Engine Overheating: Symptoms, Causes, Effects and Maintenance
Content
The evacuation of calories due to friction and part of the combustion is the role of the cooling circuit. Indeed, the motor has an ideal operating thermal range. It is too cold, his operating sets are wrong, the oil is too thick and the mixture must be fortified because the essence condenses on the cold parts. Too hot, there are not enough clearances, filling and performance are reduced, friction increases, the oil film can break and the engine can break.
If your motorcycle is air-cooled, there isn't much you can do to improve the efficiency of the cooling system other than adding a few intelligently spaced probes. However, if your motorcycle gets hot, with the exception of a very rare manufacturer design error, it is because the origin of the evil is elsewhere.
Danger, bad mix
Lack of gasoline in the engine can cause overheating. Owners of push-pull things know this! Dense motors, drilled pistons, are often the result of too small nozzles. Indeed, if there is not enough fuel, the movement of the flame front is rather slow because the droplets of gasoline cannot be found fast enough to spread. Since then, the combustion time has been extended, which heats up the engine more, especially in the exhaust area, since combustion is still maintained when the lights are turned on. Therefore, there is a risk of tightening. Another critical point: progress towards ignition. Too much in advance increases the cylinder pressure, favoring detonation. This sudden explosion of the entire fuel load suddenly requires mechanics and can even pierce the piston. This is the difference between fire and explosion. Pressure limits are not the same!
Liquid cooling
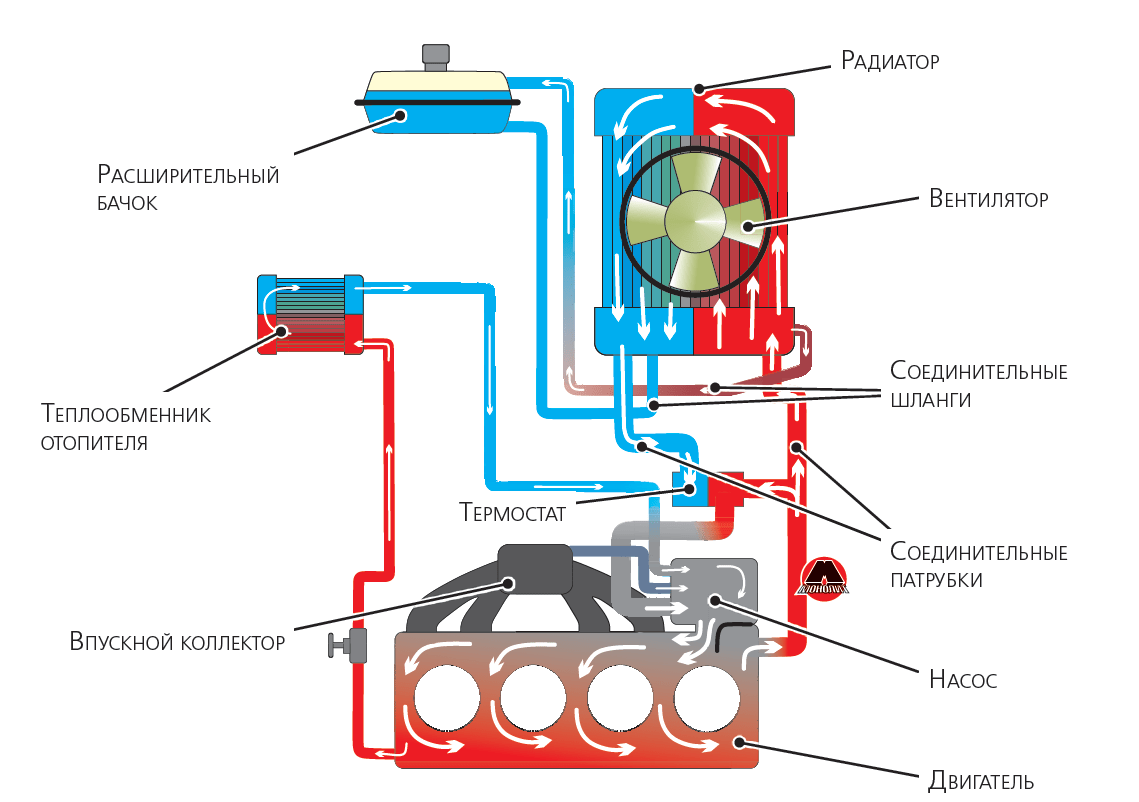
When liquid cooled, with the exception of these cash drawers, rarely seen on modern engines since the advent of electronic ignition / injection combinations, overheating is more associated with operational anomalies. Let's look at the components of the circuit one by one to find all possible failures.
Water pump
Rarely the source of the problem, she may still suffer from a training defect. Since then, the circulation of water is carried out only by a thermosyphon, that is, hot water rises, and cold water descends into the circuit, which causes circulation. This is not always sufficient to cool the engine and therefore, if in doubt, ensure that the pump rotates when starting the engine.
Nice cleaning!
Air bubbles in the cooling circuit can cause many problems. Indeed, if the water pump is stirring the air, nothing is done. Likewise, if the thermostat measures the temperature of the air bubbles ... It is not ready to trip and turn the fan! Finally, if you rely on trapped air bubbles to cool hot spots in the engine, you will be disappointed. So morality, before looking for the little beast, eliminates the bubbles at all the top of the chain.
