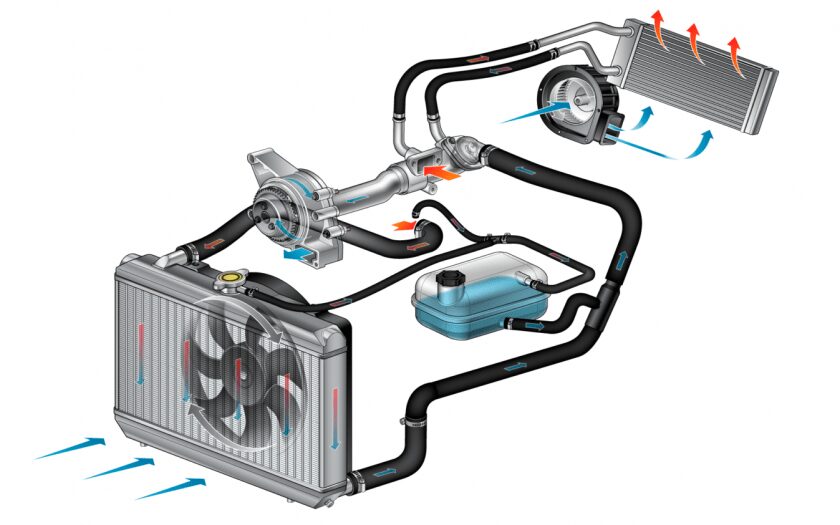
Engine cooling system device
Content
During operation, the engine parts are exposed not only to mechanical, but also to serious thermal stress. In addition to the frictional force that causes some of the components to heat up, the engine burns the air / fuel mixture. At this moment, a huge amount of thermal energy is released. The temperature, depending on the modification of the engine in some of its departments, can exceed 1000 degrees.
Metal elements expand when heated. Perekal increases their fragility. In an extremely hot environment, the air / fuel mixture will ignite uncontrollably, resulting in detonation in the unit. To eliminate problems associated with engine overheating and maintain the optimum temperature of the unit, the car is equipped with a cooling system.
Consider the structure of this system, what breakdowns appear in it, how to care for it and what varieties exist.
What is a cooling system
The purpose of the cooling system in the car is to remove excess heat from the running motor. Regardless of the type of internal combustion engine (diesel or gasoline), it will definitely have this system. It allows you to maintain the operating temperature of the power unit (about what this parameter should be, read in another review).

In addition to the main function, this system, depending on the car model, provides:
- Cooling of transmissions, turbines;
- Interior heating in winter;
- Engine lubrication cooling;
- Exhaust gas recirculation cooling.
This system has the following requirements:
- It must maintain the operating temperature of the internal combustion engine in different operating conditions;
- It should not overcool the engine, which will reduce its efficiency, especially if it is a diesel unit (the principle of operation of this type of engine is described here);
- Should allow the motor to warm up quickly (low engine oil temperature increases the wear of the unit parts, since it is thick and the pump does not pump it well to each unit);
- Should consume a minimum of energy resources;
- Maintain the temperature of the motor for a long time after it has stopped.
The device and principle of operation of the cooling system
Although structurally CO of individual car models may differ, their principle remains identical. The system device includes the following elements:
- Cooling jacket. This is part of the motor. In the block of cylinders and the cylinder head, cavities are made that make up a system of channels in the assembled internal combustion engine through which the working fluid circulates in modern engines. This is by far the most efficient way to remove heat from a cylinder block that experiences extreme temperature rises. Engineers design this element so that the coolant contacts those parts of the block wall that need to be cooled the most.

- Cooling radiator. This is a flat rectangular piece, which consists of thin metal tubes with aluminum foil ribs strung on them. Additionally, the device of this element is described in another article... Hot fluid from the motor enters its cavity. Due to the fact that the walls in the radiator are very thin, and there are a large number of tubes and fins, the air passing through them quickly cools the working environment.

