Specifications, malfunctions and self-repair of the VAZ 2105 engine
Content
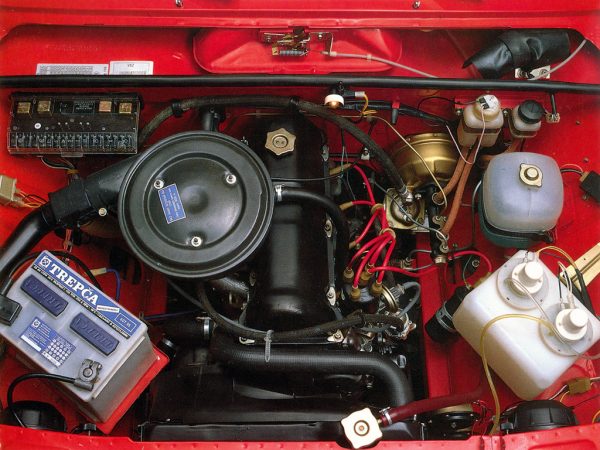
The popularity of classic VAZ models largely depends on the reliability and maintainability of their engines. Being designed in the distant seventies of the last century, they continue to "work" today. In this article we will talk about the power plants that the VAZ 2105 cars were equipped with. We will consider their technical characteristics, design, as well as the main malfunctions and how to fix them.
What engines were equipped with "five"
Throughout its history, the VAZ 2105 rolled off the assembly line with five different engines:
- 2101;
- 2105;
- 2103;
- 2104;
- 21067;
- BTM-341;
- 4132 (RPD).
They differed not only in technical characteristics, but also in the type of construction, the type of fuel consumed, as well as the method of supplying it to the combustion chambers. Consider each of these power units in detail.

