install a W-shaped powertrain in their vehicles. This modification differs from the V-shaped analogue by the additional camber of the cylinder block, which in the section has the shape of the letter W. Another type of engines that are used in modern cars is a boxer or boxer. Details of how such an engine is arranged and how it works is described in another review... An example of models with a similar unit - Subaru Forester, Subaru WRX, Porsche Cayman, etc.
Some manufacturers install a W-shaped powertrain in their vehicles. This modification differs from the V-shaped analogue by the additional camber of the cylinder block, which in the section has the shape of the letter W. Another type of engines that are used in modern cars is a boxer or boxer. Details of how such an engine is arranged and how it works is described in another review... An example of models with a similar unit - Subaru Forester, Subaru WRX, Porsche Cayman, etc.
- Fuel supply system. According to this criterion, motors are divided into two categories: carburetor and injection. In the first case, gasoline is pumped into the fuel chamber of the mechanism, from which it is sucked into the intake manifold through a nozzle. An injector is a system that forcibly sprays gasoline into the cavity in which the injector is installed. The operation of this device is described in detail. here... Injectors are of several types, which differ in the peculiarities of the location of the nozzles. In more expensive cars, the sprayers are installed directly in the cylinder head.
- Type of lubrication system. Each ICE operates under increased loads, which is why it needs high-quality lubrication. There is a modification with a wet (classic view, in which the oil is in the sump) or dry (a separate reservoir is installed for storing oil) crankcase. Details about these varieties are described separately.

- Cooling type. Most modern car engines are water cooled. In the classic design, such a system will consist of a radiator, pipes and a cooling jacket around the cylinder block. The operation of this system is described here... Some modifications of gasoline-powered power units can also be air-cooled.
- Cycle type. There are two modifications in total: two-stroke or four-stroke type. The principle of operation of the two-stroke modification is described in another article... Let's take a look at how the 4-stroke model works a little later.
- Air intake type. The air for preparing the air-fuel mixture can enter the intake tract in two ways. Most classic ICE models have an atmospheric intake system. In it, air enters due to the vacuum created by the piston, moving to the bottom dead center. Depending on the injection system, a portion of gasoline is sprayed into this stream either in front of the intake valve, or a little earlier, but in the path corresponding to a particular cylinder. In mono injection, similar to the carburetor modification, one nozzle is installed on the intake manifold, and the BTC is then sucked in by a specific cylinder. Details on the operation of the intake system are described here... In more expensive units, gasoline can be sprayed directly into the cylinder itself. In addition to the naturally aspirated engine, there is also a turbocharged version. In it, the air for the preparation of MTC is injected using a special turbine. It can be powered by the movement of exhaust gases or by an electric motor.

As for the design features, history knows several exotic power units. Among them are the Wankel engine and the valveless model. Details of several working models of motors with an unusual design are described here.
How a gasoline engine works
The vast majority of internal combustion engines used in modern cars operate on a four-stroke cycle. It is based on the same principle as any other ICE. For the unit to be able to generate the amount of energy required to spin the wheels, each cylinder must be cyclically filled with a mixture of air and gasoline. This portion must be compressed, after which it is ignited with the help of a spark that generates spark plug.
In order for the energy released during combustion to be converted into mechanical energy, the VTS must be burned in an enclosed space. The main element that removes the released energy is the piston. It is movable in the cylinder, and is fixed to the crank mechanism of the crankshaft.
When the air / fuel mixture ignites, it causes the gases in the cylinder to expand. Due to this, a large pressure is exerted on the piston, exceeding atmospheric pressure, and it begins to move to bottom dead center, turning the crankshaft. A flywheel is attached to this shaft, to which the gearbox is connected. From it, the torque is transmitted to the drive wheels (front, rear, or in the case of an all-wheel drive car - all 4).
In one cycle of the motor, 4 strokes are performed in a separate cylinder. This is what they do.
Inlet
At the beginning of this stroke, the piston is at top dead center (the chamber above it at this moment is empty). Due to the work of adjacent cylinders, the crankshaft turns and pulls the connecting rod, which moves the piston downward. At this moment, the gas distribution mechanism opens the intake valve (there can be one or two).
Through the open hole, the cylinder begins to fill with a fresh portion of the air-fuel mixture. In this case, air is mixed with gasoline in the intake tract (carburetor engine or multi-point injection model). This part of the engine can be of different designs. There are also options that change their geometry, which allows you to increase the efficiency of the engine at different speeds. Details about this system are described here.

