Which map to choose for mountain biking?
Content
This, of course, has happened to you before ... A somewhat monotonous mountain bike ride, a sudden desire for adventure, freed from the route, and there ... lost in the green 🌳. There is no more road. No more network. Often these two go together, otherwise it's not fun. And then comes the famous: "Obviously, I did not take the card."
In this article, you will find all of our tips for understanding, choosing and customizing your karts to suit your practice and the conditions in which you ride.
Technologies and types of cards
Technology:
- The card is distributed on a virtual digital carrier "ONLINE",
- The card is distributed on a physical digital carrier "OFFLINE",
- The map is distributed on paper 🗺 or in a digital document (pdf, bmp, jpg, etc.).
Types of digital cards:
- Raster maps,
- Maps of the "vector" type.
The "online" map streams continuously and requires an Internet connection to display. The "offline" map is downloaded and preinstalled in the device memory.
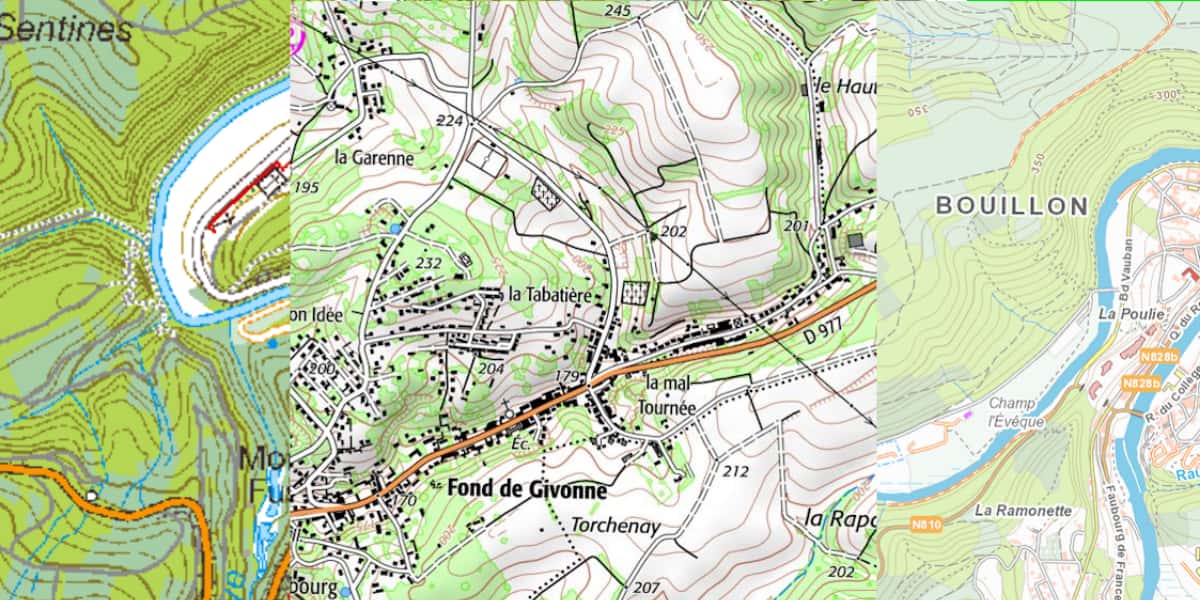
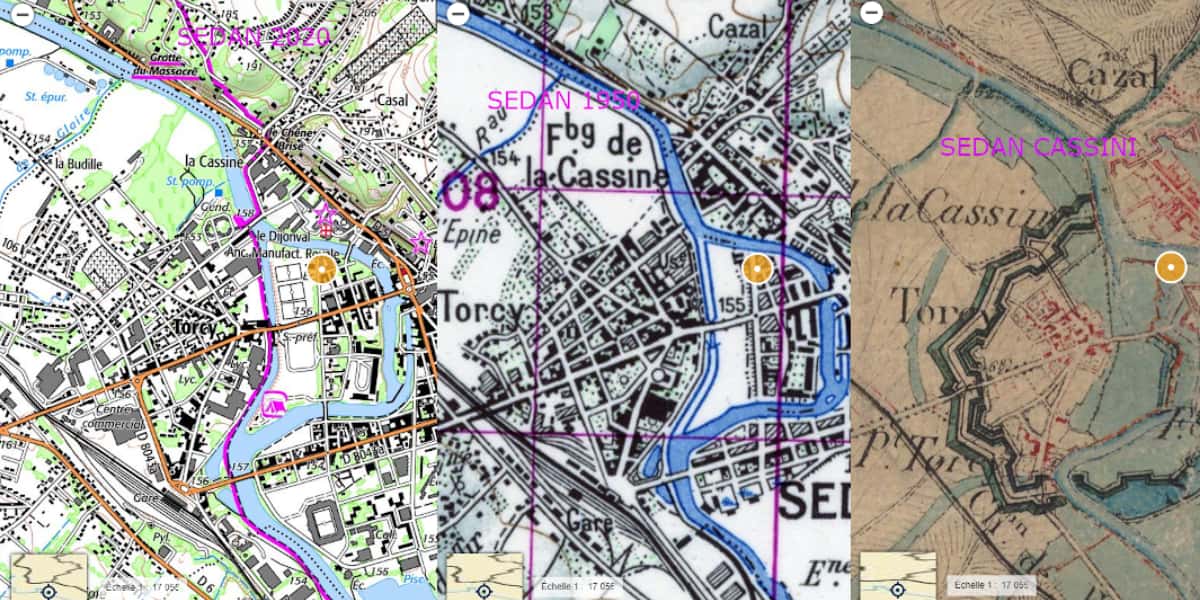
A raster map is an image, drawing (Topo) or photograph (Ortho). It is defined by a scale for paper media and a resolution (in dots per inch or dpi) for digital media. The most common example in France is the IGN Top 25 map at 1/25 on paper or 000m per pixel on digital.
