Electronic ignition system
Content
- What is an electronic ignition system
- The value of the electronic ignition system
- The composition of the ignition system of the injection engine
- The principle of operation of the electronic ignition system
- Types of electronic ignition system
- Electronic ignition malfunctions
- Advantages of Electronic Ignition Systems
- Related videos
- Questions and answers:
A car is a very complex system, even if we are faced with an old classic. The device of the vehicle includes a large number of mechanisms, assemblies and systems that, interacting with each other, allow you to carry out work on the transportation of goods and passengers.
The key unit that provides the dynamics of the car is the motor. An internal combustion engine powered by gasoline, regardless of the type of vehicle, even if it is a scooter, will be equipped with an ignition system. The principle of operation of the diesel unit differs in that the VTS in the cylinder lights up due to the injection of diesel fuel into the portion of air heated from high compression. Read about which motor is better. in another review.
We will now focus more on the ignition system. The carburetor ICE will be equipped with contact or contactless modification... There are already separate articles about their structure and the difference. With the development of electronics and its gradual introduction into vehicles, a modern car received a more improved fuel system (read about the types of injection systems here), as well as an improved ignition system.

Consider what an electronic ignition system is, how it works, its importance in the ignition of an air-fuel mixture and the dynamics of a car. Let's also see what the disadvantages of this development.
What is an electronic ignition system
If in contact and non-contact systems, the creation and distribution of a spark is performed mechanically and partially electronically, then this SZ is of an exclusively electronic type. Although the previous systems also partially use electronic devices, they have mechanical elements.
For example, a contact SZ uses a mechanical signal interrupter that activates the shutdown of the low voltage current in the coil and the generation of a high voltage pulse. It also contains a distributor that works by closing the contacts of the corresponding spark plug using a rotating slider. In a contactless system, a mechanical interrupter was replaced by a Hall sensor installed in a distributor, which has a similar structure as in the previous system (for more information about its structure and principle of operation, read in a separate review).
The microprocessor-based type of SZ is also considered contactless, but in order not to create confusion, it is called electronic. There are no mechanical elements in this modification, although it also continues to fix the speed of rotation of the crankshaft in order to determine the moment when it is necessary to supply a spark to the spark plugs.

In modern cars, this SZ consists of several important elements, the work of which is based on the creation and distribution of electrical impulses of different values. To synchronize them, there are special sensors that are not present in previous system modifications. One of these sensors is DPKV, about which there is separate detailed article.
Often, electronic ignition is inextricably linked with the operation of other systems, for example, fuel, exhaust and cooling. All processes are controlled by an ECU (electronic control unit). This microprocessor is programmed at the factory for the parameters of a particular vehicle. If a failure occurs in the software or in the actuators, the control unit fixes this malfunction and issues a corresponding notification to the dashboard (most often it is the engine icon or the Check Engine inscription).
Some problems are removed by resetting errors identified in the process of computer diagnostics. Read about how this procedure goes. here... In some cars, a standard self-diagnosis option is available, which allows you to determine what exactly the problem is, and whether it is possible to fix it yourself. To do this, you need to call the corresponding menu of the on-board system. How this can be done in some cars, it says separately.
The value of the electronic ignition system
The task of any ignition system is not simply to ignite a mixture of air and gasoline. Its device should include several mechanisms that determine the most effective moment when it would be better to do it.
If the power unit operated in only one mode, the maximum efficiency could be removed at any time. But this kind of functioning is impractical. For example, the motor does not need high revs to idle. On the other hand, when the car is loaded or picking up speed, it needs increased dynamics. Of course, this could be achieved with a gearbox with a large number of speeds, including low and high speed. However, such a mechanism would be too complex not only to use, but also to maintain.
In addition to these inconveniences, stable engine speed would not allow manufacturers to produce nimble, powerful and at the same time economical cars. For these reasons, even simple power units are equipped with an intake system that would allow the driver to independently determine what characteristics his vehicle should have in a particular case. If he needs to drive slowly, for example, to drive up to the car in front of him in a jam, then he lowers the engine speed. But for a quick acceleration, for example, before a long climb or when overtaking, the driver needs to increase the engine speed.