- Heating system radiator. This element has a design identical to the main radiator, only its size is several times smaller. It is installed in the stove module. When the driver opens the heating flap, the heater fan blows air to the heat exchanger. In addition to heating the passenger compartment, this part acts as an additional element for cooling the engine. For example, when the car is in a traffic jam, the coolant in the system can boil. Some drivers turn on interior heating and open windows.
- Cooling Fan. This element is installed near the radiator. Its design is identical to any modification of the fans. In old cars, the work of this element depended on the engine - while the crankshaft was rotating, the blades were also spinning. In modern design, this is an electric motor with blades, the size of which depends on the radiator area. It is triggered when the liquid in the circuit is very hot, and the heat transfer that occurs during the natural blowing of the heat exchanger is insufficient. This usually happens in the summer, when the car is standing or moving slowly, for example, in traffic jams.
- Pump. It is a water pump that runs continuously as long as the motor is running. This part is used in power units in which the cooling system is of a liquid type. In most cases, the pump is driven by a belt or chain drive (a timing belt or chain is put on the pulley). In vehicles with a turbocharged engine and direct injection, an additional centrifugal pump can be used.

- Thermostat. It is a small wastegate that regulates the coolant flow. Most often this part is located near the outlet of the cooling jacket. Details about the device and the principle of operation of the element are described here. Depending on the car model, it can be bimetallic or electronically driven. Any liquid-cooled vehicle is equipped with a system in which there is a small and large circle of circulation. When the ICE starts, it should warm up. This does not require the shirt to cool quickly. For this reason, the coolant circulates in a small circle. As soon as the unit has warmed up enough, the valve opens. At this moment, it blocks access to the small circle, and the liquid enters the radiator cavity, where it quickly cools. This element also applies if the system has a pump-action look.

- Expansion tank. This is a plastic container, the topmost element of the system. It compensates for the increase in the volume of coolant in the circuit due to its heating. In order for the antifreeze to have room to expand, the car owner should not fill the tank above the maximum mark. But at the same time, if there is too little liquid, then an air lock may form in the circuit during cooling, therefore it is also necessary to monitor the minimum level.

- Tank cap. It ensures the tightness of the system. However, this is not just a lid that is screwed onto the neck of the tank or radiator (more details about this detail are described separately). It must match the parameters of the vehicle's cooling system. Its device includes a valve that responds to the pressure in the circuit. In addition to the fact that this part is able to compensate for the excess pressure in the line, it allows you to increase the boiling point of the coolant. As you know from physics lessons, the higher the pressure, the more you need to heat the liquid so that it boils, for example, in the mountains, water begins to boil at an indicator of 60 degrees or less.

- Coolant. This is not just water, but a special liquid that does not freeze at negative temperatures and has a higher boiling point.
- Branch pipe. All units of the system are connected to a common line using large-section rubber pipes. They are fixed with metal clamps that prevent the rubber parts from breaking off at high pressure in the circuit.
The action of the cooling system is as follows. When the driver starts the engine, the crankshaft pulley transmits torque to the timing drive and other attachments, for example, in most cars, the water pump drive is also included in this chain. The impeller of the pump creates centrifugal force, due to which the antifreeze begins to circulate through the pipes and units of the system.
While the engine is cold, the thermostat is closed. In this position, it does not allow the coolant to flow into a large circle. Such a device allows the motor to quickly warm up and reach the desired temperature regime. As soon as the liquid is properly heated, the valve opens, and the cooling of the internal combustion engine begins to work.
The fluid moves in the following direction. When the engine warms up: from the pump to the cooling jacket, then to the thermostat, and at the end of the circle - to the pump. As soon as the valve opens, circulation goes through the larger arm. In this case, the liquid is supplied to the jacket, then through the thermostat and rubber hose (pipe) to the radiator and back to the pump. If the stove valve opens, then in parallel with the large circle, the antifreeze moves from the thermostat (but not through it) to the stove radiator and back to the pump.
When the liquid begins to expand, part of it is squeezed out through the hose into the expansion tank. Usually this element does not take part in the circulation of antifreeze.
This animation clearly shows how the CO of a modern car works:
What to fill in the cooling system?
Do not pour ordinary water into the system (although in old cars, drivers could use this liquid), since the minerals that make up it remain on the inner surfaces of the circuit at high temperatures. If in pipes with a large diameter this does not lead to a blockage of the duct for a long time, then the radiator will quickly become clogged, which makes heat exchange difficult, or even stops altogether.
Also, water boils at a temperature of 100 degrees. In addition, at low temperatures, the liquid begins to crystallize. In this state, at best, it will block the radiator ducts, but if the driver does not drain the water in time before leaving the car in the parking lot, the thin tubes of the heat exchanger will simply burst from the expansion of the crystallizing water.