Below is an illustration of a raster map such as IGN 1/25, three different sources on the same scale, located in the Ardenne Bouillon massif (Belgium), Sedan (France), Bouillon (Belgium).
The vector map is obtained from a database of digital objects. The file is a list of objects defined by a set of coordinates and an almost infinite list of characteristics (attributes). An application (smartphone) or software (website, PC, Mac, GPS) that draws a map on the screen, extracts from this file the objects included in the displayed area of the map, then draws points, lines and polygons on the screen.
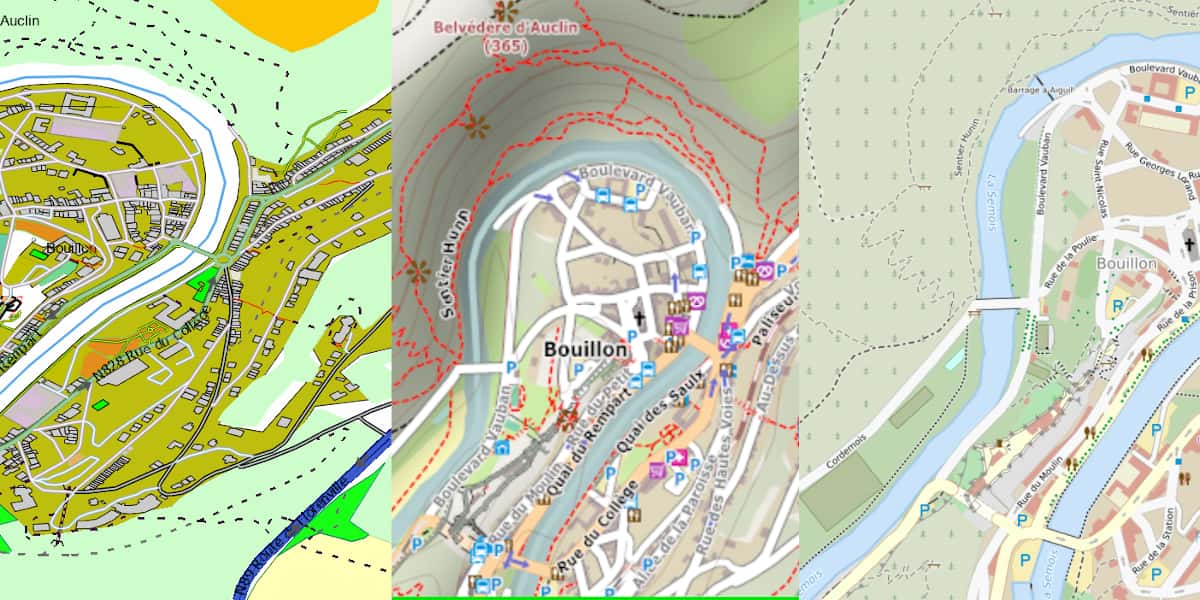
For mountain biking, the most commonly used Openstreetmap (OSM) collaborative mapping database.
Typical examples of a vector map. The initial data are identical and are all taken from OSM. The difference in appearance has to do with the software that renders the map. On the left is a mountain bike map customized by the author, in the center is 4UMAP (Standardized MTB) style presented by OpenTraveller, on the right is a mountain bike map from CalculIt Route.fr
The appearance of the raster map depends on the editor 👩🎨 (the artist who painted the picture, if you like), and the appearance of the vector map depends on the software that draws the image, depending on the end use.
For the same area, the appearance of a vector map designed for mountain biking can be completely different. And depending on the software that displays them, the mountain biking and cycling maps will also have different graphics. This site allows you to get an idea of the various possibilities.
The appearance of the raster map will always be the same.
Another important difference is the elevation representation, which is usually reliable and accurate for an IGN (raster) map, but less accurate on a vector map. Global altimeters databases are improving. Therefore, this weakness will gradually disappear.
The route calculation software (routing) of your GPS *, application or software can use the cycling of roads, trails, paths entered in the OSM database to calculate a route.
The quality and relevance of the proposed route depends on the availability, completeness and accuracy of the cycling data included in the OSM database.
(*) Garmin uses a method known as hot routes (heatmap) to plot a route using its GPS, which is the most frequently used route. See your Garmin Heatmap or Strava hatamart.
How to choose a GPS map?
Online or offline?
Usually a free online raster or vector map on a PC, Mac, or smartphone. But if you are traveling in the wild, especially in the mountains, make sure you have a mobile data network throughout the playground.
When you are "planted" in nature far away from everything, a footprint on a white or pixelated background is a great moment of privacy.
How much does a GPS card cost?
The order of magnitude ranges from 0 to 400 €; However, price is not synonymous with quality. In some countries, although the cost of the card is relatively high, the quality may be poor. Depending on where you are staying and depending on the type of card, you will need to purchase multiple cards or even cards from multiple countries (example for a Mont Blanc tour that crosses France, Switzerland and Italy).
What kind of storage should be provided for the GPS map?
The map can be represented as tiles or tiles (for example, 10 x 10 km), or it can cover an entire country or even an entire continent. If you need multiple cards, make sure you have enough memory. The larger the map, or the more maps, the more time the GPS processor must spend managing those maps. Thus, it can slow down other processing like publishing.
Should I update my GPS map regularly?
The map is partially obsolete as soon as it becomes available, due to human interference, telluric factors, or simply vegetation that deprives it of its rights. You've probably noticed that singles have an annoying tendency to evolve quickly, even fade away!
