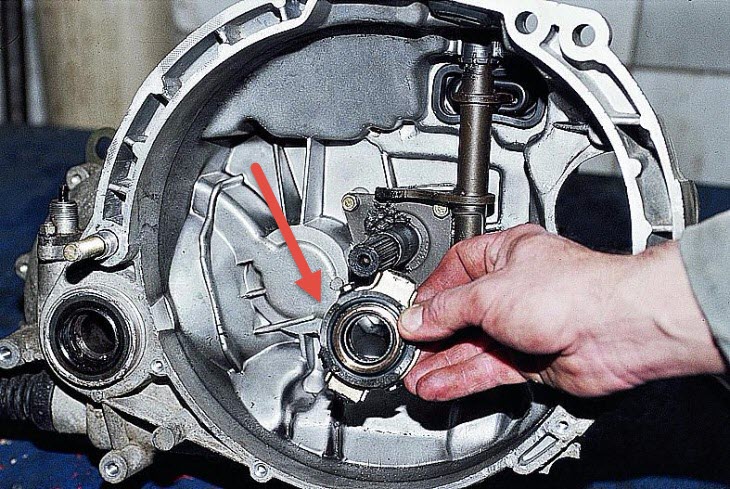
How the clutch release bearing works, malfunctions and methods of verification
Content
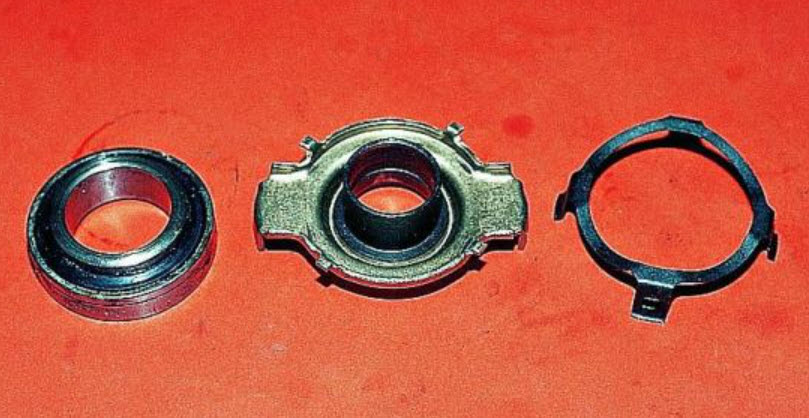
The classic clutch in a car consists of three main parts: a pressure plate with a spring, a driven plate and a release clutch. The last part is usually called the release bearing, although in fact it consists of several functional elements, but they usually work and are replaced as a whole.
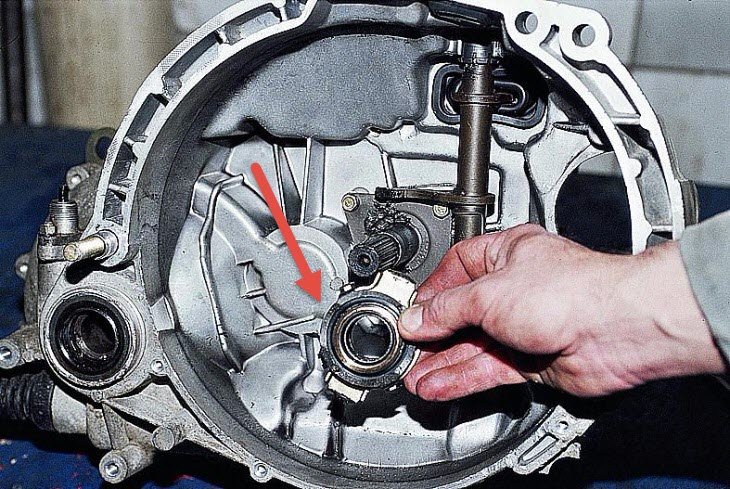
What is the function of the clutch release bearing?
The clutch during operation can be in one of three states:
- fully engaged, that is, the pressure plate (basket) with all the force of its powerful spring presses on the driven disc, forcing it to press against the surface of the flywheel to transfer all engine torque to the splines of the transmission input shaft;
- off, while the pressure is removed from the friction surfaces of the disc, its hub is slightly shifted along the splines and the gearbox opens with the flywheel;
- partial engagement, the disc is pressed with a metered force, the linings slip, the rotation speeds of the engine and gearbox shafts are different, the mode is used when starting off or in other cases when the engine torque is not enough to fully meet the needs of the transmission.