More about the device and characteristics of the VAZ-2105: https://bumper.guru/klassicheskie-modeli-vaz/poleznoe/vaz-2105-inzhektor.html
VAZ 2101 engine
The first unit installed on the "five" was the old "penny" engine. It did not differ in special power qualities, but it had already been tested and proved to be excellent.
Table: main characteristics of the VAZ 2101 engine
| The name of the characteristics | Index |
| Cylinder arrangement | Inline |
| Number of cylinders | 4 |
| Type of fuel | Gasoline AI-92 |
| Number of valves | 8 |
| The method of supplying fuel to the cylinders | Carburetor |
| The volume of the power unit, cm3 | 1198 |
| Cylinder diameter, mm | 76 |
| Piston movement amplitude, mm | 66 |
| Torque value, Nm | 89,0 |
| Unit power, h.p. | 64 |
VAZ 2105 engine
For the "five" was specially designed its own power unit. It was an improved version of the VAZ 2101 engine, which was distinguished by a large volume of cylinders with the same piston stroke.
Table: main characteristics of the VAZ 2105 engine
| The name of the characteristics | Index |
| Cylinder arrangement | Inline |
| Number of cylinders | 4 |
| Type of fuel | Gasoline AI-93 |
| Number of valves | 8 |
| The method of supplying fuel to the cylinders | Carburetor |
| The volume of the power unit, cm3 | 1294 |
| Cylinder diameter, mm | 79 |
| Piston movement amplitude, mm | 66 |
| Torque value, Nm | 94,3 |
| Unit power, h.p. | 69 |
VAZ 2103 engine
The “triple” engine was even more powerful, however, not due to an increase in the volume of the combustion chambers, but due to a modified crankshaft design, which made it possible to slightly increase the piston stroke. A crankshaft of the same design was installed on the Niva. VAZ 2103 engines from the factory were equipped with both contact and non-contact ignition systems.
Table: main characteristics of the VAZ 2103 engine
| The name of the characteristics | Index |
| Cylinder arrangement | Inline |
| Number of cylinders | 4 |
| Type of fuel | Gasoline AI-91, AI-92, AI-93 |
| Number of valves | 8 |
| The method of supplying fuel to the cylinders | Carburetor |
| The volume of the power unit, cm3 | 1,45 |
| Cylinder diameter, mm | 76 |
| Piston movement amplitude, mm | 80 |
| Torque value, Nm | 104,0 |
| Unit power, h.p. | 71,4 |
VAZ 2104 engine
The power unit of the fourth Zhiguli model, which was installed on the VAZ 2105, differed in the type of injection. Here, not a carburetor was already used, but electronically controlled nozzles. The engine has undergone some changes regarding the installation of units for the injection supply of the fuel mixture, as well as several monitoring sensors. In all other respects, it practically did not differ from the carburetor "triple" motor.
Table: main characteristics of the VAZ 2104 engine
| The name of the characteristics | Index |
| Cylinder arrangement | Inline |
| Number of cylinders | 4 |
| Type of fuel | Gasoline AI-95 |
| Number of valves | 8 |
| The method of supplying fuel to the cylinders | Distributed injection |
| The volume of the power unit, cm3 | 1,45 |
| Cylinder diameter, mm | 76 |
| Piston movement amplitude, mm | 80 |
| Torque value, Nm | 112,0 |
| Unit power, h.p. | 68 |
VAZ 21067 engine
Another unit that was equipped with the "fives" was borrowed from the VAZ 2106. In fact, this is a modified version of the VAZ 2103 engine, where all the improvements were reduced to increasing power by increasing the diameter of the cylinders. But it was this engine that made the "six" the most popular car due to the reasonable ratio of the amount of fuel consumed and the developed power.
Table: main characteristics of the VAZ 21067 engine
| The name of the characteristics | Index |
| Cylinder arrangement | Inline |
| Number of cylinders | 4 |
| Type of fuel | Gasoline AI-91, AI-92, AI-93 |
| Number of valves | 8 |
| The method of supplying fuel to the cylinders | Carburetor |
| The volume of the power unit, cm3 | 1,57 |
| Cylinder diameter, mm | 79 |
| Piston movement amplitude, mm | 80 |
| Torque value, Nm | 104,0 |
| Unit power, h.p. | 74,5 |
Engine BTM 341
BTM-341 is a diesel power unit, which was installed on classic VAZs, including the "fives". Basically, such cars were exported, but we could also meet them here. The BTM-341 engines did not differ in either special power or low fuel consumption, which is apparently why the diesel Zhiguli did not take root in the USSR.
Table: main characteristics of the BTM 341 engine
| The name of the characteristics | Index |
| Cylinder arrangement | Inline |
| Number of cylinders | 4 |
| Type of fuel | Diesel fuel |
| Number of valves | 8 |
| The method of supplying fuel to the cylinders | Direct injection |
| The volume of the power unit, cm3 | 1,52 |
| Torque value, Nm | 92,0 |
| Unit power, h.p. | 50 |
VAZ 4132 engine
Installed on the "five" and rotary engines. At first, these were prototypes, and then mass production. The VAZ 4132 power unit developed twice as much power as all other Zhiguli engines. For the most part, "fives" with rotary engines were provided by police units and special services, but ordinary citizens could also purchase them. Today it is rare, but still you can find a VAZ with an engine 4132 or similar.
Table: main characteristics of the VAZ 4132 engine
| The name of the characteristics | Index |
| The method of supplying fuel to the cylinders | Carburetor |
| Type of fuel | AI-92 |
| The volume of the power unit, cm3 | 1,3 |
| Torque value, Nm | 186,0 |
| Unit power, h.p. | 140 |
What engine can be installed on a VAZ 2105 instead of a regular one
The “Five” can be easily equipped with a power unit from any other “classic”, whether it be a carbureted VAZ 2101 or an injection VAZ 2107. However, connoisseurs of this tuning prefer engines from foreign cars. The best for these purposes are power plants from the "closest relative" - Fiat. His models "Argenta" and "Polonaise" are equipped with engines that fit our VAZs without any problems.

Fans of more powerful motors can try to install a power unit from Mitsubishi Galant or Renault Logan with a volume of 1,5 to 2,0 cm3. Here, of course, you will have to change the mounts for the engine itself and for the gearbox, however, if everything is done correctly, the result will surprise you. But it is important not to overdo it, because each body is designed for a certain load, including engine power.
Well, for those who wish to move around in a unique car, we can advise you to equip your “five” with a rotary power unit. The cost of such an engine today is 115-150 thousand rubles, but its installation will not require any alterations. It is perfect for any "classic" VAZ.

