What is a headlight corrector: types, principle of operation and malfunctions
Content
If there is a danger of blinding the driver of an oncoming vehicle with high beam headlights, head lighting, manually or automatically, switches to low beam mode. But this is not enough, even if the headlights are correctly adjusted, their position must be adjusted relative to the road in relation to a particular situation. There are both reasons for this, and the corresponding equipment as part of the vehicle's exterior lighting system.

Why you need a headlight corrector
The difference between low beam and high beam is the presence of a clear vertical boundary between the illuminated area and the shadow from the screen built into the headlight.
The role of the screen can be performed by a variety of optical schemes and principles, but the essence of the issue does not change from this - the headlights in this mode should not fall into the eyes of oncoming drivers. This reduces the illumination of the road, but you have to sacrifice efficiency in favor of safety.

The position of the cut-off line is set by the angle of inclination of the headlight relative to the car body. It is set when adjusting the external lighting on the screen with marks or an optical stand at the service station.
The safety of the adjustments is controlled during technical inspections. High-beam headlights work like searchlights and have no special restrictions on the location and light power of the beam. Although they should illuminate the road, not satellite orbits.
But having ensured the correct position of the headlight housing, the reflector and the device for limiting the geometry of the light beam relative to the body, it is impossible to guarantee the safety of the border relative to the road. But this is exactly what is important, the position of the eyes of oncoming drivers is tied to its profile.
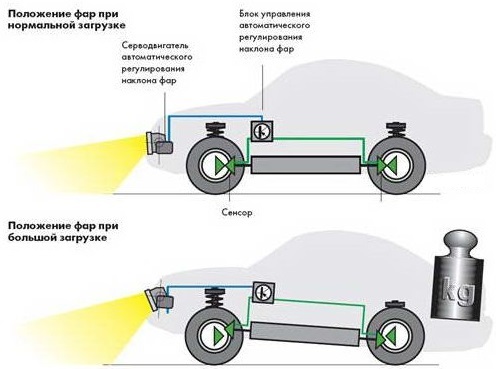
Meanwhile, the angle of the vehicle relative to the horizontal plane cannot be stable due to the soft suspension.
If you load the rear of the car, where additional passengers and the luggage compartment are most often located, then the body will receive, in aviation terms, a pitch angle for pitching, that is, it will tilt back, and the headlights will begin to shine into the sky.
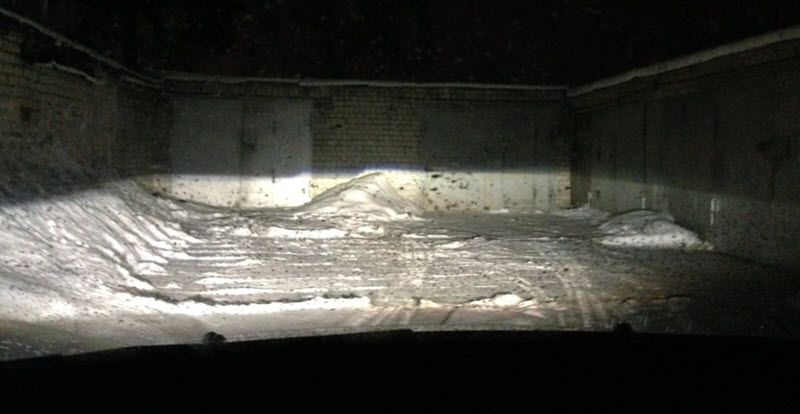

All fine adjustment will fail, oncoming cars will be blinded, which will negate the well-thought-out beam formation design with a sharp cut-off line. It is necessary to change the adjustment, but not to do this with every variable loading or unloading of the car. As a result, a device called a headlight corrector was introduced into the design.
Where is
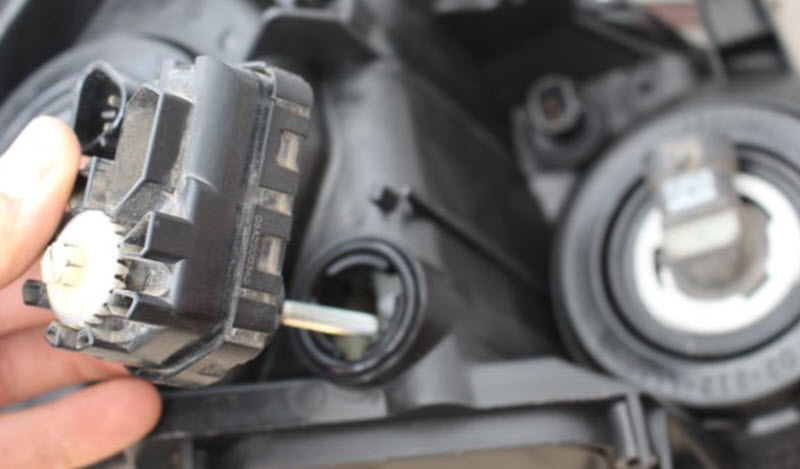
For correction, the tilt of the optical element in the headlight housing is used. The corresponding lever on the back side is actuated by the corrector actuator, which can be of the most diverse type according to the principle of operation.