How often should I update the basemap?
This can turn into a restriction on employment when the renewal budget is large. As long as the probability of getting lost or finding your way is zero or very low, there is no need to regularly renew the card; Your mind will easily merge the gaps between the map and the landscape. If the likelihood of getting lost or finding your way is proven, you should have the most recent card. Lost in order to find yourself, you need to be able to connect the map and the surrounding area, otherwise a fun walk can quickly move to the galley.
What kind of coverage of the country or attractions?
Depending on the country, even within the European Union, the coverage and quality of some maps is poor or even very poor. A raster map of 1 / 25 (or equivalent) of each country does not go beyond the boundaries of that country. This map is placed on an opaque background due to overlays, there will always be a more or less large white area on the screen on one side or the other of the border. See illustration at bottom right.
For example, for a guided tour of Mont Blanc, the map must cover three countries. Depending on whether the route will be on foot, mountain bike or bike, due to the proximity of the route to the borders, scale and availability of maps, depending on the country, raster map areas (IGN type) will be displayed in white. more or less important.
OpenStreetMap covers the entire globe, including official map data for each country. Borders are no longer a problem! 🙏
All official cartographic data (infrastructure, buildings, etc.) appears in the OSM database. Otherwise, given that it is volunteers who complete and supplement this cartographic database, the more we go down to the detailed level of detail, the more heterogeneous the coverage will be.
A concrete example of a cartographic cover crossing a border (the next trail leaves an imprint of a multi-colored line running between two countries). On the right are raster maps of Germany and Belgium, type IGN. The influence of the German IGN map masks the Belgian IGN abroad for several kilometers, the trace is superimposed on the border graphics, it is almost invisible, when the position of the maps in the list is changed, the opposite effect occurs. On the left the vector map (from OSM) is solid, there is no gap.
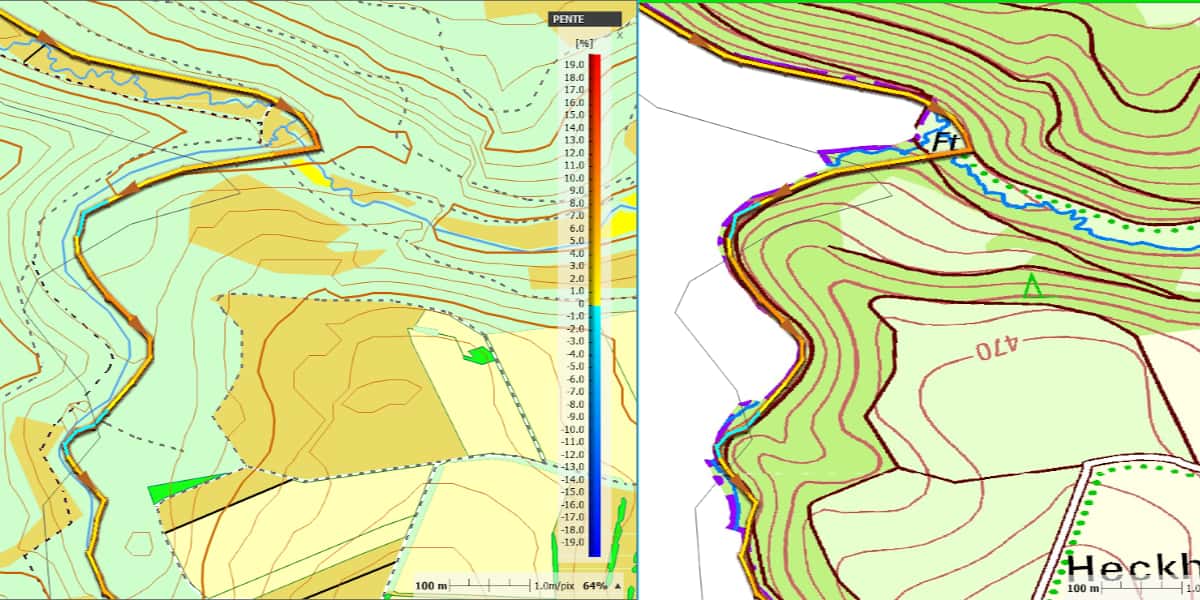
The advantage of using a reliable card
- Expect a physical collision
- Anticipate a change in direction
- Rest assured,
- Navigate and find yourself after navigation error,
- Re-route on the spot in case of an unforeseen event such as mechanical or human failure, unforeseen weather event, etc. Beware of automatic route selection, sometimes it is preferable to drive more even kilometers than to cross the pass! 😓
Card selection criteria
- 👓 card readability,
- Accuracy (freshness) of cartographic data,
- Fidelity to the relief ⛰.
A climber, hiker, steeper or orienteer will prefer a raster type map such as IGN topo (ISOM, etc.). He moves "relatively" slowly, he can get out of the way and must constantly establish a connection between what he sees on the map and on the ground. A raster map, which is a symbolic drawing of the area, is ideal for this purpose.
The cyclist 🚲 is relatively fast in his practice and has to stay on asphalt roads or “in the worst case” gravel paths, he is fully interested in using the vector map with routing as well as the road map. car road navigation, or for motorcycle, etc.
The range of MTB practice goes from the road like a cyclist to a raider. Therefore, both types of cards are suitable.
On a mountain bike, the purpose of which is to ride mainly on paths and singles, the travel speed is relatively high. A map that emphasizes the practicality of the paths and trails will be most appropriate, ie a vector map adapted for mountain biking or a UMAP type 4 raster plate ("rasterized" OSM data).
⚠️ An important aspect of a good mountain biking map is representativeness of paths and trails... The map should distinguish between roads, trails and paths by graphical representation and, if possible, highlight the criteria for suitability for cycling. If the event is planned in multiple countries or in countries without an IGN equivalent, choosing a vector map is important.