The problem of changing these modes is associated with the peculiarity of the combustion of the air-fuel mixture. In a standard situation, when the engine is not loaded and the machine is at a standstill, the BTC lights up from the spark generated by the spark plug at the moment when the piston reaches top dead center, performing a compression stroke (for all strokes of a 4-stroke and 2-stroke engine, read in another review). But when a load is placed on the engine, for example, the vehicle starts moving, the mixture should begin to ignite at the TDC of the piston or milliseconds later.
When the speed rises, due to the inertial force, the piston passes the reference point faster, which leads to a too late ignition of the fuel-air mixture. For this reason, the spark must be initiated a few milliseconds earlier. This effect is called ignition timing. Controlling this parameter is another function of the ignition system.
In the first cars for this purpose, there was a special lever in the transport compartment, by moving which the driver independently changed this UOZ depending on the specific situation. To automate this process, two regulators were added to the contact ignition system: vacuum and centrifugal. The same elements migrated to the more advanced BSZ.
Since each component made only mechanical adjustments, their effectiveness was limited. A more accurate adjustment of the unit to the desired mode is possible only thanks to electronics. This action is completely assigned to the control unit.
To understand how a microprocessor-based SZ works, you first need to understand its device.
The composition of the ignition system of the injection engine
An injection engine uses electronic ignition, which consists of:
- Controller;
- Crankshaft position sensor (DPKV);
- Toothed pulley (to determine the moment of the formation of a high-voltage pulse);
- Ignition module;
- High voltage wires;
- Spark plugs.

Let's take a look at the key elements separately.
Ignition module
The ignition module consists of two ignition coils and two high-voltage switch keys. Ignition coils have the function of converting a low voltage current into a high voltage pulse. This process occurs due to an abrupt disconnection of the primary winding, due to which a high voltage current is induced in a nearby secondary winding.
A high-voltage pulse is required to generate sufficient electrical discharge at the spark plugs to ignite the air / fuel mixture. The switch is necessary in order to turn on and off the primary winding of the ignition coil at the right time.
The operating time of this module is influenced by the motor speed. Based on this parameter, the controller determines the on / off speed of the ignition coil winding.
High voltage ignition wires
As the name suggests, these elements are designed to carry high voltage current from the ignition module to the spark plug. These wires have a large cross-section and the tightest insulation in all electronics. On both sides of each wire there are lugs that provide the maximum contact area with the candles and the contact assembly of the module.
To prevent the wires from forming electromagnetic interference (they will block the operation of other electronics in the car), high-voltage wires have a resistance of 6 to 15 thousand ohms. If the insulation of the wires even slightly breaks through, this affects the performance of the engine (the MTC ignites poorly or the engine does not start at all, and the candles are constantly flooded).
Spark plug
In order for the air-fuel mixture to ignite stably, spark plugs are screwed into the engine, onto which the high-voltage wires coming from the ignition module are put on. There is a description of the design features and the principle of operation of the candles. A separate article.
In short, each candle has a central and side electrode (there can be two or more side electrodes). When the primary winding in the coil is disconnected, a high voltage current flows from the secondary winding through the ignition module to the corresponding wire. Since the spark plug electrodes are not connected to each other, but have a precisely calibrated gap, a breakdown is formed between them - an electric arc that heats the VTS to the ignition temperature.
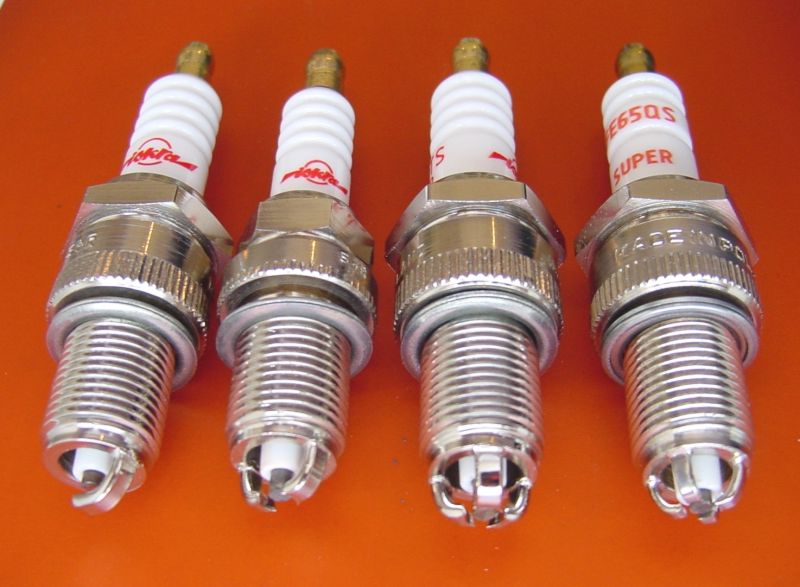