Calorstat
This general term is misplaced as it refers to a registered trademark, as if we are talking about a refrigerator instead of a refrigerator. It is a deformable thermostatic device that opens and closes the cooling system depending on whether it is cold or hot. When cold, it turns off the radiator so that the engine can raise the temperature as quickly as possible. This reduces mechanical wear and polluting emissions. Once the temperature reaches a sufficient threshold, the metal membrane deforms and allows water to circulate to the radiator. If the calorific value is scaled up or faulty, water does not circulate in the radiator, even hot, and the engine heats up.
Thermostat
This thermal switch opens and closes the electrical circuit depending on the temperature. Again, in the event of a failure, it no longer starts the fan and allows the temperature to rise inexorably. In this case, you can unplug the connector that is connected to it and trace it with a piece of wire or paper clip, which you will insulate with glue. Then the fan will run continuously (unless it falls down!). Replace the thermostat quickly because driving with an engine that is too cold increases wear, pollutant emissions and consumption.
Fun
If it does not activate, it could also be due to it being burnt out or corroded (e.g. HP Cleaner). Make sure the propeller spins smoothly and connect directly to 12V.
Radiator
It can be connected either externally (insects, leaves, gum remnants, etc.) or internally (scale). Make sure it's clean. Don't overestimate the HP cleaner on its beams because they are very fragile and flex with fear. A water jet, detergent and blower are best. Inside, you can remove tartar with white vinegar. It's chic and cheap!
Cork!
it sounds silly, but it is very important, especially in a race. Indeed, at atmospheric pressure, water boils at 100 °, but you may have noticed that it boils earlier in the mountains because the atmospheric pressure is lower. By increasing the tarnishing of the radiator cap, you will delay boiling. With a forged 1,2 bar lid, boiling water requires up to 105 ° and even 110 ° to 1,4 bar. Therefore, if you are driving in the heat, it can be helpful, even if we have seen it, it is always better to drive colder for optimal performance. At these high temperatures, the allowed air expands, which reduces engine fill and performance. But if there is no other solution, it is easy to implement! However, beware of the weak link! If the pressure rises too much, the cylinder head seal may come loose, or the hoses will crack, the couplings may leak, etc. too much is needed.
Liquid level
It's silly here too, but if the liquid level is too low, there is air instead, and it doesn't cool either. The level is controlled by the cold in the expansion chamber, the presence of which is used to compensate for the expansion of the liquid due to the rise in temperature. Why is the level dropping? This is the question you must ask yourself. Leak on the cylinder head gasket, loose couplings, leak in the radiator ... open your eyes and right. A leaking cylinder head seal can be seen either on a circuit that builds up pressure, or when there is water or molasses in the oil, or when white vapors are in the exhaust. In the first case, it is the combustion pressure that passes through the circuit, in the second case, the integrity of the chamber is not violated, but the water comes out, for example, through the pins and mixes with the oil. In both cases, the level falls. It can also happen that the leaks are internal to the engine: chain corrosion (old motorcycle) or sandblasting tablets (latoca) that jumped and let water through the oil. Good to know: If you can't afford to replace your radiator, there are anti-leak products that are incredibly effective that can save you from crashing. They can be found in Renault (live experience) and elsewhere, liquid or powder.
Which liquid should I use?
If you are competing, do not ask yourself the question, this is water, imperative. Indeed, the regulations prohibit any other liquid (grease) that might spread on the runway. In fact, during the winter, be careful about storing and transporting your mount. Remember to empty it when in doubt! With conventional fluid, drain the circuit every 5 years or so (see manufacturer's recommendations). Otherwise, its antioxidant properties deteriorate and your engine's metal protection is no longer properly provided. Refer to the manufacturer's service manuals for the type of fluid you are using. Do not mix types of liquids, you risk chemical reactions (oxidation, traffic jams, etc.).
Mineral liquid
They are often blue or green. We're talking about type C.
Organic liquid
We recognize them by their yellow, pink or red color, but each manufacturer has their own codes, so don't trust them too much. We are talking about the D / G type. They have a longer service life and better barrier properties than Type C fluids.
Symptoms, sometimes surprising, cooling problems
The heating motor warns you with its fan, which does not work on time. Watch the level of the liquid in the expansion tank, as well as for the white marks around the clamps of the water circuit, this is almost always where it flows insidiously.
An engine that does not heat up is likely to consume more because the injection will systematically enrich the mixture. The engine will have multiple failures and you will also feel gasoline in the exhaust.
The most unexpected breakdown is probably the bike that won't start! The battery is valiant, the starter is fun, there is gas and ignition. So what's going on ?! One of the reasons, among other things, may be a failure of the water temperature sensor! Indeed, it is during injection that it indicates whether to enrich the mixture or not. However, in some cases, when probing the grids, the control unit adopts a default average value (60 °) so as not to endanger the engine. Therefore, there is no more automatic enrichment (starter) at start and it is impossible to start! However, to see this, you will need a diagnostic device that will allow you to view the values accounted for for each sensor. It is not always easy to find breakdowns with modern electronics!
