Road traffic accident: concept, participants, types
Content
A traffic accident is an accident involving one or more motor vehicles. Most people will give a similar answer, whether they own cars or use public transport, and will be only partly right. An accident is a legal concept that has a specific content and a number of features.
The concept of a traffic accident
The content of the term "traffic accident" is disclosed at the legislative level and cannot be considered in a different meaning.
An accident is an event that occurred during the movement of a vehicle on the road and with its participation, in which people were killed or injured, vehicles, structures, cargo were damaged, or other material damage was caused.
A similar definition is given in paragraph 1.2 of the Rules of the Road (SDA), approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of October 23.10.1993, 1090 N XNUMX. In the above meaning, the concept is used in other regulations, contracts (hull, OSAGO, rental / leasing of vehicles, etc. .) and in the resolution of litigation.
Signs of an accident
To qualify an accident as a traffic accident, the following conditions must be met simultaneously:
- The incident must correspond to the characteristics of the event. Strictly in the legal sense, an event is a real-life phenomenon that does not depend on the will of a person. But if the so-called absolute events occur and develop completely isolated from the behavior and intentions of the participant in the relationship (natural phenomena, the passage of time, etc.), then the relative events, which include an accident, arise due to the actions or inaction of a person and unfold in the future without his participation. Passing through a traffic light (action) or non-use of emergency braking (inaction) occur at the will and with the participation of the driver, and the consequences (mechanical damage to the vehicle and other objects, injury or death of people) occur as a result of the laws of physics and changes in the body of the victim.
 The failure of the asphalt under the car is one of the few situations when an accident occurs completely without the will and participation of the driver
The failure of the asphalt under the car is one of the few situations when an accident occurs completely without the will and participation of the driver - An accident occurs while the vehicle is moving. At least one vehicle must move. Damage to a standing car by an object flying off from a passing vehicle will be an accident, even if there was no one in the damaged vehicle, and the fall of an icicle or a branch on a car left in the yard is considered as causing damage to housing and communal services, building owners, etc.
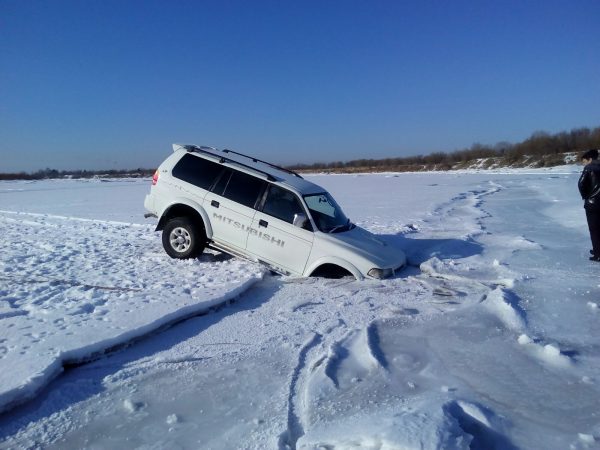
- The accident happens while on the road. Traffic rules define road traffic as the relationship that exists in the process of moving people and goods along the roads. Road, in turn, is a surface specially designed for the movement of vehicles, which also includes roadsides, tram tracks, dividing lanes and sidewalks (clause 1.2 of the SDA). The adjacent territory (courtyards, non-through courtyard roads, parking lots, sites at gas stations, residential areas and other similar surfaces not originally intended for through traffic) are not roads, but traffic on such areas must be carried out in compliance with traffic rules. Accordingly, the events that occurred on them are considered as an accident. A collision of two cars in an open field or on the ice of a river is not an accident. The culprit in causing damage will be determined based on the actual circumstances on the basis of civil law norms.
 Off-road accidents are not considered road accidents.
