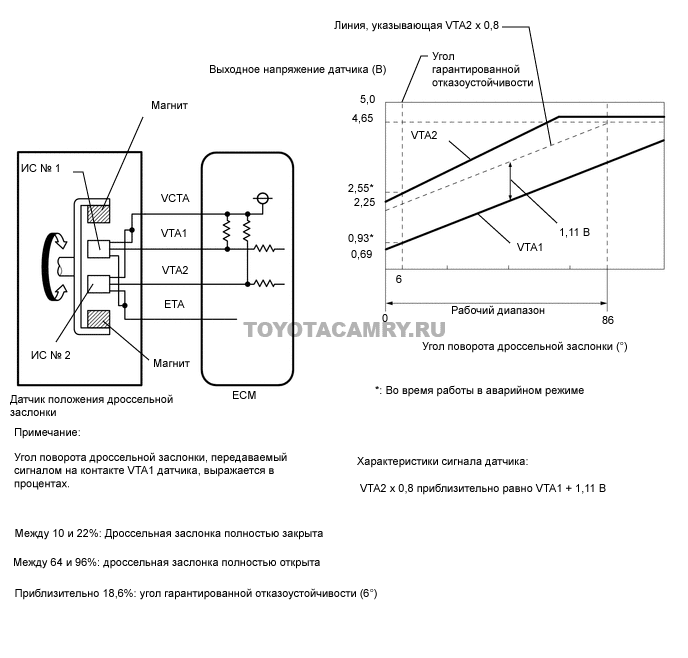
P0223 Throttle Position Sensor / Switch B Circuit High Input
Content
- OBD-II Trouble Code - P0223 - Data Sheet
- What does trouble code P0223 mean?
- Symptoms / severity
- Causes of the P0223 code
- Diagnostic and repair procedures
- Common Mistakes When Diagnosing Code P0223
- How serious is the P0223 code?
- What repairs can fix code P0223?
- Additional comments regarding code P0223?
- Need more help with your p0223 code?
OBD-II Trouble Code - P0223 - Data Sheet
High input signal in the throttle position sensor / switch B circuit
What does trouble code P0223 mean?
This Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) is a generic transmission code, which means it applies to OBD-II equipped vehicles. Although general, specific repair steps may differ depending on the brand / model.
When I came across a stored code P0223, I found that it means the powertrain control module (PCM) has detected a high voltage input from the Throttle Position Sensor (TPS) circuit or a specific Pedal Position Sensor (PPS) circuit. B refers to a specific circuit, sensor, or area of a specific circuit.
Consult a trusted source of vehicle information (all DIY data will work) for details of the vehicle in question. This code is only used in vehicles equipped with drive-by-wire (DBW) systems.
The PCM controls the DBW system using the throttle actuator motor, one or more pedal position sensors (sometimes called accelerator pedal position sensors), and multiple throttle position sensors. The sensors have a reference voltage (typically 5 V) and ground. Most TPS / PPS sensors are of the potentiometer type and complete the appropriate circuit. A pivoting axle extension on the accelerator pedal or on the throttle shaft actuates the sensor contacts. Sensor resistance changes as the pins move across the sensor PCB, causing changes in circuit resistance and signal input voltage to the PCM.
If the input signal voltage exceeds the programmed limit, for an extended period of time and under certain circumstances, code P0223 will be stored and a Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) may illuminate.
Symptoms / severity
When this code is stored, the PCM usually enters lame mode. In this mode, engine acceleration will be severely limited (unless disabled). Symptoms of a P0223 code may include:
- Stuck throttle (at all rpm)
- Limited acceleration or no acceleration
- Engine stalls when idling
- Oscillation on acceleration
- Cruise control is not working
- Loss of power
- Poor acceleration
- Engine may not start well or not start at all
- Accelerator pedal may not respond
- The Check Engine light will come on
Causes of the P0223 code
Possible causes of this engine code include:
- Open or short circuit in a chain between TPS, PPS and PCM
- Defective TPS or PPS
- Corroded electrical connectors
- Defective remote control drive motor
- Faulty Throttle Position Sensor
- Defective ECM
- Damaged, disconnected, or broken wiring harness associated with the throttle position sensor.