The spark power directly depends on the gap between the electrodes, the current strength, the type of electrodes, and the quality of ignition of the air-fuel mixture depends on the pressure in the cylinder and the quality of this mixture (its saturation).
Crankshaft position sensor (DPKV)
This sensor is an integral element in the electronic ignition system. It allows the controller to always fix the position of the pistons in the cylinders (which of them will be at the top dead center of the compression stroke at what moment). Without signals from this sensor, the controller will not be able to determine when a high voltage needs to be applied to a specific spark plug. In this case, even if the fuel supply and ignition systems are in good condition, the engine will still not start.
The sensor detects the position of the pistons by means of a ring gear on the crankshaft pulley. It has on average about 60 teeth, and two of them are missing. In the process of starting the motor, the toothed pulley also rotates. When the sensor (it works on the principle of a Hall sensor) detects the absence of teeth, a pulse is generated in it, which goes to the controller.
Based on this signal, the algorithms programmed by the manufacturer are triggered in the control unit, which determine the UOZ, the phases of fuel injection, the operation of the injectors, and the mode of operation of the ignition module. In addition, other equipment (for example, a tachometer) operates on signals from this sensor.
The principle of operation of the electronic ignition system
The system begins its work by connecting it to the battery. The contact group of the ignition switch in most modern cars is responsible for this, and in some models equipped with keyless entry and a start button for the power unit, it turns on automatically as soon as the driver presses the "Start" button. In some modern cars, the ignition system can be controlled via a mobile phone (remote start of the internal combustion engine).
Several elements are responsible for the work of the SZ. The most important of these is the crankshaft position sensor, which is installed in the electronic systems of injection engines. About what it is and how it works, read separately... It gives a signal at what point the piston of the first cylinder will perform a compression stroke. This impulse goes to the control unit (in older cars, this function is performed by a breaker and a distributor), which activates the corresponding coil winding, which is responsible for the formation of high voltage current.

At the moment the circuit is turned on, the voltage from the battery is supplied to the primary short-circuit winding. But in order for a spark to form, it is necessary to ensure the rotation of the crankshaft - only in this way can the crankshaft position sensor be able to generate an impulse to form a high-voltage energy beam. The crankshaft will not be able to start rotating on its own. A starter is used to start the motor. Details on how this mechanism works are described separately.
The starter forcibly turns the crankshaft. Together with it, the flywheel always rotates (read about the different modifications and functions of this part here). A small hole is made on the crankshaft flange (more precisely, several teeth are missing). A DPKV is installed next to this part, which works according to the Hall principle. The sensor determines the moment when the piston of the first cylinder is at top dead center by the slot on the flange, performing a compression stroke.
The pulses created by the DPKV are fed to the ECU. Based on the algorithms embedded in the microprocessor, it determines the optimal moment to create a spark in each individual cylinder. The control unit then sends a pulse to the igniter. By default, this part of the system supplies the coil with a constant voltage of 12 volts. As soon as a signal is received from the ECU, the igniter transistor closes.
At this moment, the supply of electricity to the primary short-circuit winding stops abruptly. This provokes electromagnetic induction, due to which a high voltage current (up to several tens of thousands of volts) is generated in the secondary winding. Depending on the type of system, this impulse is sent to the electronic distributor, or immediately goes from the coil to the spark plug.
In the first case, high-voltage wires will be present in the SZ circuit. If the ignition coil is installed directly on the spark plug, then the entire electrical line consists of conventional wires that are used throughout the entire electrical circuit of the vehicle's on-board system.