An example of a typed vector map for using MTB
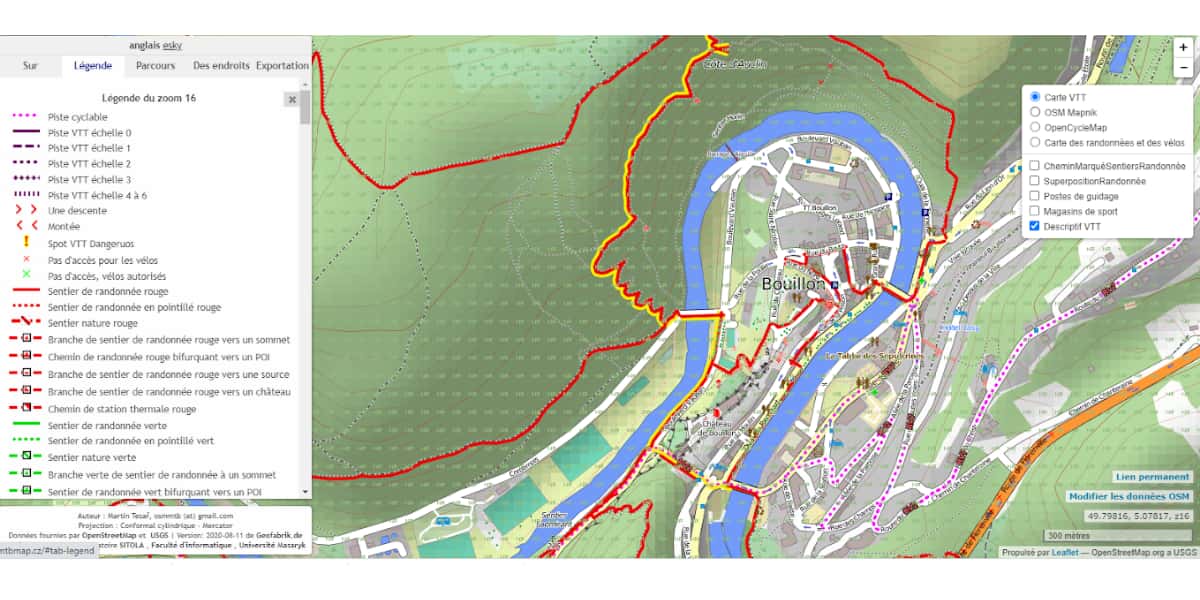
Map readability criteria
Level of detail
It is technically impossible to put everything on one card, otherwise it will be unreadable. During development, the scale of the map determines the level of detail.
- For a raster map that is always acquired at a specific scale (for example: 1 / 25), the level of detail is fixed. To see more or less detail, you need a multi-layer raster map, each layer at a different scale (different level of detail). The display software selects the displayed layer according to the zoom level (scale) requested by the screen.
- For a vector map, all digital objects are in the file, the software that draws the map on the screen selects the objects in the file according to the characteristics of the map and its scale in order to display them on the screen.
In the case of a raster map, the user will see all the elements on the map. In the case of a vector map, the program selects the elements displayed on the screen.
Below for the same geographic area, on the left is an IGN 1/25000 raster map, in the center (OSM vector 4UMAP) and on the right is a vector map with the so-called “Garmin” setting for mountain biking.
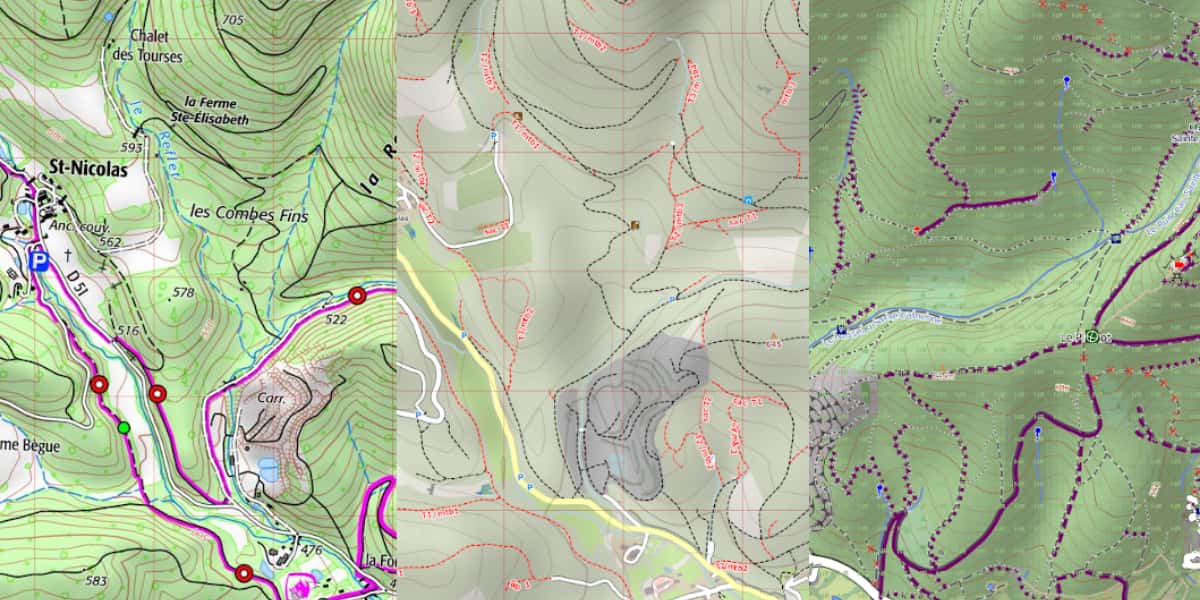
Cartographic visualization
- Card symbology is not standardized; each editor uses a different graphic 📜.
