
The structure and principle of operation of the Multitronic gearbox
Content
- What is a Multitronic transmission?
- Multitronic working principle
- How does Multitronic work?
- What is the problem with the Audi Multitronic s tronic transmission?
- How much does a multitronic contract transmission cost? - repair of multitronic audi
- In which Audi models has the Multitronic transmission been used?
- How do I know if my car has a Multitronic transmission?
- Box Multitronic: its advantages and disadvantages
- Conclusions
In order for any car to start moving, it is necessary to properly transmit the torque that the engine generates to the drive wheels of the vehicle. There is a transmission for this purpose. The general device, as well as the principle of operation of this machine system, is considered in another article... A couple of decades ago, most motorists had little choice: automakers offered them either a mechanic or an automatic.
Today there is a wide variety of transmissions. The key element in the system is the transmission. This unit provides the correct power take-off from the motor, and transmits rotational movements to the drive wheels. Depending on the modification of the gearbox, it can work without interrupting the power flow or with periodic disconnection / connection of the gearbox and the motor to change gears.
The most common modification is a mechanical box (about the principle of its operation and the device there is separate review). But for lovers of increased comfort, a large number of automatic transmissions have been developed. Separately describes the different modifications of such transmissions. Here are just a few examples of these boxes:
- Automatic transmission Tiptronic (read about it here);
- Easytronic robotic box (it is discussed in detail in another review);
- Manual transmission DSG is one of the most popular modifications of robots (for details about its pros and cons, read separately) etc.
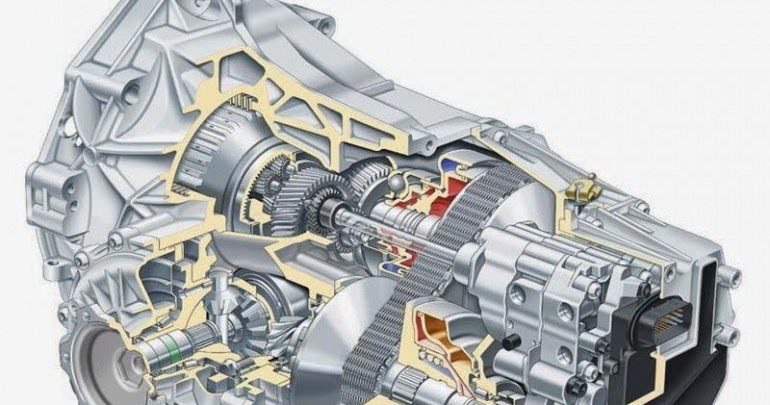
One type of transmission is a continuously variable or variator. What it is and how it works is also available. A separate article... Multitronic can be considered an improved version of this type of transmission.
Consider the multitronic gearbox device, how such a system works, what are its advantages and disadvantages, as well as some problems with the mechanisms.
What is a Multitronic transmission?
The company Audi, which is part of the VAG concern (for more details about this association, read separately), has developed a continuously variable transmission type Multitronic. Another name for the development of the s tronic Audi. The name of the transmission traces a connection with its related analogue Tiptronic. The concept "Multi" perfectly suits the type of gearbox under consideration, because the transmission of torque has a large number of gear ratios during the operation of the unit.