As soon as electricity enters the candle, a discharge is formed between its electrodes, which ignites a mixture of gasoline (or gas, in the case of using HBO) and air. Then the motor can work independently, and now there is no need for a starter. The electronics (if the start button is used) automatically disconnects the starter. In simpler schemes, the driver at this moment needs to release the key, and the spring-loaded mechanism will move the contact group of the ignition switch to the position of the system on.
As mentioned a little earlier, the ignition timing is adjusted by the control unit itself. Depending on the car model, the electronic circuit can have a different number of input sensors, according to the pulses from which the ECU determines the load on the power unit, the speed of rotation of the crankshaft and camshaft, as well as other parameters of the motor. All these signals are processed by the microprocessor and the corresponding algorithms are activated.
Types of electronic ignition system
Despite the wide variety of modifications of ignition systems, all of them can be conditionally divided into two types:
- Direct ignition;
- Ignition through the distributor.
The first electronic SZs were equipped with a special ignition module, which worked on the same principle as the contactless distributor. He distributed the high-voltage pulse to specific cylinders. The sequence was also controlled by the ECU. Despite the more reliable operation compared to the contactless system, this modification still needed improvement.
First, an insignificant amount of energy could be lost on poor quality high-voltage wires. Secondly, due to the passage of high voltage current through the electronic elements, the use of modules capable of operating under such a load is required. For these reasons, automakers have developed a more advanced direct ignition system.
This modification also uses ignition modules, only they work in less loaded conditions. The circuit of such a SZ consists of conventional wiring, and each candle receives an individual coil. In this version, the control unit turns off the transistor of the igniter of a specific short circuit, thereby saving time for distributing the pulse among the cylinders. Although this entire process takes place in a few milliseconds, even minor changes in this time can significantly affect the performance of the power unit.

As a type of direct ignition SZ, there are modifications with dual coils. In this version, the 4-cylinder motor will be connected to the system as follows. The first and fourth, as well as the second and third cylinders are parallel to each other. In such a scheme, there will be two coils, each of which is responsible for its own pair of cylinders. When the control unit supplies the cut-off signal to the igniter, a spark is generated simultaneously in a pair of cylinders. In one of them, the discharge ignites the air-fuel mixture, and the second is idle.
Electronic ignition malfunctions
Although the introduction of electronics into modern cars made it possible to provide a finer tuning of the power unit and various transport systems, this does not exclude malfunctions even in such a stable system as ignition. To determine many problems, only computer diagnostics will help. For standard maintenance of a car with electronic ignition, you do not need to take a diploma course in electronics, but the disadvantage of the system is that you can visually assess its condition only by the soot of candles and the quality of the wires.
Also, the microprocessor-based SZ is not devoid of some breakdowns that are characteristic of previous systems. Among these faults:
- Spark plugs stop working. From a separate article you can find out how to determine their serviceability;
- Breakage of the winding in the coil;
- If high-voltage wires are used in the system, then due to old age or poor insulation quality, they can break through, which leads to a loss of energy. In this case, the spark is not so powerful (in some cases it is absent at all) to ignite gasoline vapors mixed with air;
- Oxidation of contacts, which often occurs in cars that are operated in wet regions.

In addition to these standard failures, the ESP can also stop working or malfunction due to the failure of a single sensor. Sometimes the problem may lie in the electronic control unit itself.
Here are the main reasons why the ignition system may not work correctly or not function at all:
- The car owner ignores the routine maintenance of the car (during the procedure, the service station diagnoses and clears errors that can cause some electronics breakdowns);
- During the repair process, low-quality parts and actuators are installed, and in some cases, in order to save money, the driver purchases spare parts that do not correspond to a specific modification of the system;
- Influence of external factors, for example, operation or storage of the vehicle in high humidity conditions.
Problems with ignition can be indicated by factors such as:
- Increased consumption of gasoline;
- Poor reaction of the engine to pressing the gas pedal. In the case of inappropriate UOZ, pressing the accelerator pedal can, on the contrary, lower the dynamics of the car;
- The performance of the power unit has decreased;
- Unstable engine speed or it generally stalls at idle;
- The engine started to start badly.
Of course, these symptoms may indicate breakdowns in other systems, for example, a fuel system. If there is a decrease in the dynamics of the motor, its instability, then you should look at the condition of the wiring. In the case of using high-voltage wires, they can pierce, due to which there will be a loss of spark power. If the DPKV breaks down, the motor will not start at all.