For these reasons, special fluids (antifreeze or antifreeze) are used in CO, which have the following properties:
- Do not freeze at -40 frost and in some cases below;
- Boiling point - not less than 115 degrees;
- Do not foam;
- Resistant to oxidative reactions (does not contribute to the formation of corrosion in an empty system, like water);
- Does not precipitate with prolonged use;
- Does not form scale on metal parts at high temperatures;
- Lubricate the moving parts of the CO mechanisms.
It is worth mentioning that in emergency cases, instead of antifreeze or antifreeze, you can use water (preferably distilled). An example of such situations would be a radiator rush. To get to the nearest service station or garage, from time to time on the road the driver stops and replenishes the water volume through the expansion tank. This is the only situation in which it is permissible to use water.
Although there are a lot of technical fluids for cars on the market, it is not worth buying the cheapest products. It is often of lower quality and has a shorter lifespan. More details about the difference between CO fluids are described in separately... Also, you cannot mix different brands, since each of them has its own chemical composition, which can lead to a negative chemical reaction at high temperatures.
Types of cooling systems
Modern cars use a water-cooled engine, but sometimes there are models with an air system. Let's consider what elements each of these modifications will consist of, as well as on what principle they work.
Liquid cooling system
The reason for using the liquid type is that the coolant removes excess heat faster and more efficiently from parts requiring cooling. A little above, the device of such a system and the principle of its operation were described.
The coolant is circulated as long as the engine is running. The most important heat exchanger is the main radiator. Each plate threaded onto the center tube of the part increases the cooling area.
When the car stands with the internal combustion engine on, the radiator fins are poorly blown by the air flow. This leads to rapid heating of the entire system. If nothing is done in this case, the coolant in the line will boil. To solve this problem, engineers equipped the system with a forced air blower. There are several modifications of them.


One is triggered by a clutch equipped with a thermal valve that reacts to the temperature in the system. This element is driven by rotation of the crankshaft. Simpler modifications are electrically driven. It can be triggered by a temperature sensor located inside the line or by an ECU.
Air cooling system
Air cooling has a simpler structure. So, an engine with such a system has external ribs. They are enlarged towards the top to improve heat transfer in the part that gets hotter.
The device of such a CO modification will include the following elements:
- Ribs on the head and on the cylinder block;
- Air supply pipes;
- Cooling fan (in this case, it is powered by a motor on a permanent basis);
- A radiator that is connected to the unit's lubrication system.