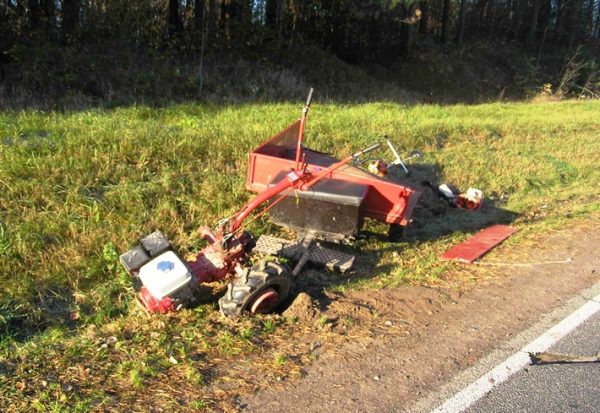
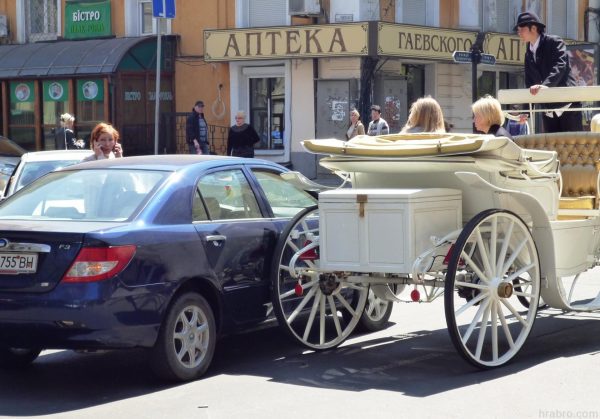
Off-road accidents are not considered road accidents. - The event involves at least one vehicle - a technical device that is structurally designed as a device for moving people and / or goods along the roads. The vehicle can be powered (mechanical vehicle) or driven by other means (muscle power, animals). In addition to the car itself (tractor, other self-propelled vehicle), traffic rules include bicycles, mopeds, motorcycles and trailers to vehicles (clause 1.2 of the traffic rules). A walk-behind tractor with special trailed equipment is not a vehicle, since, according to the original design concept, it is not intended for road traffic, although it is technically capable of transporting people and goods. A horse, elephant, donkey and other animals are not vehicles in the understanding of traffic rules due to the fact that they cannot be considered as a technical device, but a cart, carriage and other similar objects that are sometimes found on the roads fully correspond to the characteristics of the vehicle. Incidents involving such exotic vehicles will be treated as accidents.
 Motoblock accident is not an accident
Motoblock accident is not an accident - An incident must always have material and/or physical consequences in the form of injury or death of people, damage to vehicles, structures, cargo, or any other material damage. Damage to a decorative fence, for example, will be an accident even if there is not a scratch left on the car. If a car knocked down a pedestrian, but he was not injured, then the event cannot be attributed to an accident, which does not exclude a violation of traffic rules by the driver. At the same time, if a pedestrian breaks his phone or breaks his trousers as a result of a collision, then the event corresponds to the signs of an accident, since there are material consequences. To classify an event as an accident, any damage to the body is not enough. The rules for recording accidents, approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of 29.06.1995 No. 647, and adopted in accordance with them ODM 218.6.015-2015, approved by the Order of the Federal Road Traffic Agency of 12.05.2015 N 853-r, in relation to road accidents are considered:
- wounded - a person who received bodily injuries, as a result of which he was placed in a hospital for a period of at least 1 day or needed outpatient treatment (clause 2 of the Rules, clause 3.1.10 of the ODM);
- dead - a person who died directly at the scene of an accident or not later than 30 days from the consequences of injuries received (clause 2 of the Rules, clause 3.1.9 of the ODM).
Significance of qualifying an event as an accident
The correct qualification of an accident as a traffic accident is important in resolving issues of driver liability and compensation for harm. In practice, there are not so many situations in which the correct attribution of an event to an accident is decisive for resolving a dispute, but they are quite real. It is impossible to resolve them without understanding the essence of the traffic accident. For clarity, let's look at a few examples.
The first example concerns the driver leaving the scene of an accident. When moving in reverse at minimum speed, the driver hit a pedestrian, as a result of which the person fell. During the initial examination, no injuries were found, the state of health remained good. Clothing and other property were not damaged. The pedestrian did not make any claims against the driver, the incident ended with an apology and reconciliation. The participants dispersed, there was no appeal to the traffic police by mutual agreement. After some time, the pedestrian began to make material demands on the driver in connection with the appearance of pain or discovered material damage, threatening to bring him to justice under Part 2 of Art. 12.27 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation (leaving the scene of an accident). The punishment for the alleged violation is serious - deprivation of rights up to 1,5 years or arrest up to 15 days. A fair resolution of the case is possible only with the correct qualification of the event. If the event does not meet the signs of an accident in terms of the consequences, liability is excluded. The difficulty lies in the fact that the physical consequences may appear later.