An increase in the gluttony of the unit may be associated with incorrect operation of the candles, the transition of the ECU to emergency mode due to errors in it, or with a breakdown of the incoming sensor. Some modifications of the on-board systems of cars are equipped with a self-diagnosis option, during which the driver can independently identify the error code, and then carry out the appropriate repair work.
Installation of electronic ignition on a car
If the vehicle uses contact ignition, this system can be replaced with electronic ignition. True, for this it is necessary to purchase additional elements, without which the system will not work. Consider what is needed for this and how the work is done.
We prepare spare parts
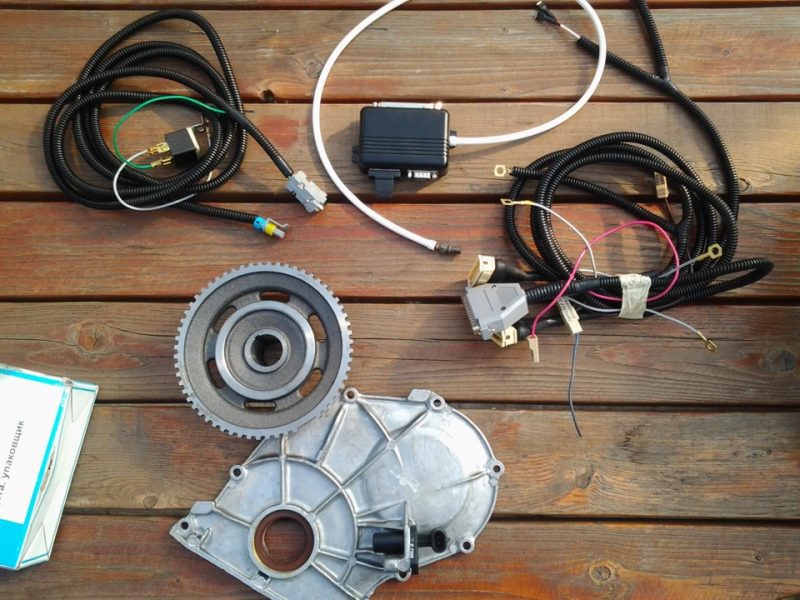
To upgrade the ignition system you will need:
- Trambler of contactless type. He, too, will distribute high voltage current through the wires to each candle. Each car has its own model of distributors.
- Switch. This is an electronic breaker, which in the contact ignition system is of a mechanical type (a slider rotating on a shaft, opening / closing the contacts of the primary winding of the ignition coil). The switch reacts to pulses from the crankshaft position sensor and opens / closes the contacts of the ignition coil (its primary winding).
- Ignition coil. Basically, this is the same coil used in the contact ignition system. In order for the candle to be able to break through the air between the electrodes, a high voltage current is needed. It is formed in the secondary winding when the primary turns off.
- High voltage wires. It is better to use new wires, rather than those that were installed on the previous ignition system.
- New set of spark plugs.
In addition to the main components listed, you will need to purchase a special crankshaft pulley with a ring gear, a crankshaft position sensor mount and the sensor itself.
Installation procedure
The cover is removed from the distributor (high-voltage wires are connected to it). The wires themselves can be removed. With the help of the starter, the crankshaft turns slightly until the resistor and motor form a right angle. After the angle of the resistor has been set, the crankshaft must not be rotated.
To correctly set the ignition moment, you need to focus on the five marks printed on it. The new distributor must be installed so that its middle mark coincides with the middle mark of the old distributor (for this, before removing the old distributor, a corresponding mark must be applied to the motor).
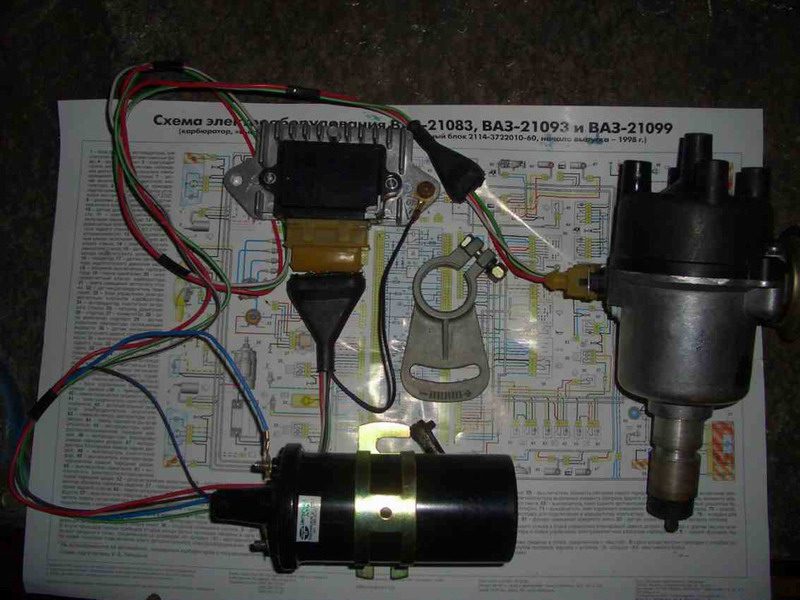

