What is a lambda probe. How does the oxygen sensor regulate the operation of the internal combustion engine
Today's cars are literally crammed with all sorts of sensors that control tire and brake pressure, antifreeze and oil temperature in the lubrication system, fuel level, wheel speed, steering angle and much more. A number of sensors are used to regulate the operating modes of the internal combustion engine. Among them is a device with the mysterious name lambda probe, which will be discussed in this article.
The Greek letter lambda (λ) denotes a coefficient that characterizes the deviation of the composition of the air-fuel mixture supplied to the internal combustion engine cylinders from the optimal one. Note that in the Russian-language technical literature for this coefficient, another Greek letter is often used - alpha (α).
The maximum efficiency of the internal combustion engine is achieved at a certain ratio of air and fuel volumes entering the cylinders. In such a mixture of air, exactly as much as is needed for complete combustion of the fuel. No more, no less. This ratio of air and fuel is called stoichiometric.
For power units running on gasoline, the stoichiometric ratio is 14,7, for diesel units - 14,6, for liquefied gas (propane-butane mixture) - 15,5, for compressed gas (methane) - 17,2.
For a stoichiometric mixture, λ = 1. If λ is greater than 1, then there is more air than required, and then they speak of a lean mixture. If λ is less than 1, the mixture is said to be enriched.
A lean mixture will reduce the power of the internal combustion engine and worsen fuel economy. And at a certain proportion, the internal combustion engine will simply stall.
In the case of operation on an enriched mixture, the power will increase. The price of such power is a big waste of fuel. A further increase in the proportion of fuel in the mixture will cause ignition problems and unstable operation of the unit. The lack of oxygen will not allow the fuel to burn completely, which will dramatically increase the concentration of harmful substances in the exhaust. Gasoline will partially burn out in the exhaust system, causing a defect in the muffler and catalyst. This will be indicated by pops and dark smoke from the exhaust pipe. If these symptoms appear, the air filter should be diagnosed first. Perhaps it is simply clogged and does not let air into the internal combustion engine.
The engine control unit constantly monitors the composition of the mixture in the cylinders and regulates the amount of injected fuel, dynamically maintaining the value of the coefficient λ as close to 1 as possible. True, a slightly lean mixture is usually used in the possibility, in which λ = 1,03 ... This is the most economical mode, in addition, it minimizes harmful emissions, since the presence of a small amount of oxygen makes it possible to burn carbon monoxide and hydrocarbons in the catalytic converter.
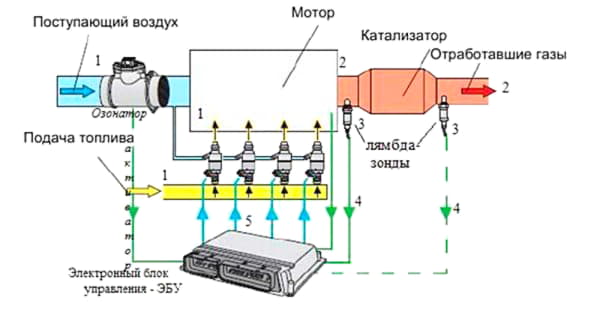
The lambda probe is precisely the device that monitors the composition of the air-fuel mixture, giving a corresponding signal to the engine ECU.

It is usually installed at the inlet of the catalytic converter and reacts to the presence of oxygen in the exhaust gases. Therefore, the lambda probe is also called a residual oxygen sensor or simply an oxygen sensor.
The sensor is based on a ceramic element (1) made of zirconium dioxide with the addition of yttrium oxide, which acts as a solid-state electrolyte. Platinum coating forms electrodes - external (2) and internal (3). From the contacts (5 and 4), the voltage is removed, which is supplied through the wires to the computer.
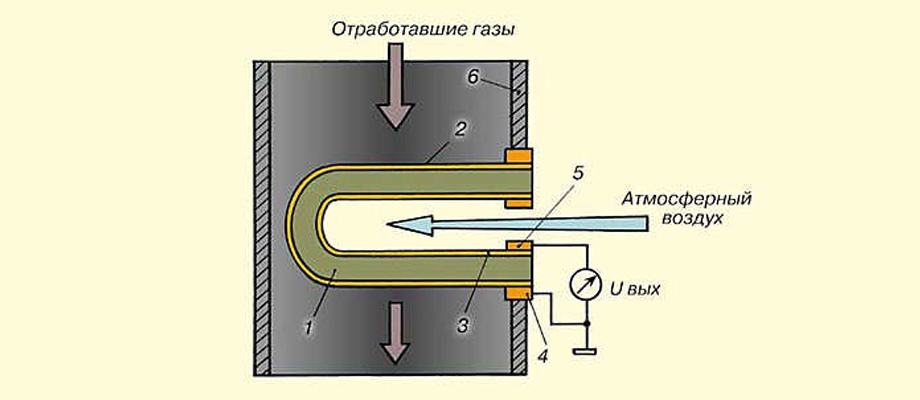
The outer electrode is blown with heated exhaust gases passing through the exhaust pipe, and the inner electrode is in contact with atmospheric air. The difference in the amount of oxygen on the outer and inner electrode causes a voltage to appear on the signal contacts of the probe and the corresponding reaction of the ECU.
In the absence of oxygen at the outer electrode of the sensor, the control unit receives a voltage of about 0,9 V at its input. As a result, the computer reduces the fuel supply to the injectors, leaning the mixture, and oxygen appears on the outer electrode of the lambda probe. This results in a decrease in the output voltage generated by the oxygen sensor.