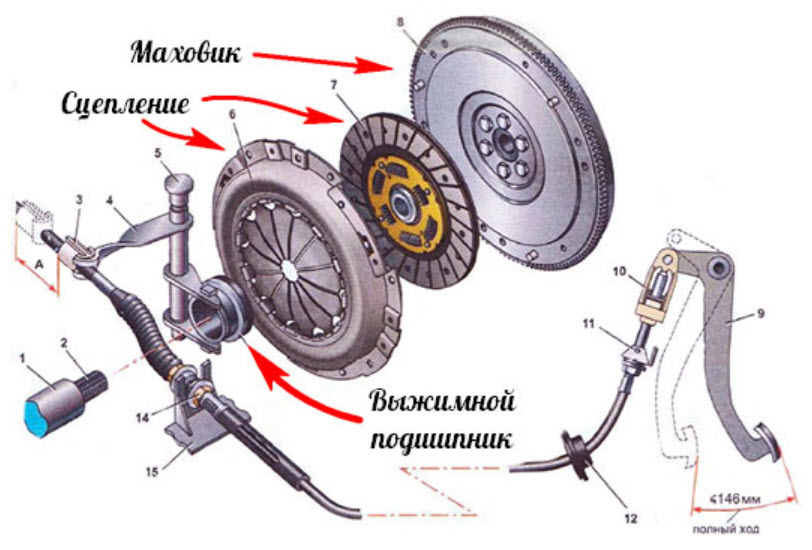
To control all of these modes, you must remove some of the force from the basket spring or release the disk completely. But the pressure plate is fixed on the flywheel and rotates with it and the spring at high speed.
Contact with the petals of the diaphragm spring or the levers of the coil spring set is possible only through the bearing. Its outer clip mechanically interacts with the clutch release fork, and the inner one is directly brought to the contact surface of the spring.
Part location
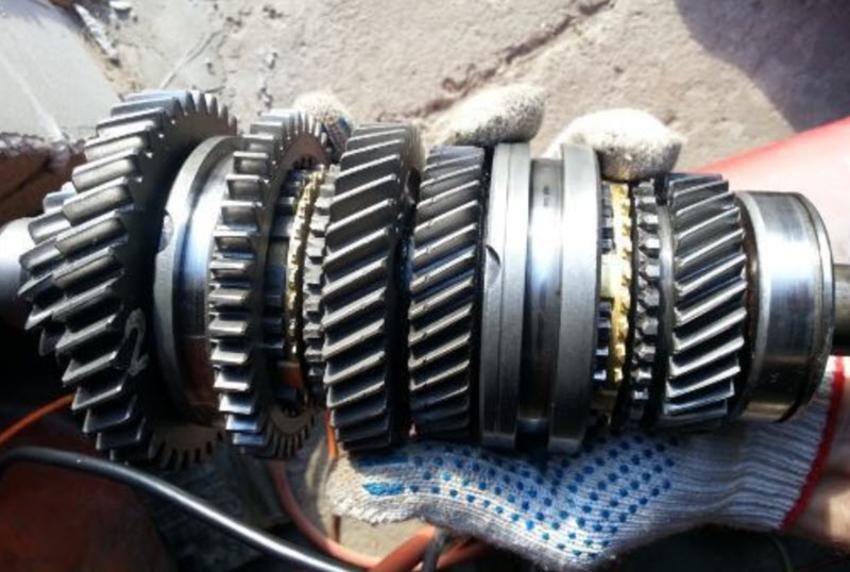
The release bearing clutch is located inside the clutch housing, which connects the engine block to the gearbox. The input shaft of the box protrudes from its crankcase, and on the outside it has splines for sliding the hub of the clutch disc.
The part of the shaft located on the side of the box is covered with a cylindrical casing, which acts as a guide along which the release bearing moves.

Устройство
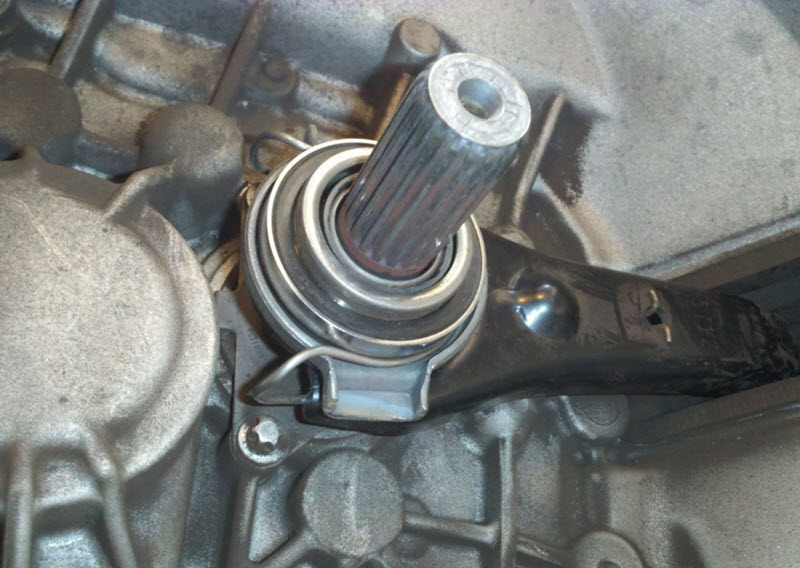
The release clutch consists of a housing and a bearing directly, usually a ball bearing. The outer clip is fixed in the clutch body, and the inner one protrudes and comes into contact with the basket petals or an additional adapter disk pressed against them.