The wires connected to the ignition coil are disconnected. Next, the old distributor is unscrewed and dismantled. The new distributor is installed in accordance with the mark on the motor.
After installing the distributor, we proceed to replace the ignition coil (the elements for contact and non-contact ignition systems are different). The coil is connected to the new distributor using a central three-pin wire.
After that, a switch is installed in the free space of the engine compartment. You can fix it on the car body using self-tapping screws or screws. After that, the switch is connected to the ignition system.
After that, a toothed pulley with a gap for the crankshaft position sensor is installed. A DPKV is installed near these teeth (for this, a special bracket is used, fixed on the cylinder block housing), which is connected to the switch. It is important that the skipping of the teeth coincides with the top dead center of the piston in the first cylinder on the compression stroke.
Advantages of Electronic Ignition Systems
Although the repair of the microprocessor ignition system will cost a motorist a pretty penny, and diagnostics of malfunctions are additional costs, compared to the contact and contactless SZ, it functions more stably and reliably. This is its main advantage.
Here are a few more advantages of the ESP:
- Some modifications can be installed even on carburetor power units, which makes it possible to use them on domestic cars;
- Due to the absence of a contact distributor and a breaker, it becomes possible to increase the secondary voltage up to one and a half times. Thanks to this, the spark plugs create a "fat" spark, and the ignition of the HTS is more stable;
- The moment of formation of a high-voltage pulse is determined more accurately, and this process is stable in different operating modes of the internal combustion engine;
- The working resource of the ignition system reaches 150 thousand kilometers of the car's mileage, and in some cases even more;
- The motor runs more stably, regardless of the season and operating conditions;
- You do not need to spend a lot of time for prophylaxis and diagnostics, and adjustment in many cars occurs due to the installation of the correct software;
- The presence of electronics allows you to change the parameters of the power unit without interfering with its technical part. For example, some motorists carry out a chip tuning procedure. About what characteristics this procedure affects, and how it is carried out, read in another review... In short, this is the installation of other software that affects not only the ignition system, but also the timing and quality of fuel injection. The program can be downloaded from the Internet for free, but in this case you need to be completely sure that the software is of high quality and really suits a particular car.
Although electronic ignition is more expensive to maintain and repair, and most of the work must be performed by a specialist, this disadvantage is offset by more stable performance and other advantages that we have considered.
This video shows how to independently install the ESP on the classics:
Related videos
Here is a short video on how the process of switching from a contact ignition system to an electronic one looks like:


Watch this video on YouTube
Questions and answers:
Where is the electronic ignition system used? All modern cars, regardless of class, are equipped with such an ignition system. In it, all impulses are generated and distributed exclusively thanks to electronics.
How does electronic ignition work? DPKV fixes the TDC moment of the 1st cylinder on the compression stroke, sends a pulse to the ECU. The switch sends a signal to the ignition coil (general and then high-voltage current to the spark plug or individual).
What is included in the electronic ignition system? It is connected to the battery, and has: an ignition switch, a coil / s, spark plugs, an electronic control unit (performs the function of a switch and a distributor), input sensors.
What are the advantages of a contactless ignition system? More powerful and stable spark (there is no loss of electricity at the contacts of the breaker or distributor). Thanks to this, the fuel burns efficiently and the exhaust is cleaner.


2 comment
Mervin
Please do you think it is possible that I could get some information
Abdul Basit Al-Nabhani
God bless you and may God reward you well