Also check out the VAZ 2105 generator device: https://bumper.guru/klassicheskie-modeli-vaz/generator/generator-vaz-2105.html
The main malfunctions of VAZ 2105 engines
If we do not take into account the power plants BTM 341 and VAZ 4132, the VAZ 2105 engines differ little from each other. They have a similar design, and, therefore, they have the same malfunctions. The main signs that the motor is out of order are:
- the impossibility of its launch;
- unstable idling;
- violation of the normal temperature regime (overheating);
- drop in power;
- exhaust color change (white, gray);
- the occurrence of extraneous noise in the power unit.
Let's find out what the listed symptoms may indicate.
Inability to start the engine
The power unit will not start when:
- lack of voltage on the spark plugs;
- malfunctions in the power system that prevent the flow of the fuel-air mixture into the cylinders.
The absence of a spark on the electrodes of the candles may be due to a malfunction:
- the candles themselves;
- high-voltage wires;
- ignition distributor;
- ignition coils;
- interrupter (for cars with contact ignition);
- switch (for cars with contactless ignition)
- Hall sensor (for vehicles with contactless ignition system);
- ignition lock.
Fuel may not enter the carburetor, and from there into the cylinders due to:
- clogging of the fuel filter or fuel line;
- malfunction of the fuel pump;
- obstruction of the carburetor inlet filter;
- malfunction or incorrect adjustment of the carburetor.
Unstable operation of the power unit at idle
Violation of the stability of the power unit at idle may indicate:
- malfunctions of the carburetor solenoid valve;
- failure of one or more spark plugs, breakdown of insulation or violation of the integrity of the current-carrying core of a high-voltage wire;
- burning of breaker contacts;
- improper adjustment of the quantity and quality of the fuel used to form the fuel-air mixture.
More about the VAZ 2105 ignition system: https://bumper.guru/klassicheskie-modeli-vaz/elektrooborudovanie/zazhiganie/kak-vystavit-zazhiganie-na-vaz-2105.html
Overheating
The normal temperature of a running VAZ 2105 engine is 87–950C. If her performance exceeds the limit of 950C, the engine is overheating. This can lead not only to burning the cylinder block gasket, but also to jamming of moving parts inside the power unit. Causes of overheating can be:
- insufficient coolant level;
- low-quality antifreeze (antifreeze);
- faulty thermostat (looping the system in a small circle);
- clogged (clogged) cooling radiator;
- airlock in the cooling system;
- failure of the radiator cooling fan.
Power reduction
Engine power may decrease when:
- use of low-quality fuel;
- incorrectly set moment and ignition timing;
- burning of breaker contacts;
- violation of the regulation of the quality and quantity of fuel used to form the fuel-air mixture;
- wear of piston group parts.
Exhaust color change
The exhaust gases of a serviceable power unit are in the form of steam and smell exclusively of burnt gasoline. If thick white (blue) gas comes out of the exhaust pipe, this is a sure sign that oil or coolant is burning in the cylinders along with the fuel. Such a power unit will not “live” for a long time without a major overhaul.
The causes of thick white or bluish exhaust are:
- burnout (breakdown) of the cylinder head gasket;
- damage (crack, corrosion) of the cylinder head;
- wear or damage to parts of the piston group (cylinder walls, piston rings).
Knocking inside the engine
A working power unit makes many different sounds, which, merging, form a pleasant rumbling, indicating that all components and mechanisms are working smoothly. But if you hear extraneous noises, in particular, knocks, this should alert you. They are a sure sign of a serious problem. In the engine, such sounds can be made by:
- valves;
- piston pins;
- connecting rod bearings;
- main bearings;
- timing chain drive.
Valves knock due to:
- unregulated increase in the thermal gap;
- wear (fatigue) of springs;
- camshaft lobes wear.
The knock of the piston pins usually occurs when the ignition timing is not adjusted correctly. At the same time, the fuel-air mixture ignites ahead of time, which provokes the occurrence of detonation.
Faulty connecting rod and main bearings of the crankshaft also cause extraneous noise in the engine. When they wear out, the gap between the moving elements of the crankshaft increases, which causes play, accompanied by a high-frequency knock.
As for the timing chain, it can create extraneous sounds in cases of stretching and a malfunction of the damper.
Repair of the VAZ 2105 engine
Most malfunctions of the power unit can be eliminated without removing it from the car. Especially if they relate to ignition, cooling or power systems. But if we are talking about malfunctions in the lubrication system, as well as the failure of the elements of the piston group, the crankshaft, then dismantling is indispensable.
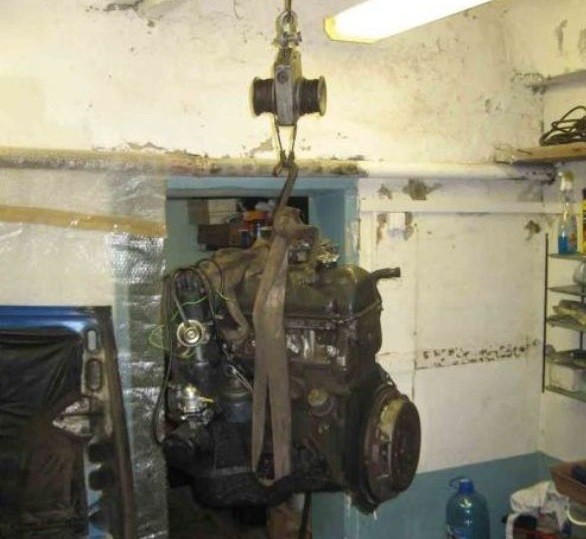
Removing the engine
Dismantling the power unit is not so much a laborious process as it requires special equipment, namely a hoist or other device that will allow you to pull a heavy engine out of the engine compartment.
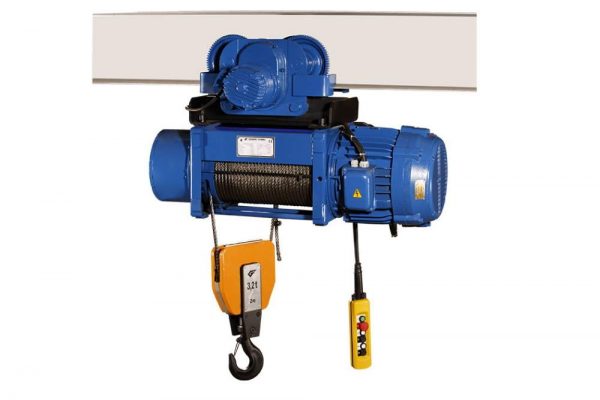

