Density and viscosity of transformer oil
Transformer oil density
The characteristic features of all brands of transformer oils are considered to be the possibly lower dependence of the density index on external temperature and the lower value of the thickening point (for example, for oil of the TKp brand, the latter is -45°C, and for the T-1500 - even -55 ° C).
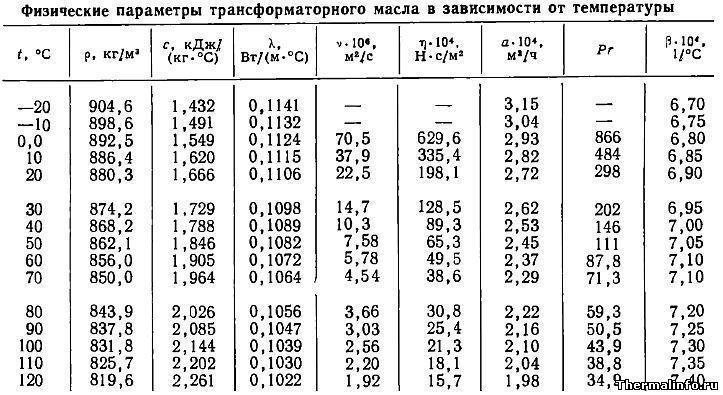
Standard transformer oil density ranges vary depending on oil density in the range (0,84…0,89)×103 kg / m3. Other factors that affect density include:
- Chemical composition (presence of additives, the main of which is ionol).
- Thermal conductivity.
- Viscosity (dynamic and kinematic).
- Thermal diffusivity.
To calculate a number of performance characteristics, the density of the transformer oil is taken as a reference value (in particular, to determine the conditions of internal friction affecting the cooling capacity of the medium).


Density of used transformer oil
In the process of extinguishing possible electrical discharges that may occur inside the transformer housing, the oil becomes contaminated with the smallest particles of electrical insulation, as well as products of chemical reactions. At high local temperatures, they can occur in an oily environment. Therefore, over time, the density of the oil increases. This leads to a decrease in the cooling capacity of the oil and the appearance of possible conduction bridges that reduce the electrical safety of the transformer. This oil needs to be replaced. It is carried out after a certain number of hours of operation of the device, which is usually indicated by its manufacturer. However, if the transformer is operated under boundary conditions, the need for replacement may appear earlier.


For products based on paraffins, an increase in the density of transformer oil is also due to the fact that the oxidation products (sludge) are insoluble and settle at the bottom of the tank. This sediment acts as an obstacle to the cooling system. In addition, the excess volume of macromolecular compounds increases the pour point of the oil.
Testing the actual values of the density index is carried out in the following sequence:
- Oil samples are taken from different locations of the tank. The fact is that the destruction of a dielectric is inversely proportional to its water content, which means that the dielectric strength of transformer oil decreases as the water content increases.
- Using a densitometer, measure the density of the oil and compare it with the recommended values.
- Depending on the number of hours the oil has been running in the transformer, either the specified volume of new oil is added, or the old one is carefully filtered out.


Viscosity of transformer oil
Viscosity is a characteristic that affects heat transfer inside the oil reservoir. Viscosity calculation always remains an important operating parameter when choosing an oil for any type of power electrical device. It is especially important to know the viscosity of transformer oil at extreme temperatures. According to the requirements of the state standard, the determination of kinematic and dynamic viscosity is carried out at temperatures of 40°C and 100°C. When the transformer is predominantly used outdoors, an additional measurement is also performed at a temperature of 15°C.
The accuracy of viscosity determination increases if the refractive index of the medium is also examined in parallel with a refractometer. The smaller the difference in viscosity values obtained at different test temperatures, the better the oil. To stabilize the viscosity indicators, it is recommended to periodically hydrotreat transformer oils.


Watch this video on YouTube