- A raster map is defined in pixels per inch (eg, photograph, drawing). Scaling shrinks or increases the pixels per inch of the map to match the scale requested by the screen. The map will look "slobbering" as soon as the scale value requested on the screen is greater than the map.
IGN raster map Total map size 7 x 7 km, sufficient to cover a loop of 50 km, screen display scale 1/8000 (normal mountain bike scale) on the left, the map is created at a scale of 0,4, 1 m / pixel (4000/100), computer size 1,5 MB, on the left, the map is created at a scale of 1 m / pixel (15000/9), computer size is XNUMX MB.
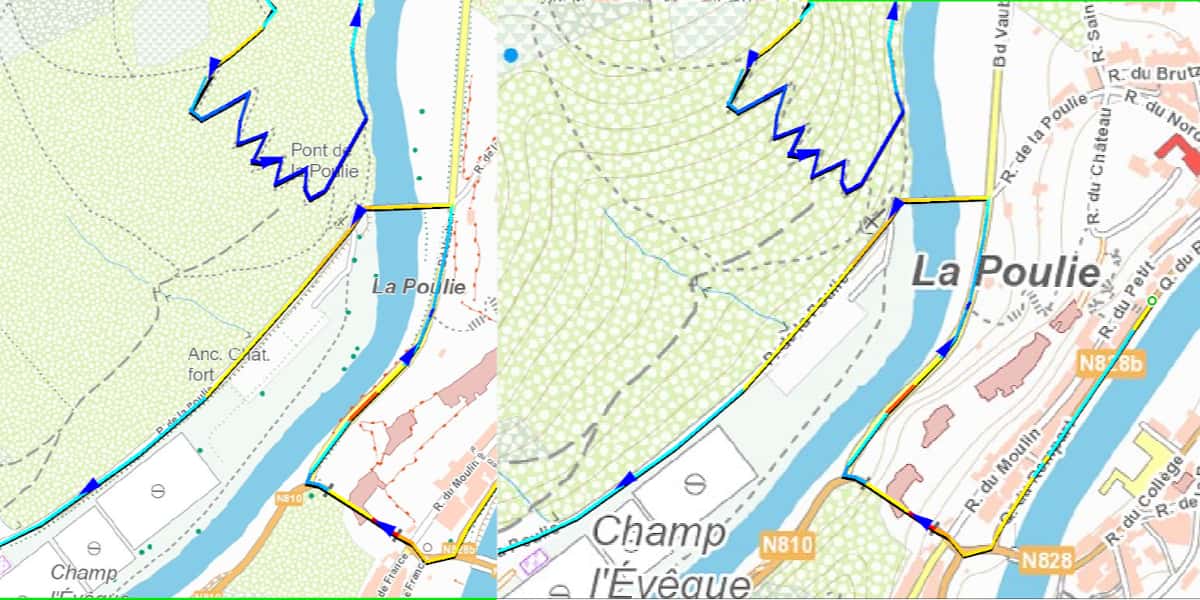
- Vector map is always clear on the screen, regardless of scale.
Vector map from OSM, covering the same screen area as above, map size 18 x 7 km, computer size 1 MB. Screen display scale 1/8000 The graphic aspect is independent of the scale factor (scaling).
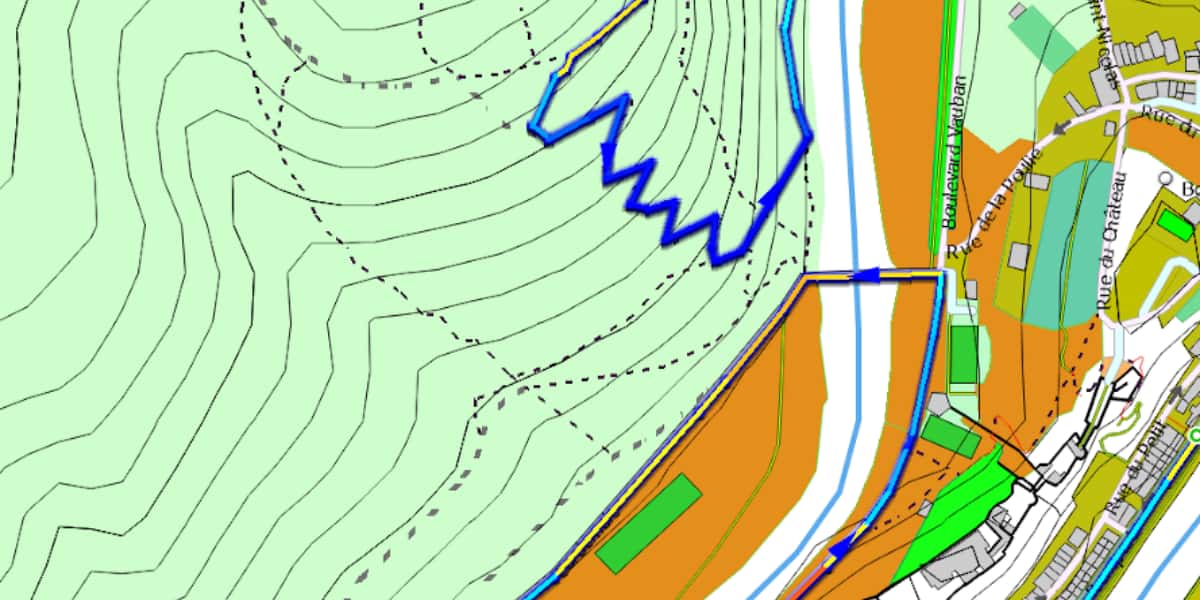
The illustration below compares in terms of rendering (for use on mountain bikes at the same scale) the Gamin TopoV6 map on the left, in the center of IGN France 1 / 25 (which starts to blur at this scale) and OSM '000. U-card "(OpenTraveller)
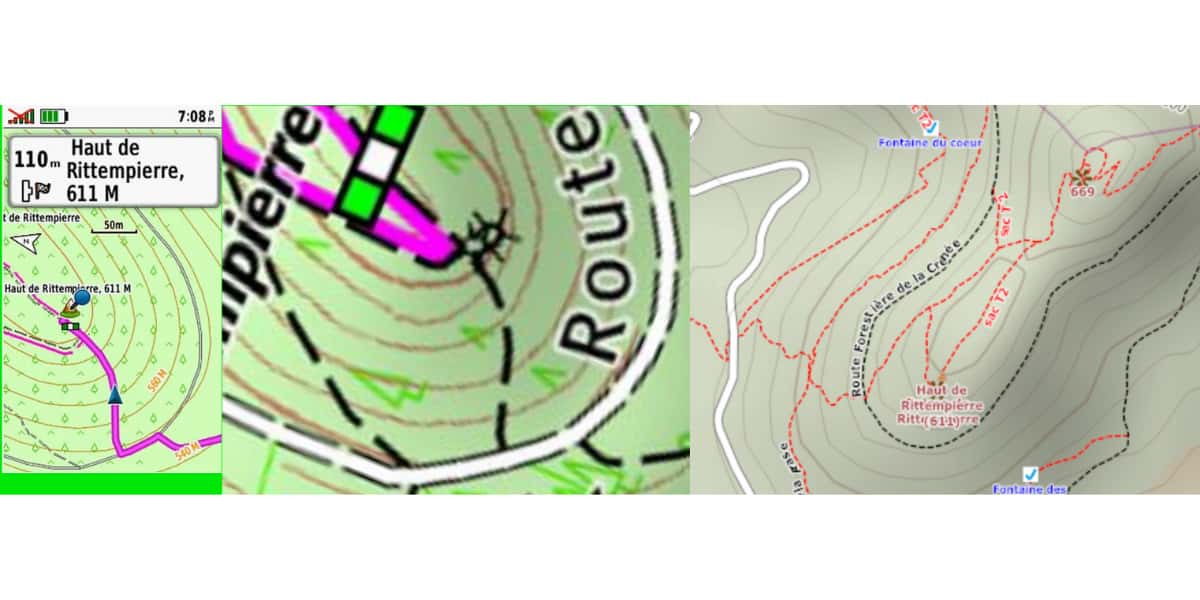
Map contrast and colors
Most applications, sites or software have menus for selecting and selecting a map, such as OpenTraveller or UtagawaVTT.
- For a raster map, the principle is the same as for displaying an image. The original map design (as shown in the photo) needs to have good contrast, and the screen quality in terms of brightness or contrast is important to get a readable map in all sunlight conditions.