The release force from the clutch pedal or electronic control actuators is transmitted through a hydraulic or mechanical drive system to the release housing, which causes it to move towards the flywheel, compressing the basket spring.

When the force is removed, the clutch is activated due to the force of the spring, and the release bearing moves to its extreme position towards the box.
There are systems with a normally engaged or disengaged clutch. The latter are used in preselective dual clutch gearboxes.
Types
Bearings are divided into those working with a gap, that is, springs completely extending from the petals, and backlash-free, always pressed against them, but with different forces.
The latter are most widely used, since the working stroke of the engagement clutch with them is minimal, the clutch works more accurately and without unnecessary acceleration of the inner clutch release at the moment it touches the supporting surface of the petals.
In addition, bearings are classified according to the way they are driven, although this only applies to their design.
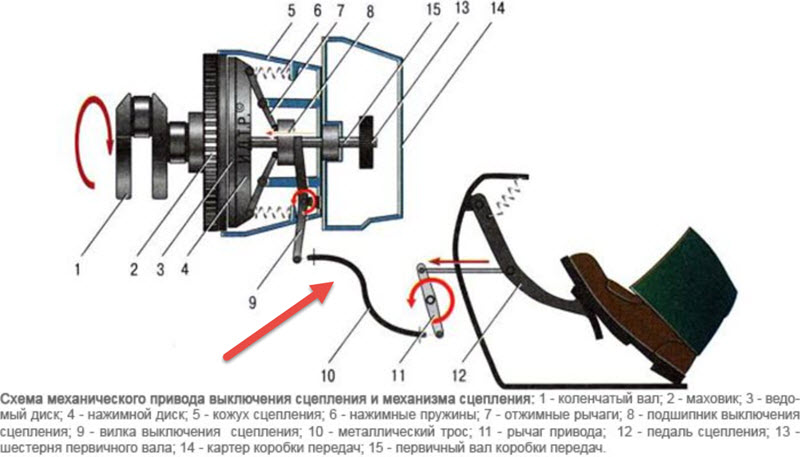
Mechanical drive
With a mechanical drive, the pedal is usually connected to a sheath cable, through which the force is transmitted to the release fork.
The fork is a two-arm lever with an intermediate ball joint. On the one hand, it is pulled by a cable, the other pushes the release bearing, covering it from two sides, avoiding distortion due to its floating landing.
Combined
Combined hydraulic drive reduces the effort on the pedals and runs more smoothly. The design of the fork is similar to mechanics, but it is pushed by the rod of the working cylinder of the drive.
The pressure on its piston is exerted by hydraulic fluid supplied from the clutch master cylinder connected to the pedal. The disadvantage is the complexity of the design, the increased price and the need for hydraulic maintenance.
Hydraulic drive
The fully hydraulic drive is devoid of parts such as fork and stem. The working cylinder is combined with the release bearing into a single hydro-mechanical clutch located in the clutch housing, only a pipeline approaches it from the outside.