In versions with direct injection, only air enters the cylinder at the intake stroke. Gasoline is sprayed when the compression stroke is completed in the cylinder.
When the piston is at the very bottom of the cylinder, the timing mechanism closes the intake valve. The next measure begins.
Compression
Further, the crankshaft turns (also under the action of pistons operating in adjacent cylinders), and the piston begins to lift through the connecting rod. All valves in the cylinder head are closed. The fuel mixture has nowhere to go and is compressed.
As the piston moves to TDC, the air-fuel mixture heats up (an increase in temperature provokes strong compression, also called compression). The compression force of the BTC portion affects the dynamic performance. Compression may vary from motor to motor. Additionally, we suggest that you familiarize yourself with the topics what is the difference between the degree of compression and compression.
When the piston reaches the extreme point at the top, the spark plug creates a discharge, due to which the fuel mixture ignites. Depending on the engine speed, this process can begin before the piston fully rises, immediately at this moment or a little later.

In a gasoline direct injection engine, only air is compressed. In this case, fuel is sprayed into the cylinder before the piston rises. After that, a discharge is created and gasoline begins to burn. Then the third measure begins.
Working stroke
When VTS is ignited, combustion products expand in the space above the piston. At this moment, in addition to the inertial force, the pressure of the expanding gases begins to act on the piston, and it moves downward again. In contrast to the intake stroke, mechanical energy is no longer transferred from the crankshaft to the piston, but on the contrary - the piston pushes the connecting rod and thus turns the crankshaft.
Some of this energy is used to perform other strokes in adjacent cylinders. The rest of the torque is removed by the gearbox and transferred to the drive wheels.

During the stroke, all valves are closed so that the expanding gases act exclusively on the piston. This cycle ends when the element moving in the cylinder reaches the bottom dead center. Then the last measure of the cycle begins.
Issue
By turning the crankshaft, the piston moves up again. At this moment, the exhaust valve opens (one or two, depending on the type of timing). Waste gases must be removed.
As the piston moves up, the exhaust gases are squeezed out into the exhaust tract. Additionally, its function is described here... The stroke ends at the top of the piston. This completes the motor cycle and starts a new one with the intake stroke.
The completion of the stroke is not always accompanied by the complete closure of a particular valve. It so happens that the intake and exhaust valves remain open for a while. This is necessary to improve the efficiency of airing and filling the cylinders.

So, the rectilinear movement of the piston is converted into rotation due to the specific design of the crankshaft. All classic piston motors are based on this principle.
If the diesel unit operates only on diesel fuel, then the gasoline version can operate not only on gasoline, but also on gas (propane-butane). More details about how such an installation will work is described here.
The main elements of a gasoline engine
In order for all strokes in the engine to be performed in a timely manner and with maximum efficiency, the power unit must consist only of high-quality parts. The device of all piston internal combustion engines includes the following parts.
Cylinder block
In fact, this is the body of the gasoline engine, in which the channels of the cooling jacket, the places for attaching the studs and the cylinders themselves are made. There are modifications with separately installed cylinders.

Basically, this part is made from cast iron, but in order to save weight on some car models, manufacturers can make aluminum blocks. They are more fragile in comparison with the classical analogue.
Piston
This part, which is part of the cylinder-piston group, takes on the action of the expanding gases and provides pressure on the crankshaft crank. When the intake, compression and exhaust strokes are performed, this part creates a vacuum in the cylinder, compresses the mixture of gasoline and air, and also removes combustion products from the cavity.

The structure, varieties and principle of operation of this element are described in detail. in another review... In short, on the side of the valves, it can be flat or with recesses. From the outside, it is connected with a steel pin to the connecting rod.
To prevent the exhaust gases from leaking into the piston space when pushing the exhaust gases during the working stroke, this part is equipped with several O-rings. About their function and design there is A separate article.
Pitman
This part connects the piston to the crankshaft crank. The design of this element depends on the type of engine. For example, on a V-shaped engine, two connecting rods of each pair of cylinders are attached to one crankshaft connecting rod journal.