Such situations can be staged with the aim of further extortion of money. Fraudsters present witnesses of the incident and even a video of the event. Faced with illegal actions, you should not rely only on your own strength. It is extremely difficult to get out of such situations without qualified help.
The second case, when the qualification of an event as an accident is of fundamental importance, is compensation for damage. The insured has entered into a CASCO agreement under a special program, according to which the insured risk is only an accident, regardless of the insured's fault in causing damage. When entering a fenced land plot with an individual residential building (suburban house, dacha, etc.), the driver incorrectly chose the lateral interval and made a lateral collision with the gate wings, the car was damaged. Compensation for damage by the insurer is possible if the accident qualifies as a traffic accident. The entrance to the site is usually carried out from the road or the adjacent territory, in connection with which the event that occurred during such an entry, in my opinion, is clearly an accident and the insurer is obliged to make a payment.
The situation is more complicated when the event with the vehicle occurred inside the local area. Such incidents, it seems, should not be considered as accidents. The adjacent territory is not intended not only for through passage, but also for traffic in general, and therefore cannot be considered as a road or territory adjacent to the road.
Video: what is an accident
Categories of road accident participants
The concept of a participant in an accident is not disclosed in the legislation, but obviously follows from the philological meaning of the expression. Only individuals can be members. The rules of the road highlight the following categories (clause 1.2 of the SDA):
- driver - a person driving a vehicle, a driver leading pack animals, riding animals or a herd along the road (teaching driving is equated to a driver);
- cyclist - a person who controls a bicycle;
- passenger - a person, except for the driver, who is in the vehicle (on it), as well as a person who enters the vehicle (gets on it) or leaves the vehicle (gets off it);
- pedestrian - a person who is outside the vehicle on the road or on a pedestrian or bicycle path and does not work on them (pedestrians are equated to persons moving in wheelchairs without an engine, driving a bicycle, moped, motorcycle, carrying a sledge, cart, children's or invalid wheelchair, as well as using roller skates, scooters and other similar means for movement).


In relation to the accident and in connection with it, other concepts are used:
- vehicle owner (car owner) - the owner or any other person legally owning the vehicle (rent, economic management, etc.);
- guilty of an accident (perpetrator of an accident) - a person through whose fault an accident occurred;
- guilty of causing damage (perpetrator of damage) - a person who, as a result of an accident, caused harm to life and health or property damage (usually the same as the culprit of the accident, but sometimes the driver can be found guilty, for example, a mechanic who released a faulty car on a flight, the owner domestic animals, allowing them to enter the road, etc.);
- victim - a person whose life and health or property was harmed (the victim is often called a person who has suffered only property damage, in contrast to the victim);
- victim - a person whose life and health has been harmed.
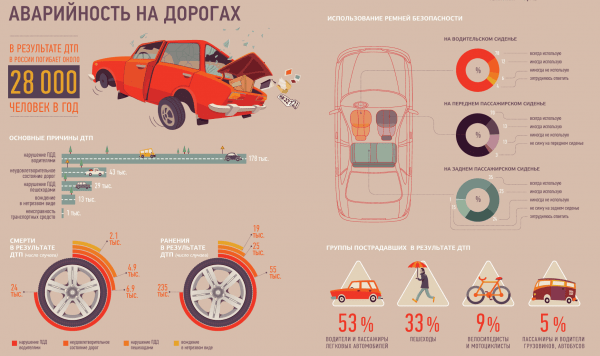
The main causes of road accidents
The vast majority of accidents occur for subjective reasons, in whole or in part. In one way or another, the fault of the participant in the incident is almost always present. Exceptions may be cases when accidents occur as a result of some objective and completely independent of human will events: subsidence of asphalt under a passing car, lightning strikes a car, etc. An animal that ran out onto the road, pits and potholes, and other external factors , which a person could have expected and avoided, are not considered as the only causes of accidents. In the best case, in addition to traffic violations committed by the driver, for example, a violation by road services of the rules and regulations for road maintenance is established. A car malfunction is also not a self-sufficient cause of an accident, since the driver is obliged to check and ensure the vehicle is in good condition on the way before leaving (clause 2.3.1 of the SDA).