In addition to the telfer, you will also need:
- garage with a viewing hole;
- set of wrenches;
- Screwdriver Set;
- a dry vessel with a volume of at least 5 liters for draining the coolant;
- chalk or marker for making marks;
- a pair of old blankets or covers to protect the paintwork of the front fenders when dismantling the motor.
To remove the engine:
- Drive the car into a viewing hole.
- Completely remove the hood, having previously marked the contours of the canopies with a marker or chalk. This is necessary so that when installing it, you do not have to suffer with setting gaps.
- Drain the coolant from the cylinder block.
 To drain the coolant, unscrew the drain plug on the cylinder block
To drain the coolant, unscrew the drain plug on the cylinder block - Disconnect and remove the battery.
- Loosen the clamps on all pipes of the cooling system, dismantle the pipes.
 To remove the pipes, you need to loosen the clamps of their fastening.
To remove the pipes, you need to loosen the clamps of their fastening. - Disconnect the high voltage wires from the spark plugs, coil, ignition distributor, oil pressure sensor.
- Loosen the clamps on the fuel lines. Remove all fuel hoses going to the fuel filter, fuel pump, carburetor.
 The fuel lines are also secured with clamps.
The fuel lines are also secured with clamps. - Unscrew the nuts securing the intake pipe to the manifold.
 To disconnect the intake pipe, unscrew the two nuts
To disconnect the intake pipe, unscrew the two nuts - Disconnect the starter by unscrewing the three nuts securing it to the clutch housing.
- Unscrew the upper bolts securing the gearbox to the engine (3 pcs).
 At the top of the gearbox is attached with three bolts
At the top of the gearbox is attached with three bolts - Disconnect and remove the air and throttle actuators on the carburetor.
- Remove the coupling spring from the inspection hole and unscrew the bolts securing the clutch slave cylinder. Take the cylinder to the side so that it does not interfere.
- Unscrew the lower bolts securing the gearbox to the engine (2 pcs).
 At the bottom of the gearbox is attached with two bolts
At the bottom of the gearbox is attached with two bolts - Unscrew the bolts fixing the protective cover (4 pcs).
 The protective cover is held on by 4 bolts.
The protective cover is held on by 4 bolts. - Unscrew the nuts securing the power unit to the supports.
 The engine is mounted on two supports
The engine is mounted on two supports - Securely fasten the chains (belts) of the hoist to the engine.
 The easiest way to lift the engine is with an electric hoist.
The easiest way to lift the engine is with an electric hoist. - Carefully lift the motor, loosening it, to remove it from the guides.
- Move the engine with a hoist and place it on a workbench, table or floor.
Video: engine removal
Replacing the earbuds
To replace the liners, you must:
- Clean the power plant from dust, dirt, oil drips.
- Using a 12mm hex wrench, unscrew the drain plug and drain the oil from the sump.