Mostly high-strength steel is used for the manufacture of this part, but sometimes aluminum counterparts are also found.
Crankshaft
This is a shaft that consists of cranks. Connecting rods are connected to them. The crankshaft has at least two main bearings and counterweights that compensate for vibrations for even rotation of the shaft axis and damping the inertia force. More details about the device of this part are described separately.

On one side, a timing pulley is installed on it. On the opposite side, a flywheel is attached to the crankshaft. Thanks to this element, it is possible to start the motor using a starter.
Valves
In the upper part of the engine in the cylinder head are installed valves... These elements open / close the inlet and outlet ports for the desired stroke.

In most cases, these parts are spring loaded. They are driven by a timing camshaft. This shaft is synchronized with the crankshaft using a belt or chain drive.
Spark plug
Many motorists know that a diesel engine works by heating compressed air in a cylinder. When diesel fuel is injected into this medium, the air-fuel mixture is immediately ignited by the air temperature. With a gasoline unit, the situation is different. For the mixture to ignite, it needs an electric spark.

If the compression in a gasoline internal combustion engine is increased to a value close to that in a diesel engine, then, having a higher octane number, gasoline with strong heating can ignite earlier than necessary. This will damage the unit.
The plug is powered by the ignition system. Depending on the car model, this system may have a different device. Details about the varieties are described here.
Gasoline engine auxiliary working systems
No internal combustion engine can operate independently without auxiliary systems. In order for the car engine to start at all, it must be synchronized with such systems:
- Fuel. It supplies gasoline along the line to the injectors (if it is an injection unit) or to the carburetor. This system is involved in the preparation of military-technical cooperation. In modern cars, the air / fuel mixture is electronically controlled.
- Ignition. It is an electrical part that supplies the motor with a stable spark for each cylinder. There are three main types of these systems: contact, contactless and microprocessor type. All of them determine the moment when a spark is needed, generate a high voltage and distribute the impulse to the corresponding candle. None of these systems will work if faulty crankshaft position sensor.
- Lubricating and cooling. In order for the engine parts to withstand heavy loads (constant mechanical load and exposure to very high temperatures, in some departments it rises to more than 1000 degrees), they need high-quality and constant lubrication, as well as cooling. These are two different systems, but the lubrication in the motor also allows heat to be removed to some extent from highly heated parts, such as pistons.
- Exhaust. So that a car with a running engine does not frighten others with a deafening sound, it receives a high-quality exhaust system. In addition to the quiet operation of the machine, this system ensures the neutralization of harmful substances contained in the exhaust (for this, the machine must be present catalytic converter).
- Gas distribution. This is part of the engine (the timing is in the cylinder head). The camshaft opens the intake / exhaust valves alternately, so that the cylinders perform the appropriate stroke on time.

These are the main systems thanks to which the unit can operate. In addition to them, the power unit can receive other mechanisms that increase its efficiency. An example of this is a phase shifter. This mechanism allows you to remove the maximum efficiency at any engine speed. It adjusts the height and timing of the valve opening, which affects the dynamics of the machine. The principle of operation and types of such mechanisms are considered in detail. separately.
How to maintain the performance of a gasoline engine after many years of operation?
Every car owner thinks about how to extend the working life of the power unit of his car. Before we consider what he can do for this, it is worth considering the most important factor affecting the health of the motor. This is the build quality and technology that the automaker uses when making this or that power unit.
Here are the basic steps every motorist should follow:
- Carry out maintenance of your car in accordance with the regulations established by the manufacturer;
- Pour only high-quality gasoline into the tank, and the appropriate type of engine;
- Use engine oil designed for a specific internal combustion engine;
- Do not use aggressive driving style, often bringing the engine to maximum revs;
- Carry out breakdown prevention, for example, adjusting valve clearances. One of the most important elements of a motor is its belt. Even if visually it seems that it is still in good condition, it is still necessary to replace it as soon as the time indicated by the manufacturer comes. This item is described in detail. separately.