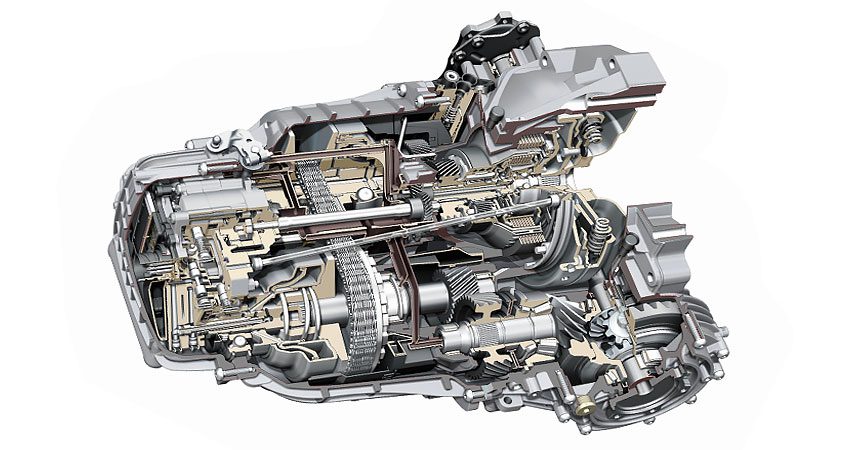
The design of this variator will consist of:
- A multi-disc clutch of a friction type designed for forward movement (the device is considered in more detail here);
- A multi-disc clutch of a friction type, which is responsible for the reverse of the car;
- Planetary mechanism;
- Chain transmission (unlike standard variators, this modification is no longer equipped with a belt, but with a chain, which increases the working resource of the device);
- Intermediate gear;
- Main transmission;
- Differential (this mechanism is considered in detail in another review);
- ECU or electronic control unit.
The multi-plate clutch, which is responsible for forward and reverse travel, acts as a clutch basket, which breaks the transmission of torque during the transition between modes (forward speed, parking, reverse, etc.). The planetary element is designed to move the machine in reverse. Otherwise, the transmission of torque will occur from the drive pulley (the clutch is connected to it through the intermediate shaft) to the driven pulley due to the steel chain. The driven pulley is connected to the final drive.
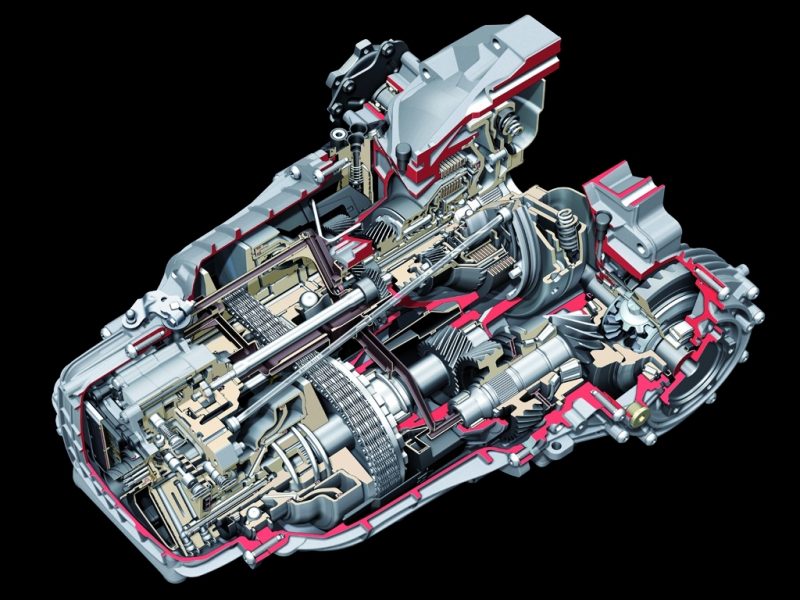
To control the gear ratio, a hydraulic unit is used (it moves the walls of the pulleys to change the diameter of each of them), as well as several sensors. Sensors in the electronic system are responsible for:
- Determination of the position of the lever located on the selector;
- Working fluid temperature control;
- Transmission oil pressure;
- Turns of the shafts at the entrance and exit from the checkpoint.
The control unit is stitched at the factory. Based on the signals received from all sensors, various algorithms are activated in the microprocessor, which change the gear ratios between the pulleys.
We'll look at how each of these components works a little later. Now let's discuss a little what the CVT attracts many car owners. If we compare a torque converter automatic with a variator, then the first type of transmission requires more fuel to move the car. Also, in it, the change in speeds does not always occur at the most optimal operating mode of the internal combustion engine for the high-quality dynamics of the vehicle.