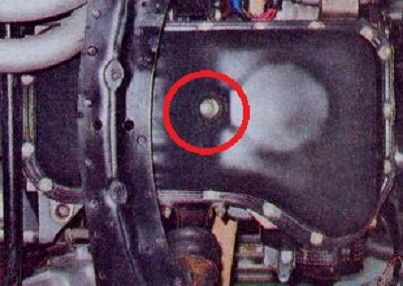 The plug is unscrewed with a 12 hex wrench
The plug is unscrewed with a 12 hex wrench - Using a 10 wrench, unscrew the 12 bolts securing the pan to the crankcase. Remove tray.
- Remove the ignition distributor and carburetor from the power unit.
- Remove the valve cover by unscrewing 8 nuts with a 10 wrench.

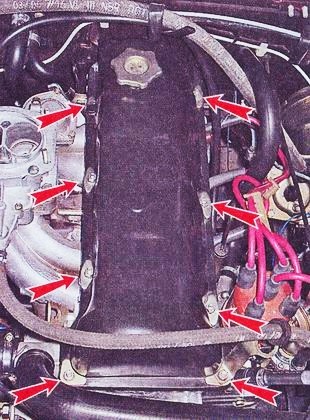 Cover fixed with 8 nuts
Cover fixed with 8 nuts - Bend the edge of the lock washer that secures the camshaft star mounting bolt with a large slotted screwdriver or mounting spatula.

 To unscrew the bolt, you need to bend the edge of the washer
To unscrew the bolt, you need to bend the edge of the washer - Using a 17 wrench, unscrew the camshaft star bolt.

 To unscrew the bolt, you need a key for 17
To unscrew the bolt, you need a key for 17 - Using a 10 wrench, unscrew the two nuts securing the timing chain tensioner. Remove tensioner.

 The tensioner is attached with two nuts.
The tensioner is attached with two nuts. - Remove the camshaft sprocket together with the chain drive.
- Using a 13 socket wrench, unscrew the 9 nuts securing the camshaft bed. Remove it along with the shaft.

 "Bed" is fixed with 9 nuts
"Bed" is fixed with 9 nuts - Using a 14 wrench, unscrew the nuts securing the connecting rod caps. Remove insert covers.

 To remove the cover, you need a key for 14
To remove the cover, you need a key for 14 - Remove the connecting rods from the crankshaft, pull out all the liners.

 Inserts are located under the covers
Inserts are located under the covers - Using a 17 wrench, unscrew the bolts securing the main bearing caps.
- Dismantle the covers, remove the thrust rings.
- Remove the main bearings from the cylinder block and covers.