This modification works according to the following principle. The fan blows air through the air ducts to the fins of the cylinder head. So that the internal combustion engine does not overcool and does not experience difficulty in igniting the air-fuel mixture, valves can be installed in the air ducts that block the access of fresh air to the unit. This is necessary in order to maintain a more or less constant operating temperature.
Although such CO is capable of removing excess heat from the motor, it has several significant disadvantages compared to its liquid counterpart:
- In order for the fan to work, part of the engine power is used;
- In some parts, parts are excessively hot;
- Due to the constant operation of the fan and the maximum open motor, such vehicles make a lot of noise;
- It is difficult to simultaneously provide high-quality interior heating and cooling of the unit;
- In such designs, the cylinders must be separate for better cooling, which complicates the design of the engine (the cylinder block cannot be used).
For these reasons, automakers rarely use such a system in their products.
Typical breakdowns in the cooling system
Any malfunction can seriously affect the operation of the power unit. The very first thing a CO breakdown is led to is overheating of the internal combustion engine.
Here are the most common failures in the power unit cooling system:
- Damage to the radiator. This is the most common malfunction, since this part consists of thin tubes that rupture under excessive pressure, combined with the destruction of the walls due to scale and other deposits.
- Violation of the tightness of the circuit. This often happens when the hose clamps are not tightened sufficiently. Due to the pressure, the antifreeze begins to seep through the weak connection. The volume of the fluid gradually decreases. If there is an old expansion tank in the car, it can burst from the pressure of air. This mainly occurs at the seam, which is not always noticeable (if a gust has formed at the top). Since the proper pressure is not created in the system, the coolant can boil. Depressurization can also occur due to the natural aging of the rubber parts of the system.
- Failure of the thermostat. It is designed to switch the heating mode of the system to cooling the internal combustion engine. It can stay closed or open. In the first case, the engine will quickly overheat. If the thermostat remains open, the engine will warm up for too long, which will make it difficult to ignite the VTS (in a cold engine, the fuel does not mix well with air, since the sprayed droplets do not evaporate and do not form a uniform cloud). This affects not only the dynamics and stability of the unit, but also the degree of pollution of the emission. If there is a catalyst in the exhaust system of the car, then poorly burned fuel will accelerate the clogging of this element (about why the car needs a catalytic converter, it is described here).
- Breakdown of the pump. Most often, the bearing fails in it. Since this mechanism is in constant connection to the timing drive, the seized bearing will quickly collapse, which will lead to abundant coolant leakage. To prevent this from happening, most motorists also change the pump when replacing the timing belt.
- The fan does not work even when the antifreeze temperature has risen to critical values. There are several reasons for this breakdown. For example, the wiring contact may oxidize or the clutch valve may fail (if the fan is installed on the motor drive).
- Airing the system. Air locks can appear during the replacement of the antifreeze. More often in this case, the heating circuit suffers.
Traffic regulations do not restrict the use of vehicles with faulty engine cooling. However, every motorist who saves his money will not delay the repair of a specific CO unit.


You can check the tightness of the circuit as follows:
- In the cold line, the level of antifreeze should be between the MAX and MIN marks. If, after a trip in a cooled system, the level has changed, then the liquid is evaporating.
- Any leaks of liquid on the pipes or on the radiator are a sign of depressurization of the circuit.
- After a trip, some types of expansion tanks deform (become more rounded). This indicates that the pressure in the circuit has increased. In this case, the tank should not hiss (there is a crack in the upper part or the valve of the plug does not hold).
If a malfunction was found, the broken part must be replaced with a new one. As for the formation of air locks, they block the movement of fluid in the circuit, which can cause the engine to overheat or stop heating the passenger compartment. This malfunction can be identified and corrected as follows.