- Throttle body malfunction
- Throttle position sensor that is not aligned
Diagnostic and repair procedures
A good starting point is always to check the Technical Service Bulletins (TSB) for your particular vehicle. Your problem may be a known issue with a known manufacturer-released fix and could save you time and money while troubleshooting.
I would have access to a diagnostic scanner, digital volt / ohmmeter (DVOM) and vehicle information source like All Data (DIY) to diagnose the P0223 code.
I would take the first step of my diagnosis by visually inspecting all wiring and connectors associated with the system. I also like to check the throttle body for signs of carbon build-up or damage. Excessive carbon build-up that keeps the throttle body open at startup may result in a P0223 code being stored. Clean any carbon deposits from the throttle body according to the manufacturer's recommendations and repair or replace faulty wiring or components as necessary, then retest the DBW system.
Then I connect the scanner to the car diagnostic port and retrieve all stored DTCs. I write it down just in case I need the order in which the codes were stored. I also like to save any associated freeze frame data. These notes can be helpful if P0223 turns out to be intermittent. Now I am clearing the codes and test drive the car. If the code is cleared, I continue to diagnose
Power surges and mismatches between TPS, PPS and PCM can be detected using the scanner data stream. Narrow your data stream to display only relevant data for a faster response. If no spikes and / or inconsistencies are found, use the DVOM to obtain real-time data from each sensor individually. To obtain real-time data using the DVOM, connect the test leads to the appropriate signal and ground circuits and observe the DVOM display while the DBW is running. Note voltage surges when slowly moving the throttle valve from closed to fully open. The voltage typically ranges from 5V closed throttle to 4.5V wide open throttle. If surges or other abnormalities are found, suspect that the sensor being tested is defective. An oscilloscope is also a great tool for verifying sensor performance.
Additional diagnostic notes:
- Some manufacturers require the throttle body, throttle actuator motor, and all throttle position sensors to be replaced together.
A mechanic can diagnose a P0223 code by visually inspecting the throttle body and everything connected to it to make sure everything is working properly. This includes checking that the throttle position sensor is properly aligned with the throttle body and that the throttle body itself is good.
This check also includes checking that all electrical connectors are connected and secured properly. If the throttle body and all associated parts pass the visual inspection, the next step is to test the throttle position sensor to make sure it is putting out the correct voltage with a digital multimeter using the manufacturer's recommended procedure.
If the throttle position sensor fails the voltage test, the mechanic will replace the throttle position sensor at the customer's request. If the throttle position sensor passes the voltage test, the mechanic then uses a high tech scan tool to check the ECM for faults as it is one of the last untested parts in this system.
Common Mistakes When Diagnosing Code P0223
An easy mistake to make when diagnosing a P0223 code is to replace the throttle position sensor first. It is always recommended to fully test all parts of a failing system in order to correctly diagnose the root cause of the problem. This will help you avoid wasting time and money.
How serious is the P0223 code?
This code can cause the vehicle to perform much worse than it should, resulting in code P0223 ranking high on the severity scale. I would recommend having the vehicle diagnosed and repaired as soon as possible to save fuel and time while driving.
What repairs can fix code P0223?
- Throttle Position Sensor Replacement
- Replacing the engine control module
- Connect, repair or replace the wiring associated with the throttle position sensor.
- Repair or throttle valve replacement
- Throttle Position Sensor Adjustment
Additional comments regarding code P0223?
First of all, to prevent getting code P0223, it is recommended to clean the throttle body regularly. The throttle body should be cleaned with a throttle body cleaner and wiped with a clean towel at least once a year or whenever the air filter is changed. This will ensure smooth throttle operation and may help prevent problems in the future.
Need more help with your p0223 code?
If you still need help with DTC P0223, post a question in the comments below this article.
NOTE. This information is provided for informational purposes only. It is not intended to be used as a repair recommendation and we are not responsible for any action you take on any vehicle. All information on this site is protected by copyright.