There are several universal rules in the traffic rules that allow you to establish the driver's fault in almost any accident. For example, clause 10.1 of the SDA - the driver must choose the speed within such limits to ensure constant control over the movement, clause 9.10 of the SDA - the driver must observe the interval to the vehicle in front and the side interval, etc. Accidents only through the fault of pedestrians occur in rare cases and are possible, perhaps, only with an unexpected exit to the roadway in the wrong place or at a prohibitory traffic light.


Thus, the fundamental and main cause of an accident is a violation by the driver of the Rules of the Road. A more detailed classification is possible based on specific traffic rules. The main reasons include:
- Violation of the speed limit (clause 10.1 of the SDA). Often, drivers confuse the wrong choice of speed with exceeding the maximum permissible value for a given area (paragraphs 10.2 - 10.4 of the SDA) or determined by the relevant road signs. In fact, the correct choice of speed mode does not depend on the limit indicators and is determined based on the current situation. In itself, exceeding the maximum permissible speed cannot lead to an accident, an accident occurs due to the inability to stop in the selected driving mode. The driver of a car moving at a speed of 100 km/h in the city can have time to brake or maneuver with sufficient visibility and free road, while at a speed of 30 km/h on icy asphalt, when braking, the car will lose control and collide with another car. The braking distance on wet asphalt increases up to one and a half times, and on an ice-crusted road - 4-5 times compared to dry asphalt.
- Departure to a prohibiting traffic light or traffic controller. The circumstances and consequences of such a breach are clear.
- Incorrect choice of interval to the vehicle in front or side interval. Sudden braking of the vehicle in front is not usually the cause of the accident. The driver behind must choose a safe distance that allows him to stop in an emergency. Often, drivers try to avoid a collision with the front car by maneuvering and collide with a vehicle moving in the other lane in the same direction, or drive into the oncoming lane. Traffic rules do not provide for the possibility of maneuvering in case of danger. The driver's actions should only be aimed at reducing speed up to a stop.
- Departure to the oncoming lane (clause 9.1 of the SDA). The reasons for leaving may be overtaking in violation of the rules, an attempt to avoid a collision with an obstacle that has arisen in front, the wrong choice of the location of the car on a road without markings, intentional actions, etc.
- Violation of the rules for turning (clause 8.6 of the SDA). A significant number of drivers violate the rules for turning at intersections. At the end of the maneuver, the vehicle should be in its own lane, but in fact, a partial passage is made in the oncoming lane, resulting in a collision with an oncoming vehicle.
- Other traffic violations.
Other circumstances that are often cited as causes of traffic accidents are in fact factors that increase the likelihood of an event or additional causes. These include:
- The physical condition of the driver. Fatigue, poor health reduce attentiveness and slow down the reaction. For bus drivers, including urban, truckers and some other categories, a special mode of work is provided, which implies mandatory rest between flights and during the journey. Violation of the prescribed norms is one of the factors affecting the accident rate. A direct ban on driving in a sick or tired state, along with intoxication, is contained in clause 2.7 of the SDA.
- distracting factors. Loud music, especially listening to headphones, extraneous noise and conversations in the cabin, paying attention to passengers (for example, small children) or animals inside the car distract the driver from traffic control. This does not allow timely response to changing conditions.
 Engaging in extraneous matters while driving is a reliable way to get into an accident
Engaging in extraneous matters while driving is a reliable way to get into an accident - Weather. They have a versatile and multifactorial impact on traffic. Rain and snow reduce both visibility and traction of the asphalt, fog can limit the visibility of the road to tens of meters compared to several kilometers in clear weather, bright sun blinds the driver, etc. Adverse weather conditions cause additional driver stress, which leads to a fast fatigue.
- The condition of the road surface is a favorite topic for drivers. In fairness, it should be noted that in recent years a significant length of both highways and city roads has been repaired and restored, but the problem is so significant that it is not yet necessary to speak of a generally satisfactory quality. It is useful for the driver to remember some maximum permissible indicators of road flaws (GOST R 50597–93), in case of deviation from which it is possible to bring road and other relevant services to responsibility for road accidents:
- width of a separate pothole - 60 cm;
- the length of a single pothole is 15 cm;
- the depth of a single pothole is 5 cm;
- deviation of the grate of the storm water inlet from the level of the tray - 3 cm;
- deviation of the manhole cover from the level of coverage - 2 cm;
- deviation of the rail head from the coating - 2 cm.