Principle of operation
With manual correction, the driver shifts the position of the regulator in the cabin smoothly or to one of several fixed positions.
Through a mechanical, electrical or hydraulic connection, the movement is transmitted to the optical element. The driver sees how the position of the light beam on the road changes, and selects the position with the best visibility into the distance, but without the blinding effect.
Automatic correction is able to independently track changes in the angle of inclination of the body, maintaining the position of the light beam relative to the road.
This saves the driver from manual work and associated spot position errors and forgetfulness. Security increases significantly. Indeed, to get into a serious accident, one unsuccessful case of blinding is enough.
Types of headlight correctors
The variety of correctors is caused by the eternal theme of trade-off between the effectiveness of the technique and its cost.
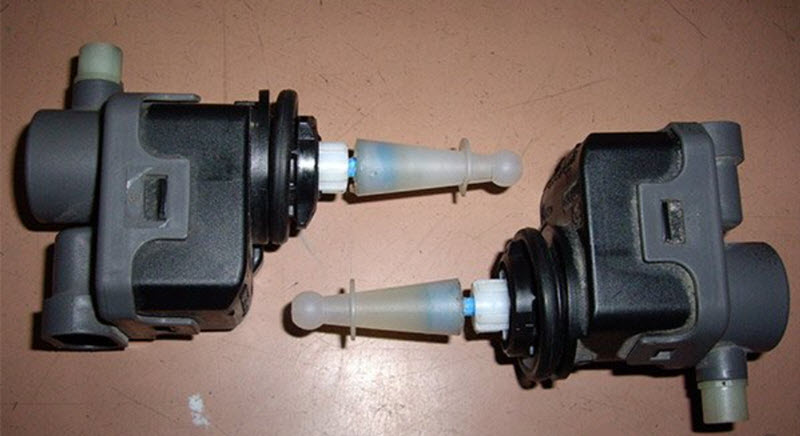


Mechanical
The simplest solution is to have an adjusting screw in the headlight with easy access from under the hood.
The driver will save a lot when buying a car, but will be forced to open the hood with each load change and manually set the cut-off line of the low beam. Using several attempts or using a specially marked screen.
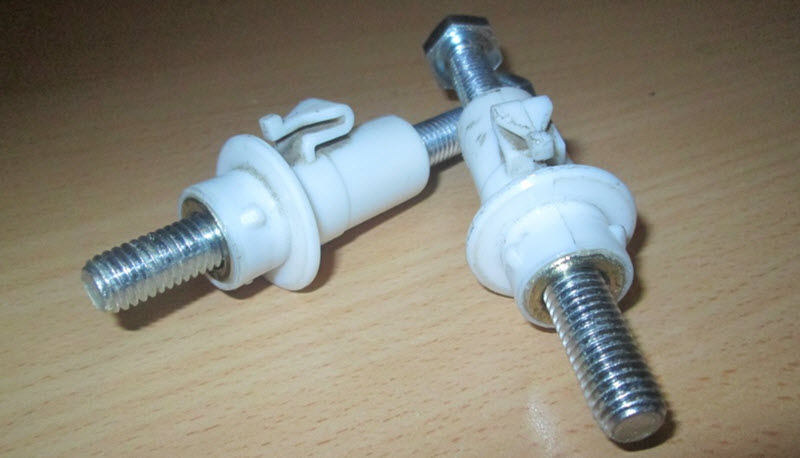