Remove the tank cap, start the engine. The unit works for a couple of minutes. In this case, we open the heater flap. If there is a plug in the system, air must be forced into the reservoir. To speed up this process, you need to place the car with its front end on a hill.
Airing of the heater radiator can be eliminated by placing the car sideways on a small hill so that the pipes are located above the heat exchanger. This will ensure the natural movement of air bubbles through the channels to the expander. In this case, the motor must run at idle speed.
Cooling system care
Usually CO breakdowns occur at maximum loads, namely during driving. Some faults cannot be fixed on the road. For this reason, you should not wait until the car needs repair. To extend the service life of all elements of the system, it must be serviced on time.
Carrying out preventive work, it is necessary:
- Check the condition of the antifreeze. To do this, in addition to visual inspection (it must retain its original color, for example, red, green, blue), you should use a hydrometer (how it works, read here) and measure the density of the liquid. If the antifreeze or antifreeze has changed its color and become dirty or even black, then it is unsuitable for further use.
- Check the tension of the drive belt. In most cars, the pump works synchronously with the gas distribution mechanism and the crankshaft, so a weak timing belt tension will primarily affect the stability of the engine. If the pump has an individual drive, then its tension must be rechecked.
- Clean debris from engine and heat exchanger periodically. Dirt on the motor surface interferes with heat transfer. Also, the radiator fins must be clean, especially if the machine is operated in an area where poplar blooms profusely or small foliage is flying. Such small particles impede the high-quality passage of air between the tubes of the heat exchanger, due to which the temperature in the line will rise.
- Check the operation of the thermostat. When the car starts, you need to pay attention to how quickly it warms up. If it very quickly heats up to a critical temperature, then this is the first sign of a failed thermostat.
- Check the operation of the fan. In most cases, this element is triggered by a thermal sensor installed on the radiator. It so happens that the fan does not turn on due to oxidized contacts, and no voltage is supplied to it. Another reason is a non-working thermal sensor. This malfunction can be identified as follows. The contacts on the sensor are closed. In this case, the fan should turn on. If this happens, then it is necessary to replace the sensor. Otherwise, you need to take the car to a car service for diagnostics. In some vehicles, the fan is controlled by an electronic control unit. Sometimes failures in it lead to unstable fan operation. The scan tool will detect this problem.
Flushing the engine cooling system
System flushing is also worth mentioning. This preventive procedure keeps the cavity of the line clean. Many motorists neglect this procedure. Depending on the car model, you need to flush the system once a year or every three years.


Basically, it is combined with the replacement of antifreeze. We will briefly consider what signs indicate the need for flushing, and how to correctly perform it.
Signs it's time to flush
- During engine operation, the coolant temperature arrow constantly shows strong heating of the internal combustion engine (close to the maximum value);
- The stove began to give off heat poorly;
- Regardless of whether it is cool outside or warm, the fan began to work more often (of course, this does not apply to situations when the car is in a traffic jam).
Flushing the cooling system
Do not use plain water for CO flushing. Often it is not foreign particles that lead to clogging, but scale and deposits accumulated in the narrow part of the circuit. Acid copes well with scale. Fat and mineral deposits are removed with alkaline solutions.
Since the effect of these substances is neutralized when mixed, they cannot be used simultaneously. However, do not use purely acidic or alkaline solutions. They are too aggressive, and after use, a neutralization process must be carried out before adding fresh antifreeze.
Better to use neutral washes, which can be found in any auto chemical store. On the packaging of each substance, the manufacturer indicates for which types of contamination it can be used: either as a prophylaxis or to combat complex deposits.


The flushing itself must be carried out in accordance with the instructions indicated on the container. The main sequence is as follows:
- We warm up the internal combustion engine (do not bring the fan to turn on);
- We drain the old antifreeze;
- Depending on the agent (it can be a container with an already diluted composition or a concentrate that needs to be diluted in water), the solution is poured into an expansion tank, as in the usual replacement of antifreeze;
- We start the engine and let it run for up to half an hour (this time is indicated by the washing manufacturer). During the operation of the engine, we also turn on the interior heating (open the heater tap so that the flushing circulates along the interior heating circuit);
- The cleaning liquid is drained;
- We flush the system with a special solution or distilled water;
- Fill in fresh antifreeze.
It is not necessary to go to the service station to perform this procedure. You can do it yourself. The performance of the motor and its service life depend on the cleanliness of the highway.
Additionally, watch a short video on how to flush it on a budget and without harming the system:


Watch this video on YouTube
Questions and answers:
How does the cooling system work? Liquid CO consists of a radiator, a large and small circle, pipes, a water cooling jacket of the cylinder block, a water pump, a thermostat, and a fan.
What are the types of engine cooling systems? The motor can be air or liquid cooled. Depending on the design of the internal combustion engine lubrication system, it can also be cooled due to the circulation of oil through the channels of the block.
What kind of coolants are used in the cooling system of a passenger car? The cooling system uses a mixture of distilled water and an anti-freeze agent. Depending on the composition of the coolant, it is called antifreeze or antifreeze.







