What is and what does a car body consist of?
Content
A car is made up of many elements that work together seamlessly. The main ones are considered to be the engine, chassis and transmission. However, they are all fixed to the carrier system, which ensures their interaction. The carrier system can be presented in different variants, but the most popular is the car body. It is an important structural element that secures the vehicle's components, accommodates passengers and cargo in the cabin, and also absorbs all loads while driving.
Purpose and requirements
If the engine is called the heart of the car, then the body is its shell or body. Be that as it may, it is the body that is the most expensive element of the car. Its main purpose is to protect passengers and internal components from environmental influences, placement of seats and other elements.
As an important structural element, certain requirements are imposed on the body, including:
- corrosion resistance and durability;
- relatively small mass;
- required rigidity;
- optimal shape to ensure the repair and maintenance of all vehicle units, ease of loading luggage;
- ensuring the required level of comfort for passengers and the driver;
- ensuring a certain level of passive safety in a collision;
- compliance with modern standards and trends in design.
Body layout
The load-bearing part of the car can consist of a frame and a body, only a body, or be combined. The body, which performs the functions of a load-bearing part, is called a load-bearing body. This type is most common on modern cars.
Also, the body can be made in three volumes:
- one-volume;
- two-volume;
- three-volume.
One-piece is designed as a one-piece body that integrates the engine compartment, the passenger compartment and the luggage compartment. This layout corresponds to passenger (buses, minibuses) and utility vehicles.
Two-volume has two zones of space. The passenger compartment, combined with the trunk, and the engine compartment. This layout includes a hatchback, station wagon and crossover.
Three-volume consists of three compartments: passenger compartment, engine compartment and luggage compartment. This is the classic layout that sedans match.
Different layouts can be viewed in the figure below, and read in more detail in our article on body types.
Устройство
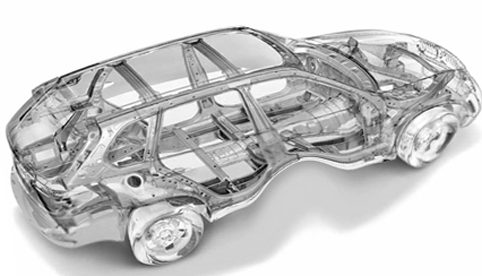
Despite the variety of layouts, the body of a passenger car has common elements. These are shown in the figure below and include:
- Front and rear side members. They are rectangular beams that provide structural rigidity and vibration damping.
- Front shield. Separates the engine compartment from the passenger compartment.
- Front struts. They also provide rigidity and anchoring the roof.
- Roof.
- Back pillar.
- Rear wing.
- Luggage panel.
- Middle rack. Provides body rigidity, made of durable sheet steel.
- Thresholds.
- Central tunnel where various elements are located (exhaust pipe, propeller shaft, etc.). Also increases rigidity.
- Base or bottom.
- Wheel well niche.
The design may be different depending on the type of body (sedan, station wagon, minibus, etc.). Particular attention is paid to structural elements such as spars and struts.
Hardness
Rigidity is the property of a car body to resist dynamic and statistical loads during operation. It directly affects handling.
The higher the stiffness, the better the car's handling.
Stiffness depends on body type, overall geometry, number of doors, size of car and windows. The attachment and position of the windshield and rear windows also play an important role. They can increase the hardness by 20-40%. For a greater increase in rigidity, various reinforcement struts are installed.
The most stable are hatchbacks, coupes and sedans. As a rule, this is a three-volume arrangement, which has additional partitions between the luggage compartment and the engine. Lack of rigidity is shown by the body of the station wagon, passenger, minibus.
There are two parameters of stiffness - bending and torsion. For torsion, the resistance is checked under pressure at opposite points relative to its longitudinal axis, for example, when hanging diagonally. As already mentioned, modern cars have a one-piece monocoque body. In such structures, rigidity is provided mainly by spars, transverse and longitudinal beams.
Materials for manufacture and their thickness
The strength and rigidity of the structure can be increased by the thickness of the steel, but this will affect the weight. The body must be light and strong at the same time. This is achieved through the use of low carbon steel sheet. Individual parts are made by stamping. The parts are then firmly spot-welded together.
The main steel thickness is 0,8-2 mm. For the frame, steel with a thickness of 2-4 mm is used. The most important parts, such as spars and struts, are made of steel, most often alloyed, with a thickness of 4-8 mm, heavy vehicles - 5-12 mm.
The advantage of low carbon steel is that it can be formed well. You can make a part of any shape and geometry. Minus low corrosion resistance. To increase resistance to corrosion, steel sheets are galvanized or copper is added. The paintwork also protects against corrosion.
The least important parts that do not bear the main load are made of plastics or aluminum alloys. This reduces the weight and cost of the structure. The figure shows the materials and their strength depending on the purpose.
Aluminum body
Modern designers are constantly looking for ways to reduce weight without losing rigidity and strength. Aluminum is one of the promising materials. The weight of aluminum parts in 2005 in European cars was 130 kg.
Foam aluminum material is now actively used. It is a very light and at the same time tough material that absorbs impact in a collision well. The foam structure provides high temperature resistance and sound insulation. The disadvantage of this material is its high cost, about 20% more expensive than traditional counterparts. Aluminum alloys are widely used by the concerns "Audi" and "Mercedes". For example, due to such alloys, it was possible to significantly reduce the weight of the Audi A8 body. It is only 810 kg.
In addition to aluminum, plastic materials are considered. For example, the innovative Fibropur alloy, which is almost as hard as steel sheets.
The body is one of the most important structural components of any vehicle. The mass, handling and safety of the vehicle largely depend on it. The quality and thickness of materials affects durability and corrosion resistance. Modern car manufacturers are increasingly using CFRP or aluminum to reduce structural weight. The main thing is that the body can provide the highest possible safety for passengers and the driver in the event of a collision.