Pneumatic
The pneumatic drive eliminates the need to open the hood, the regulator is placed on the dashboard, and the force to the headlight is transmitted through the air line.
Usually a vacuum is used in the intake manifold of the engine. Occurs very rarely.
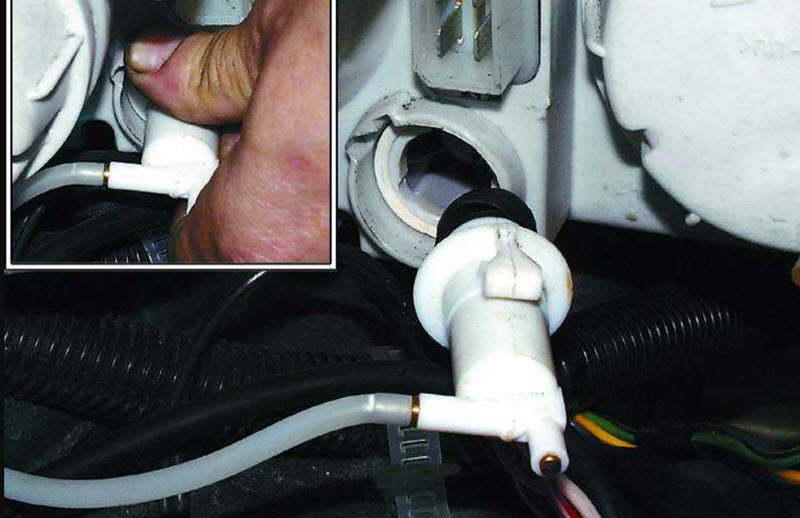


Гидравлический
The hydraulic drive is convenient, it is used in brakes, clutch control and other numerous cases. It will work no less effectively in transferring force from the adjusting handle in the passenger compartment to the slave cylinder near the headlight.
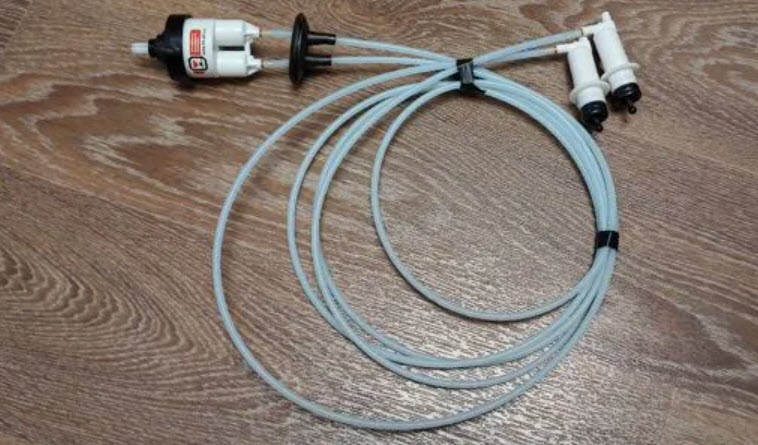


Of course, the system here is much simpler and cheaper, since the pressures are small, plastic parts and cheap silicone fluid are used.
Electromechanical
Electric adjustments allow you to get rid of fluid or pneumatic actuators. Moving the handle causes synchronous working out of the corrector servo drive on the headlight.
In circuitry, this can be difficult, but in mass production it is cheaper than mechanics with a cable or hydraulic drives. In addition, such nodes make it quite easy to implement automatic maintenance of the light border.
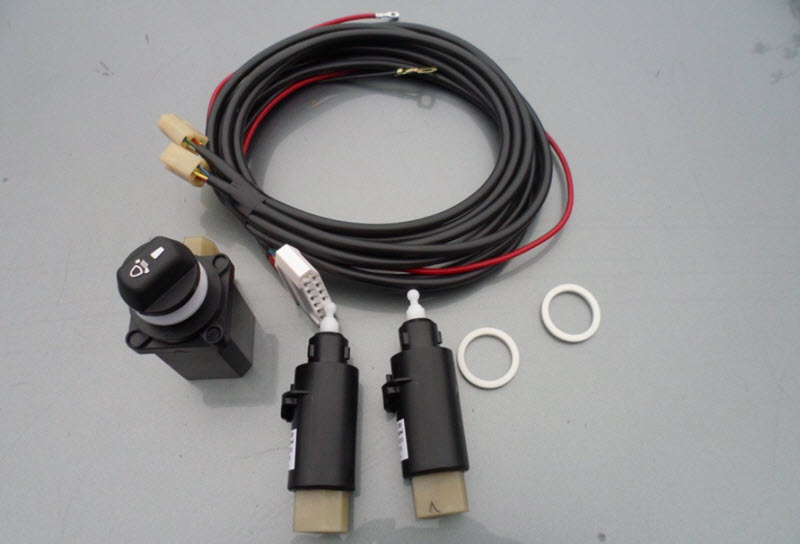