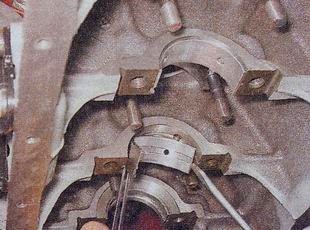 The main bearings are located under the covers and in the cylinder block
The main bearings are located under the covers and in the cylinder block - Dismantle the crankshaft.
- Rinse the crankshaft in kerosene, wipe with a clean dry cloth.
- Install new bearings and thrust washers.
- Lubricate all bearings with engine oil.
- Install the crankshaft to the cylinder block.
- Replace main bearing caps. Tighten and tighten the bolts of their fastening with a torque wrench, observing the tightening torque of 64,8–84,3 Nm.
- Install the connecting rods on the crankshaft. Tighten the nuts with a torque wrench, observing a tightening torque of 43,4–53,4 Nm.
- Assemble the engine in reverse order.
Video: inserting earbuds
Replacing rings
To replace the piston rings, follow p.p. 1-14 of the previous instruction. Next you need:
- Push the pistons out of the cylinders one by one along with the connecting rods.
- Thoroughly clean the surfaces of the pistons from carbon deposits. To do this, you can use kerosene, fine sandpaper and a dry rag.
- Use a screwdriver to remove the old rings.

 Old rings can be removed with a screwdriver
Old rings can be removed with a screwdriver - Put on new rings, observing the correct orientation of the locks.
- Using a special mandrel for rings (it is possible without it), push the pistons into the cylinders.

 Pistons with new rings are more convenient to install in cylinders using a special mandrel
Pistons with new rings are more convenient to install in cylinders using a special mandrel
Further assembly of the engine is carried out in the reverse order.
Video: installing piston rings
Oil pump repair
Most often, the oil pump fails due to wear on its cover, drive and driven gears. Such a malfunction is eliminated by replacing worn parts. To repair the oil pump, you must:
- Run p.p. 1-3 of the first instruction.
- Using a 13 wrench, unscrew the 2 oil pump mounting bolts.

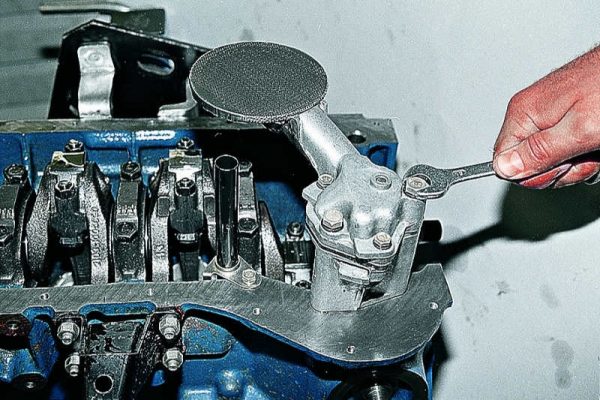 The oil pump is attached with two bolts.
The oil pump is attached with two bolts. - Using a 10 wrench, unscrew the 3 bolts securing the oil intake pipe.

 The pipe is fixed with 3 bolts
The pipe is fixed with 3 bolts - Disconnect the pressure reducing valve.
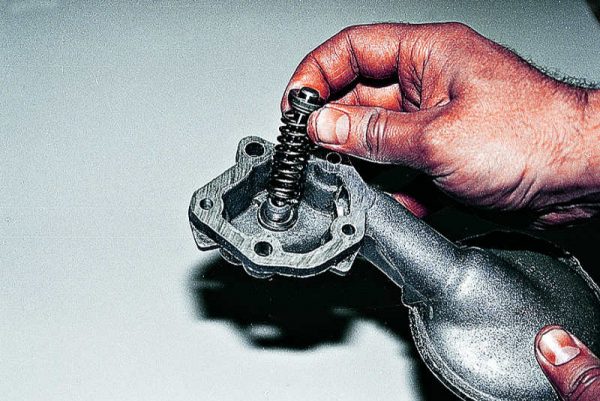
 The valve is located inside the pump housing
The valve is located inside the pump housing - Remove the cover from the oil pump.

 Under the cover are the driving and driven gears.
Under the cover are the driving and driven gears. - Remove the drive and driven gears.
- Examine the elements of the device. If they show visible signs of wear, replace the defective parts.
- Clean the oil pickup screen.

 If the mesh is clogged, it must be cleaned
If the mesh is clogged, it must be cleaned - Assemble the device in reverse order.
- Assemble the engine.
Video: oil pump repair


Watch this video on YouTube
As you can see, self-repair of the VAZ 2105 engine is not particularly difficult. It can be carried out in the conditions of your own garage without the involvement of specialists.