- For a vector map, in addition to the screen quality mentioned above, the criteria used or used by the software or application will make the map "sexy" or not. Therefore, before purchasing, it is important to evaluate the visualization of the map drawn by the application or by the software used on the screen of the selected device.
In the case of GPS, the user can sometimes adapt the contrast of vector map objects:
- Garmin Topo map by modifying, editing or replacing the * .typ file.
- GPS TwoNav is a *.clay file located in the same directory as the map. It can be changed using the Land program.
Accuracy and Reliability Criteria
Generally:
- The map, as soon as it is published, contains deviations from reality on the ground, this is due to natural evolution (tellurism), seasons (vegetation), human intervention 🏗 (construction, attendance, etc.).
- A card sold or distributed by an organization is always behind the field. These differences depend on the date the database was frozen, the date earlier than the distribution date, the frequency of the updates, and, above all, the end user's susceptibility to these updates.
- The “free” vector maps available for download will always be newer and better suited to the landscape than their commercial counterparts and raster maps.
OpenStreetMap is a collaborative database 🤝 so updates are ongoing. Free map software users will draw directly from the latest OSM version.
Cycle criteria
OpenStreetMap allows a contributor to inform about cyclic paths and trails and specify MTB characteristics for a single file. These data are not filled in systematically, this is done at the direction of the authors 😊.
To find out if this data is in the database, we recommend using OpenTraveller and a 4 UMap basemap. In the example below, the singles are in red, the paths are in black, and the MTB cycling criterion is placed as a label attached to the path or singles.