Automatic correctors with an electromechanical drive contain sensors in the suspension that measure the position of its levers.
Data, usually in the form of a variable resistance, is transmitted to the electronic unit, which works out the resulting mismatch between the preset and the current position.
The headlights always look where they should, even when driving over bumps in the road. The next step will be only purely electro-optical control with a light matrix that blocks the illumination of the oncoming driver's eyes.
Typical malfunctions
Manual adjustment systems according to the hydraulic principle, especially mechanical screws, are very reliable, there is nothing to break there. In the event of a hydraulic failure, the assembly is replaced as a set.
Electromechanical correctors are more modern and less reliable. More precisely, theoretically they can be made practically eternal, but manufacturers always save.
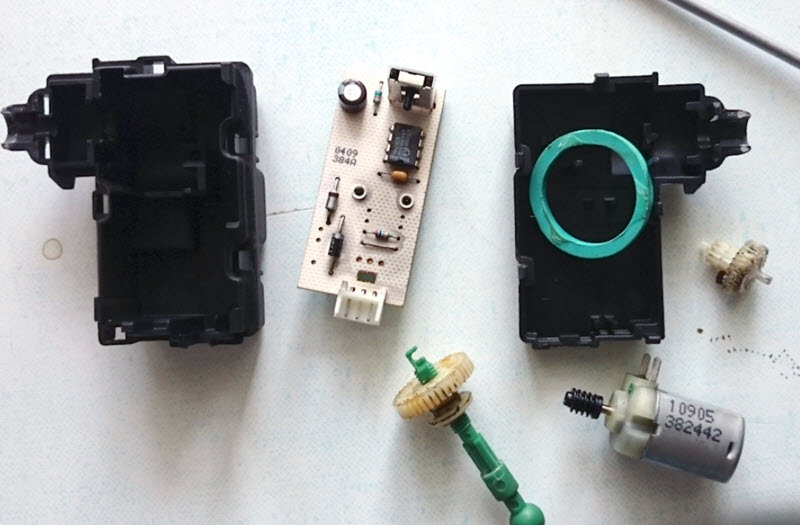

As a result, potentiometric sensors, servo collectors and plastic gears of gearboxes fail (wipe).
Replacement is carried out for individual nodes, these are sensors, actuators, plastic rods. Electronic circuits can only fail if moisture enters and corrodes the contacts in the wiring.
Adjustment and repair
After repair by replacing individual components, the corrector will require adjustment, that is, setting the nominal illumination limit.
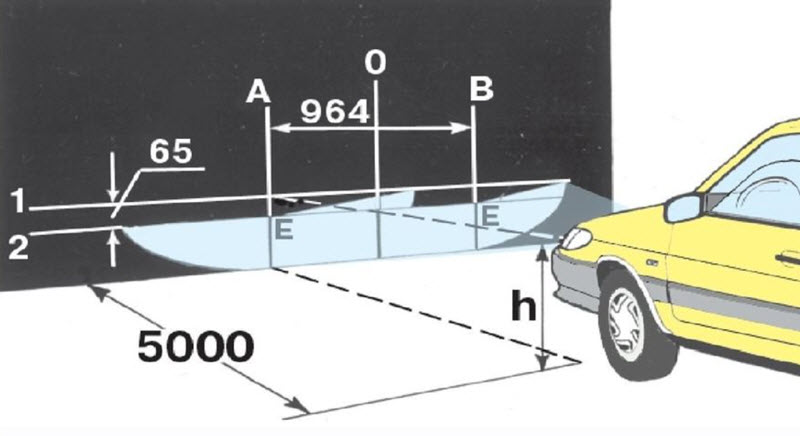
For this, a marked screen is used, set at a distance specified in the repair documentation for a particular car model.
The headlights are set according to the angle of the light beam in the neutral position of the regulator, after which it is checked that it works out the movement of the border up and down.


Watch this video on YouTube
The position of automatic sensors in the suspension is controlled by the readings of the scanner, which reads the information transmitted by them to the control unit at a certain test load, that is, the position of the suspension arms.
In more complex cases, the distance from the sensor to the road is controlled, which will also require the installation method. A successful result can be considered the independence of the position of the light boundary from the vehicle load from zero to maximum.