- Alcohol, drug or toxic intoxication. Violation of clause 2.7 of traffic rules in itself cannot lead to an accident, but a state of intoxication has a catastrophic effect on a person’s reaction and coordination, and prevents an adequate assessment of the traffic situation. By virtue of the general legal and social attitude, a drunk driver is very likely to be “brought” to responsibility for an accident and damage caused, even if he actually does not commit other traffic violations and the accident occurs as a result of the actions of another participant.
 The state of intoxication catastrophically affects the reaction and adequacy of the driver
The state of intoxication catastrophically affects the reaction and adequacy of the driver
Other factors contributing to road accidents include improper supervision of domestic animals, the actions of wild animals, natural phenomena, improper maintenance of objects adjacent to the roads (for example, when trees, poles, structures, etc. fall on the road) and other circumstances, which can significantly increase the risk of an accident. The contributing factors also include insufficiently qualified training of drivers in driving schools, and shortcomings in car designs. Supporters of esoteric teachings may see karma in the cause of an accident, but this is already an amateur.
Types of traffic accidents
In theory and practice, there are several options for qualifying an accident. According to the severity of the consequences, incidents are divided:
- with a fatal outcome, taking into account the previously given concept of a person who died as a result of an accident;
- with bodily injury;
- with material damage.
According to the severity of the consequences, accidents are distinguished, which entailed:
- material damage;
- light bodily injuries - a short-term health disorder or a slight permanent loss of general ability to work (note 1 to article 12.24 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation);
- medium-degree bodily injury - a non-life-threatening long-term health disorder or a significant permanent loss of general ability to work by less than one third (note 2 to article 12.24 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation);
- serious bodily injury - life-threatening harm, loss of vision, speech, hearing or any organ or loss of its functions by an organ, termination of pregnancy, mental disorder, drug addiction or substance abuse, permanent disfigurement of the face, significant permanent loss of general working capacity for at least one third, complete loss of professional ability to work (Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of August 17.08.2007, 522 No. XNUMX);
- the death of the victim;
- especially grave consequences (death of 4 or more people, injury of 15 or more people).
The severity of bodily injury is determined by a medical examination.
By the nature of the incident, they distinguish (Appendix G to ODM 218.6.015–2015):
- collision of vehicles with each other or with a train;
- overturning - loss of stability not due to a collision or collision, exit from the road (for example, with a critical slope of the road, as a result of a gust of wind, etc.);
- collision with a standing vehicle;
- collision with an obstacle (any immovable object, except for a vehicle);
- collision with a pedestrian, including when a pedestrian collided with a car;
- collision with a cyclist, including when a cyclist collided with a car;
- collision with horse-drawn vehicles (both animals and the device driven by them), including when such transport collided with a car;
- falling of a passenger in the process of movement (for example, in a bus);
 A passenger falling on a bus is also an accident.
A passenger falling on a bus is also an accident. - other accidents:
- collision with other animals, except for horse-drawn vehicles;
- exit from the road;
- cargo drop;
- dropping an object;
- collision with a person who is not a pedestrian (traffic police officer, road worker, etc.).
Somewhat conventionally, accidents can be divided into accounting and non-accountable. The conditionality lies in the fact that, according to clause 3 of the Rules for Accounting for Accidents, all accidents are subject to registration, and the obligation is assigned not only to the Department of Internal Affairs, but also directly to the owners of vehicles - legal entities, road authorities and road owners. But the state statistical reporting includes information only about accidents that resulted in the death and / or injury of people (clause 5 of the Rules), with some exceptions (if an accident occurred as a result of a suicide attempt, encroachment on life and health, during auto competitions and some others).


In the literature, there is the concept of "contactless accident", which means an event that meets all the signs of an accident, but in the absence of interaction between the cars of the participants, and the consequences occur as a result of a collision with an object or a collision with another car. A fairly common phenomenon - the driver "cut" or braked sharply, thereby creating an emergency. If an accident occurs as a result, the question arises of the involvement of such a driver in the incident. Cases of bringing to responsibility and imposing obligations to compensate for damage caused as a result of an event provoked by such actions are rare.