If the amount of oxygen passing through the external electrode rises to a certain value, then the voltage at the sensor output drops to approximately 0,1 V. The ECU perceives this as a lean mixture, and corrects it by increasing fuel injection.
In this way, the composition of the mixture is dynamically controlled, and the value of the coefficient λ constantly fluctuates around 1. If you connect the oscilloscope to the contacts of a properly working lambda probe, we will see a signal close to a pure sinusoid.
A more accurate correction with less fluctuations in lambda is possible if an additional oxygen sensor is installed at the outlet of the catalytic converter. At the same time, the operation of the catalyst is monitored.
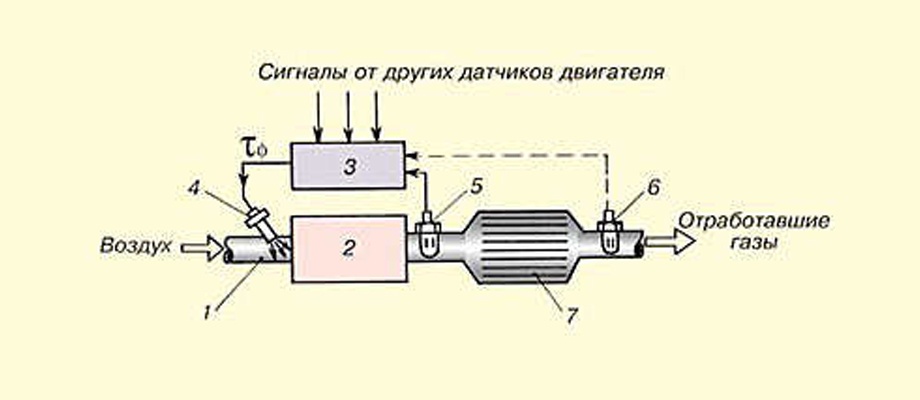
- intake manifold;
- ICE;
- ECU;
- fuel injectors;
- main oxygen sensor;
- additional oxygen sensor;
- catalytic converter.
Solid-state electrolyte acquires conductivity only when heated to about 300...400 °C. This means that the lambda probe is inactive for some time after the start of the internal combustion engine, until the exhaust gases warm it up sufficiently. In this case, the mixture is regulated on the basis of signals from other sensors and factory data in the computer's memory. To speed up the inclusion of the oxygen sensor in operation, it is often supplied with electrical heating by embedding a heating element inside the ceramic.
each sensor sooner or later starts to act up and requires repair or replacement. The lambda probe is no exception. In Ukrainian real conditions, it works properly for an average of 60 ... 100 thousand kilometers. A number of reasons can shorten its life.
- Poor quality fuel and questionable additives. Impurities can contaminate the sensitive elements of the sensor.
- Contamination with oil entering the exhaust gases due to problems in the piston group.
- The lambda probe is designed to operate at high temperatures, but only up to a certain limit (about 900 ... 1000 ° C). Overheating due to incorrect operation of the internal combustion engine or ignition system can damage the oxygen sensor.
- Electrical problems - oxidation of contacts, open or shorted wires, and so on.
- mechanical defects.
Except in the case of impact defects, the residual oxygen sensor usually dies slowly, and signs of failure appear gradually, becoming more pronounced only over time. Symptoms of a faulty lambda probe are as follows:
- Increased fuel consumption.
- Decreased engine power.
- Deterioration in dynamics.
- Jerks during the movement of the car.
- Floating idle speed.
- Exhaust toxicity increase. It is determined mainly with the help of appropriate diagnostics, less often manifested by a pungent odor or black smoke.
- Overheating of the catalytic converter.
It should be borne in mind that these symptoms are not always associated with a malfunction of the oxygen sensor, therefore, additional diagnostics are required to determine the exact cause of the problem.
you can diagnose the integrity of the wiring by dialing with a multimeter. You should also make sure that there is no short circuit of the wires to the case and to each other.
diagnose the resistance of the heating element, it should be approximately 5 ... 15 ohms.
The supply voltage of the heater must be close to the voltage of the onboard power supply.
It is quite possible to solve problems associated with wires or a lack of contact in the connector, but in general, the oxygen sensor cannot be repaired.
Cleaning the sensor from contamination is very problematic, and in many cases is simply impossible. Especially when it comes to a shiny silver coating caused by the presence of lead in gasoline. The use of abrasive materials and cleaning agents will finish off the device completely and irrevocably. Many chemically active substances can also damage it.
The recommendations found on the net for cleaning the lambda probe with phosphoric acid give the desired effect in one case out of a hundred. Those who wish can try.
Disabling a faulty lambda probe will switch the fuel injection system to the average factory mode registered in the ECU memory. It may turn out to be far from optimal, so the failed one should be replaced with a new one as soon as possible.
Unscrewing the sensor requires care so as not to damage the threads in the exhaust pipe. Before installing a new device, the threads should be cleaned and lubricated with thermal grease or graphite grease (make sure that it does not get on the sensitive element of the sensor). Screw in the lambda probe with a torque wrench to the correct torque.
Do not use silicone or other sealants when mounting the oxygen sensor.
Compliance with certain conditions will allow the lambda probe to remain in good condition longer.
- Refuel with quality fuel.
- Avoid questionable fuel additives.
- Control the temperature of the exhaust system, do not allow it to overheat
- Avoid multiple starts of the internal combustion engine in a short period of time.
- Do not use abrasives or chemicals to clean the oxygen sensor tips.