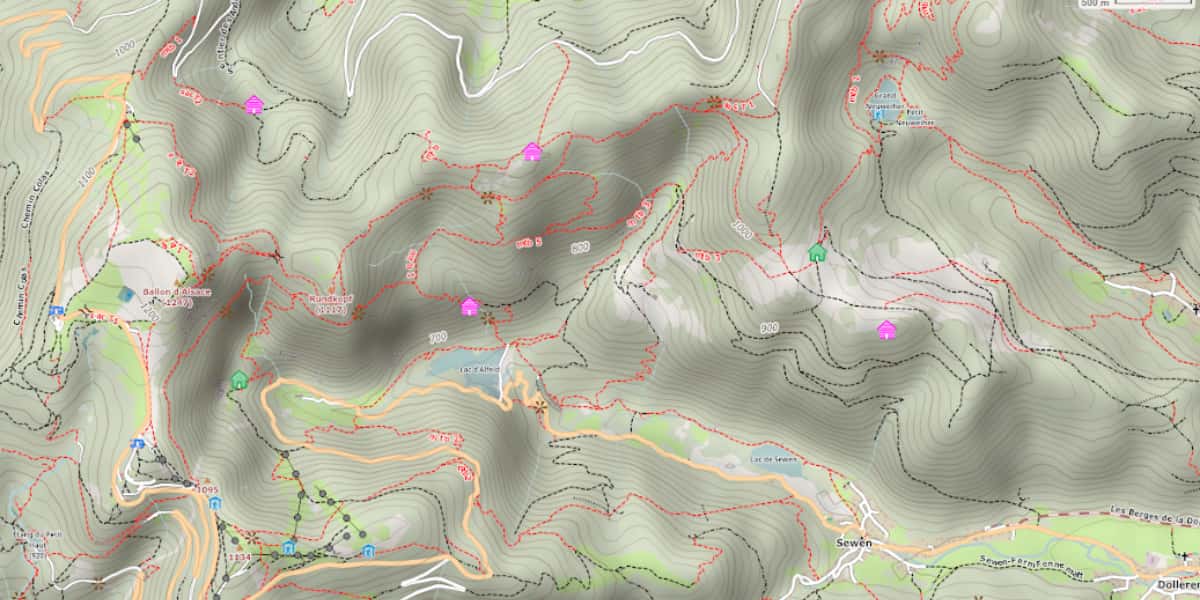
Example of legend (legend) used by Freizeitkarte (free vector map for Garmin GPS)

The image below demonstrates the lack of uniformity in MTB cycling presentation. In addition to the reliability of the map for mountain biking, this data is useful for routers to calculate and suggest appropriate routes for mountain biking.
All major roads are there, which is a guarantee of quality for cyclists. The main cycling routes (Eurovelo routes, Cycling routes, etc.) are marked in red and purple. The card can be used by people who travel frequently by bike (for example, packing bicycles, roaming).
Paths and trails suitable for mountain biking are marked in purple. The path density is the same between the purple spots, they are not typical for MTB practice in the database because it is due to the lack of local participants.
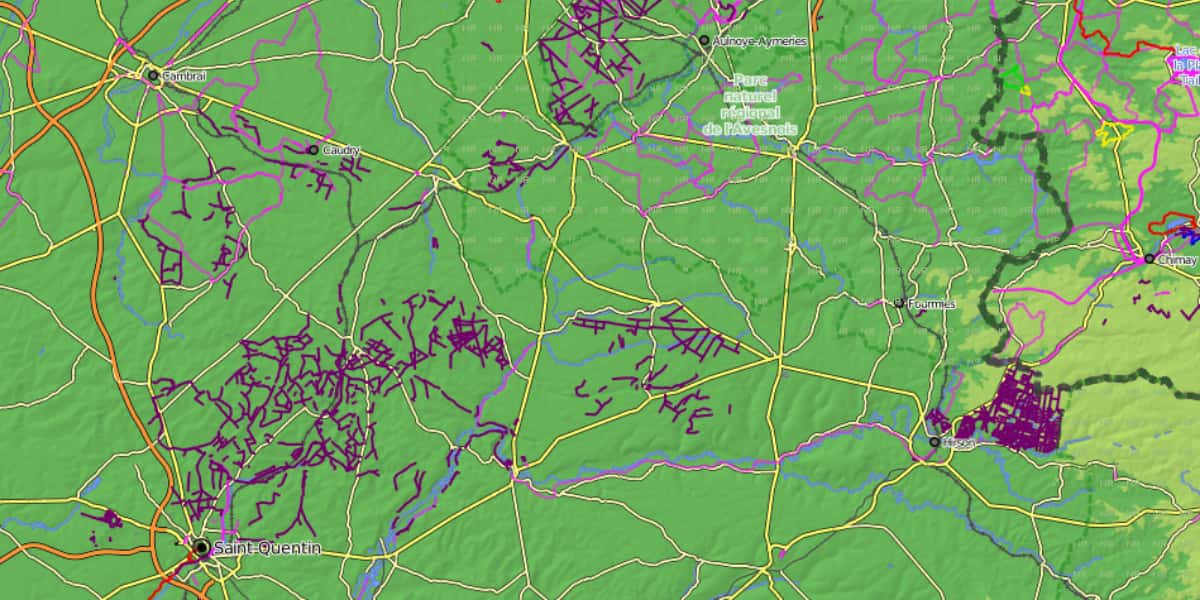
Card personalization
Personalization is about revealing the characteristics of the MTB card. For example, for XC mountain biking, the purpose of this personalization is to bring out the graphics of roads, trails, trails, singles (graphic aspect, color, etc.). For Enduro MTB customization, the map can emphasize the graphics and appearance of trails on points (chevrons, dashes, etc.) Specifically, the range of possibilities is very wide.
Most GPS or smartphone app vendors have their own settings. User 👨🏭 has no control.
- In Garmin, the graphic aspect of the map is defined in a file in the format .typ, this file can be replaced or edited with a text editor. You can find it online for download, or you can create your own customization. [Working method for developing your .typ is from this link] (http://paraveyron.fr/gps/typ.php).
- TwoNav has a similar principle, the configuration file is in * .clay format. It must have the same name as the map and be in the same macarte_layers.mvpf (OSM map) macarte_layers.clay (appearance) directory. The setting is done directly on the screen using the Land software via a dialog box.
The following image shows the principle of setting using LAND and limiting all settings.
- On the left, a "dialog box" develops layers of objects, in the center is a map, on the right is a dialog box dedicated to objects of the "path" type used to characterize an object, color, shape, etc. The possibilities are extensive and beyond the scope of this article.
- The main limit is the “always” contribution level. In this example, the track follows a single enduro or DH (downhill). Unfortunately, these features are not included in the map data.