Since the motor is one of the most key components of a car, every motorist should listen to its work and be attentive to even minor changes in its functioning. Here's what may indicate a malfunction of the power unit:
- In the process of work, extraneous sounds appeared or vibrations increased;
- The internal combustion engine has lost dynamism and recoil when pressing the gas pedal;
- Increased gluttony (high gas mileage may be associated with the need to warm up the engine in winter or when changing driving style);
- The oil level drops steadily and the grease needs to be constantly refilled;
- The coolant began to disappear somewhere, but there are no puddles under the car, and the tank is tightly closed;
- Blue smoke from the exhaust pipe;
- Floating revolutions - they themselves rise and fall, or the driver needs to constantly gas up so that the engine does not stall (in this case, the ignition system may be faulty);
- It starts poorly or does not want to start at all.
Each motor has its own subtleties of work, so the motorist needs to familiarize himself with all the nuances of the operation and maintenance of the unit. If the motorist can replace / repair some parts or even mechanisms in the car on his own, it is better to entrust the repair of the unit to a specialist.
Additionally, we suggest reading about which reduces the work of the gasoline engine.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Universal Gasoline Engines
If we compare a diesel unit and a gasoline unit, then the advantages of the second include:
- High dynamics;
- Stable work at low temperatures;
- Quiet operation with small vibrations (if the unit is correctly configured);
- Relatively inexpensive maintenance (if we are not talking about exclusive motors, for example, boxers or with the EcoBoost system);
- Large working resource;
- There is no need to use seasonal fuel;
- Cleaner exhaust due to less impurities in gasoline;
- With the same volumes as a diesel engine, this type of internal combustion engine has more power.
Given the high dynamics and power of gasoline units, most sports cars are equipped with just such power plants.
In terms of service, these modifications also have their own advantage. Consumables for them are cheaper, and the maintenance itself does not need to be carried out so often. The reason is that the parts of the gasoline engine are subject to less stress than analogs used in diesel engines.

Although the driver should be careful about which gas station he fills his car at, the gasoline option is not as demanding on fuel quality as compared to the diesel one. In the worst case that can happen, the nozzles will quickly clog.
Despite these advantages, these motors have some disadvantages, which is why many motorists prefer diesel. Here is some of them:
- Despite the power advantage, an identical displacement unit will have less torque. For commercial trucks, this is an important parameter.
- A diesel engine with a similar displacement will consume less fuel than this type of unit.
- As for the temperature regime, the gasoline unit can overheat in traffic jams.
- Gasoline ignites more easily from extraneous heat sources. Therefore, a car with such an internal combustion engine is more fire hazardous.
To make it easier to choose which unit the car should be with, the future car owner must first decide what he wants from his iron horse. If the emphasis is on endurance, high torque and economy, then you obviously need to choose a diesel engine. But for the sake of dynamic driving and cheaper maintenance, you should pay attention to the gasoline counterpart. Of course, the budget service parameter is a loose concept, because it directly depends on the class of the motor and the systems that are used in it.
At the end of the review, we suggest watching a small video comparison of gasoline and diesel engines:
Questions and answers:
How does a gasoline engine work? The fuel pump supplies gasoline to the carburetor or injectors. At the end of the compression stroke of gasoline and air, the spark plug creates a spark that ignites the BTC, causing the expanding gases to push the piston out.
How does a four-stroke engine work? Such a motor has a gas distribution mechanism (a head with a camshaft is located above the cylinders, which opens / closes the intake and exhaust valves - through them, BTC is supplied and exhaust gases are removed).
How does a two-stroke engine work? Such an engine does not have a gas distribution mechanism. In one revolution of the crankshaft, two strokes are performed: compression and working stroke. The filling of the cylinder and the removal of the exhaust gases take place simultaneously.


 Some manufacturers install a W-shaped powertrain in their vehicles. This modification differs from the V-shaped analogue by the additional camber of the cylinder block, which in the section has the shape of the letter W. Another type of engines that are used in modern cars is a boxer or boxer. Details of how such an engine is arranged and how it works is described
Some manufacturers install a W-shaped powertrain in their vehicles. This modification differs from the V-shaped analogue by the additional camber of the cylinder block, which in the section has the shape of the letter W. Another type of engines that are used in modern cars is a boxer or boxer. Details of how such an engine is arranged and how it works is described 