The prevalence of the phenomenon led to the introduction in May 2016 in clause 2.7 of the SDA of the concept of dangerous driving and the establishment of a ban on drivers to perform a number of actions (repeated rebuilding, violations of distance and intervals, etc.). With the innovation, a legal justification has arisen for presenting property claims against “dashing” drivers, but the difficulty lies in the fact that such road users prefer not to pay attention to the accident that has occurred and calmly continue to move. It is not always possible to prove the involvement of a particular person in causing harm, even if it is possible to fix the car number and the circumstances of the incident.

Another specific type of accident is a covert accident. A person who has committed a traffic violation and committed a traffic accident is hiding from the scene. It is possible to prove his involvement by conducting a trace examination if the car number is known. It also raises the question of the involvement of a particular driver, if several people are allowed to drive a car. Theoretically, situations are possible when the victim is hiding from the scene.
Actions after an accident
The procedure for the participants in an accident after an accident is determined by clauses 2.6 - 2.6.1 of the SDA. In general, involved drivers are required to:
- stop driving and leave the car at the stop;
- turn on the alarm;
- install an emergency stop sign;
- leave all the items related to the accident in their places (keep the scree, flying and falling objects, etc.).
If there are victims, it is required to provide them with first aid, call an ambulance and the police at cellular numbers 103 and 102 or at a single number 112, if necessary, send them to the nearest medical facility with passing transport, and if it is not available, take them on their own and return to the place.


Drivers are obliged to clear the road after fixing the initial location of cars (including by photo and video filming):
- in case of injury or death of people only in cases where the passage of other vehicles is impossible;
- in the absence of victims in cases where the passage of other vehicles is difficult.
In the absence of victims in an accident, disputes between the participants on the circumstances of the accident and on the damage received, the drivers have the right not to notify the police. They may choose to:
- draw up documents at the nearest traffic police post or in a police unit, having previously fixed the location of vehicles;
- draw up documents without calling the traffic police in cases provided for in Art. 11.1 of the Federal Law of April 25.04.2002, 40 No. XNUMX-FZ “On OSAGO”;
- do not file an incident if none of the participants insists on it.


In the absence of victims, but if there are disagreements in the circumstances of the incident and about the injuries received, the participants are obliged to notify the traffic police and wait for the arrival of the outfit. Upon receipt of an instruction from the traffic police, the incident can be registered at the nearest traffic police post or in a police unit with a preliminary fixation of the location of the vehicles.
Compensation for damages and non-pecuniary damage
An accident is inextricably linked to issues of compensation for harm. The liability for damages and compensation for non-pecuniary damage lies with the person responsible for the accident. Based on the circumstances, the mutual fault of the participants in the event or the fault of several drivers can be established if a mass accident has occurred. When compensating for damages under OSAGO, the fault of several participants is recognized as equal, until otherwise established, the payment is made proportionally.
It should be understood that the traffic police does not establish guilt in causing damage and even guilt in an accident. The police reveals and determines violations of the Rules of the road in the actions of the participants. In the general case, the violator of traffic rules is guilty of causing damage, but in disputable situations, the establishment of guilt or the degree of guilt is possible only in court.
Fines and other penalties for road accidents
Violation of traffic rules does not necessarily constitute an administrative offense. The violator cannot be brought to administrative responsibility if the corresponding article in the Code of Administrative Offenses is not provided for the violation committed. A typical example is a common cause of accidents - the wrong choice of speed. For such actions, responsibility is not established, if at the same time the maximum permissible speed provided for the given territory or established by road signs was not exceeded.


In the field of traffic safety violations, the following types of administrative penalties are applied:
- a warning;
- fines (most often fines range from 500 to 500 rubles);
- deprivation of the right to drive vehicles for a period of 1 to 24 months;
- arrest up to 15 days;
- Compulsory work lasting from 100 to 200 hours.
For drunk driving by a person subjected to administrative punishment for a similar offense or for refusing to undergo a medical examination, criminal liability is possible up to imprisonment for up to 24 months.
Strict observance of the Rules of the Road reduces to a minimum, and possibly eliminates the likelihood of getting into a traffic accident. There is a belief among highly qualified professional drivers that it is easy to avoid an accident due to one's own fault, but a real driver should be able to avoid accidents due to the fault of other road users. Attentiveness and accuracy behind the wheel eliminate the problems not only of the driver himself, but also of those around him.