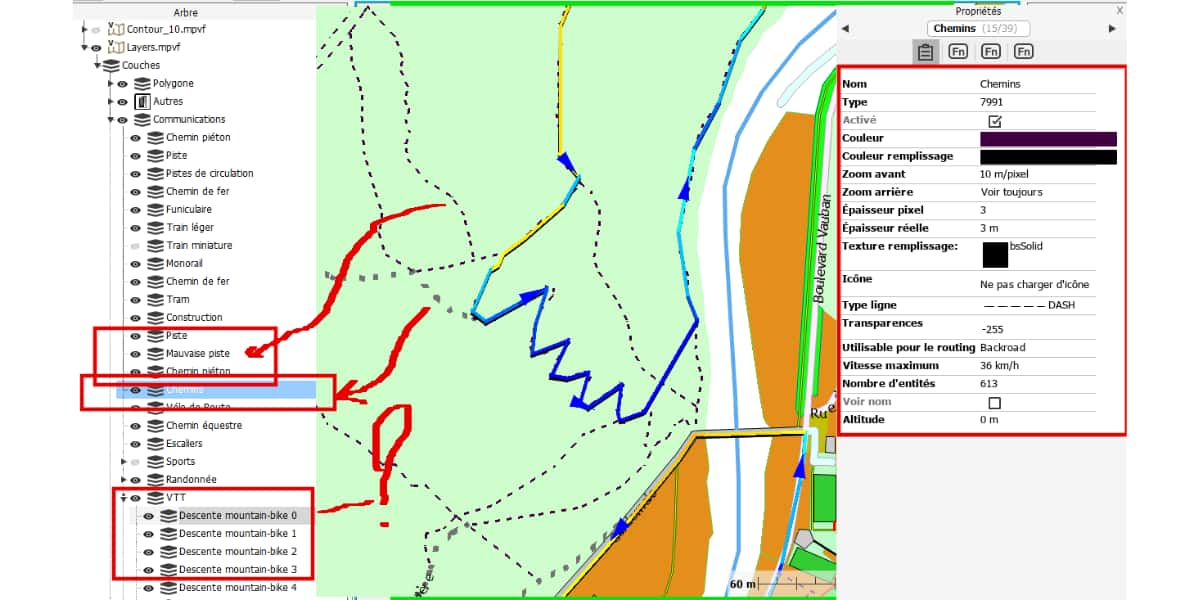
- The other limit itself is not a cartographic one, but a flaw in the GPS screen or smartphone that can be mitigated by tweaking without fixing.
Recommendations
For GPS
| supplier | Costs | Cards | Raster / Vector |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bryton | for free | High-end GPS only Bryton Custom Openstreetmap Cycling Pre-installed and available for modification | V |
| Garmin | Paid | Mouse Vx Vector enriched with IGN data or equivalent (outside France) Editable graphical view Customizable cycling or mountain biking. | V |
| Paid | Bird eye Equivalent topo 1/25 IGN ou Equivalent to ortho IGN (aerial photo) | R | |
| for free | Free card OpenStreetMap The graphical view is configured by the map depending on the activity | V | |
| for free | Alexis card | V | |
| for free | OpenTopoMap | V | |
| for free | OpenMTBmap | V | |
| for free | Mobac | R | |
| Hammerhead Karoo | for free | Dedicated bike-specific OpenStreetMap, pre-installed, with country-specific changes. | V |
| Lezyne | Smartphone map (app) | ||
| TwoNav | Paid | IGN Low Resolution Topographic Image (Purchase by country, department, region or 10 x 10 km slab) IGN Ortho TomTom (exclusively for cycling ..) OpenStreetMap is user configurable. | R R V V |
| for free | Any type of map with Earth tool, paper scan, JPEG, KML, TIFF, etc. IGN High Definition Topo (via Mobac) High Definition IGN Ortho (Via Mobac) OpenStreetMap is user configurable. | R R R V | |
| Wahoo | for free | Pre-installed and modifiable Wahoo Openstreetmap setting. | V |
Please note that KAROO's very latest offering for GPS cycling uses Android OS which is potentially compatible with the same capabilities as a smartphone, you just need to install the right app in it to have a smartphone with GPS.
For smartphone
Smartphone apps 📱 usually offer routable online maps from OSM with custom settings, cycling, mountain biking, etc.
The user should find out:
- behavior, excluding mobile data coverage and roaming charges outside France,
- the ability to add maps without connecting
- that the map covers all of your getaways if you have big travel plans.
Be careful because some apps will only be usable within the country, although most are universal.
Which card to choose for which outdoor practice?
| Raster map | Vector map | |
|---|---|---|
| XC MTB | ⭐️ | ⭐️⭐️ |
| MTB DH | ⭐️ | ⭐️⭐️ |
| Enduro MTB | ⭐️ | ⭐️⭐️ |
| MTB Walk / Trek | ⭐️⭐️⭐️ | |
| Mountain biking / family | ⭐️⭐️⭐️ | |
| walking | ⭐️⭐️⭐️ | |
| Sports Cycling | ⭐️ | ⭐️⭐️ |
| Cycling distance between bikes | ⭐️⭐️ | ⭐️ |
| pebble | ⭐️ | ⭐️⭐️ |
| Raid | ⭐️⭐️⭐️ | |
| orientation | ⭐️⭐️⭐️ | |
| Rock Climbing | ⭐️⭐️⭐️ |
Useful links
- Osm Map Wiki for Garmin
- Changing the Appearance of Garmin Topo Vx Maps
- Free maps for Garmin GPS
- Install Freizcarte on Garmin GPS Navigator
- How to Create Free Garmin Maps
- How to create an OpenStreetMap basemap
- TwoNav how to create a vector map with precise contour lines