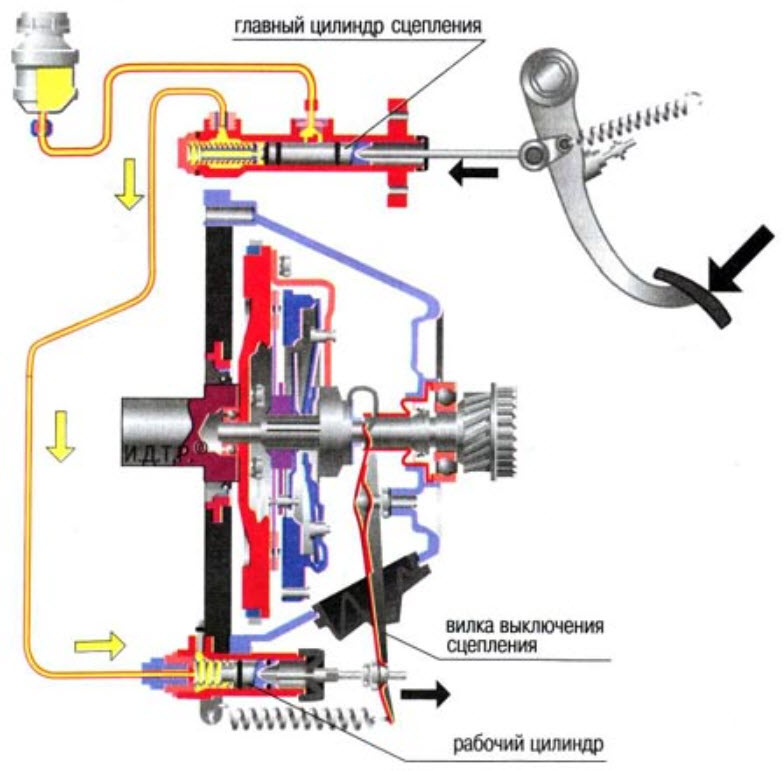
This allows you to increase the tightness of the crankcase and increase the accuracy of work, getting rid of intermediate parts.
There is only one drawback, but it is significant for owners of budget cars - you have to change the release bearing assembly with the working cylinder, which dramatically increases the cost of the part.
Malfunctions
Release bearing failure is almost always due to normal wear and tear. Most often, it is accelerated due to leakage of the cavity of the balls, aging and washing out of the lubricant.
The situation is aggravated at high thermal loads due to frequent clutch slips and overheating of the entire crankcase space.

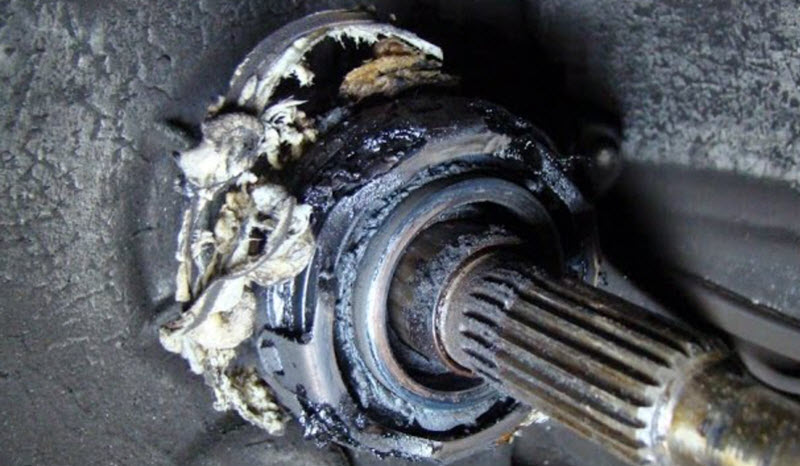
Sometimes the release bearing loses its mobility, wedging on its guide. The clutch, when turned on, begins to vibrate, its petals wear out. There are characteristic jerks when starting off. A complete failure with a broken plug is possible.

Verification methods
Most often, the bearing shows its problems with a hum, whistle and crunch. For different structures, the manifestation can be found in different modes.
If the drive is made with a gap, then with proper adjustment, the bearing does not touch the basket without pressing the pedal and does not manifest itself in any way. But as soon as you try to squeeze the clutch, a rumble appears. Its volume depends on the pedal stroke, the spring has a non-linear characteristic and at the end of the stroke the force and sound weaken.
In the most common cases, the gap is not provided, the bearing is constantly pressed against the basket, and its sound only changes, but does not disappear. Therefore, it is confused with the noise of the input shaft of the box.
The difference is that the gearbox shaft does not rotate when the gear is engaged, the clutch is depressed and the machine is stationary, which means it cannot make noise.
Replacing the release bearing
In modern cars, the resource of all component parts of the clutch is approximately equal, so the replacement is done as a kit. The kits are still sold, the package contains a basket, disc and release bearing.
An exception is the case of combining the clutch release with the working cylinder of the hydraulic drive. This part is not included in the kit, it is purchased separately, but it should be changed for any problems with the clutch.
The gearbox is removed for replacement. On some cars, it is only moved away from the engine, working through the resulting gap. This technique saves time only with a highly qualified master. But doing this is not recommended, since there are places in the clutch housing that require visual inspection.
For example, the fork, its support, the input shaft oil seal, the thrust bearing at the end of the crankshaft and the flywheel.


Watch this video on YouTube
It is always better to remove the box completely. After that, replacing the release bearing will not be difficult, it is simply removed from the guide, and a new part takes its place.
The guide should be lightly lubricated unless the specific kit instructions clearly state that lubrication is not required.