The production of the variator takes less materials, and the manufacturing technology is somewhat simpler. But, despite this, in comparison with classic boxes, in which torque is transmitted through gears, the variator is a rather unusual power take-off unit. As we have already noticed, instead of a belt, a steel chain is used to rotate the driven shaft.
The chain is installed between two tapered pulleys. These elements are attached to the drive and driven shafts. Each pulley is capable of changing its diameter due to the movement of the side elements. The smaller the distance between the walls in the pulley, the larger the diameter will be in the shaft axis. The construction of the variator is lighter in comparison with a conventional automatic transmission. This makes it possible to use this development in small-sized city cars, for which weight is important, because they often get a weak engine under the hood.
Another distinctive feature of the Multitronic variator is the absence of a torque converter. In all automatic transmissions, except for robotic options (here read more about how the robot differs from the machine), this mechanism is used. First of all, it is needed so that the driver can safely start the engine, and the car can start moving correctly. Instead, the Multitronic system is equipped with a clutch package (multi-plate friction element for reverse and forward gears) and a dual-mass flywheel (for details on how it differs from a conventional flywheel, see in another article).
Multitronic working principle
The operation of the Multitronic transmission is almost identical to the classic variator. The conventional variant has one feature that many motorists dislike. At constant speed, the transmission runs quietly and the motor is almost inaudible. But when the driver presses the gas pedal to the floor, the engine speed jumps, and the car accelerates slowly. Of course, this applies to the work of the first variators that appeared in the 1980s and 90s.
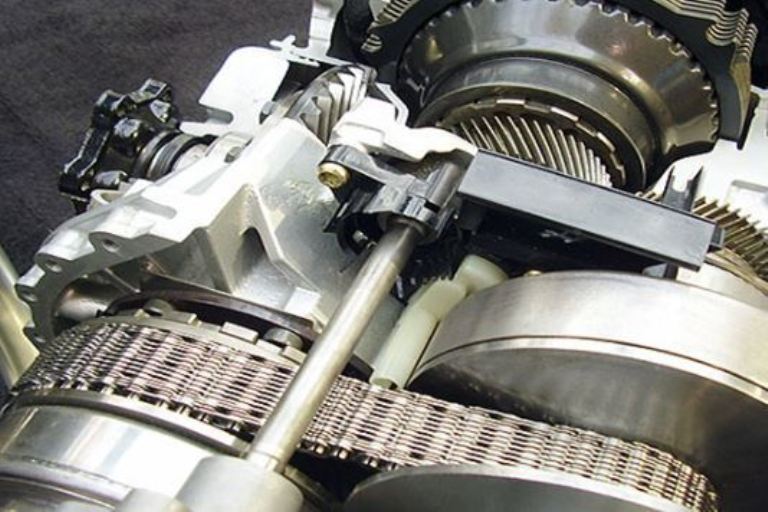
To eliminate this effect, manufacturers began to introduce virtual gears into the transmission. Each of them relies on its own ratio of the diameters of the pulley axles. The simulation of gear shifting is controlled using a lever installed on the gearbox selector or paddle shifters.
This principle of operation also has a multitronic from Audi, which was updated in 2005. With measured driving, the box raises / lowers the speed of the vehicle in the same way as a conventional CVT. But for dynamic acceleration, the "Sport" mode is used, which imitates the operation of an automatic transmission (the gear ratio between the pulleys is not smooth, but fixed).
How does Multitronic work?
So, basically, a multitronic will work in the same way as a classic variator equipped with a torque converter. When the engine is running, the power take-off takes place through two pulleys connected by a chain. The operating mode depends on the driver's settings (to which position he moves the lever on the selector). Gradually accelerating the car, the transmission changes the distance between the lateral parts of the pulleys, increasing the diameter on the leading one, and decreasing on the driven one (the same principle has a chain transmission on a mountain bike).
The driven pulley is connected to the final drive, which in turn is connected to a mechanism designed to turn each drive wheel. The whole process is controlled by an ECU. Consider what is the peculiarity of the work of some of the main elements of this transmission.
Multi-disc clutches
As stated earlier, the role of the clutches is to provide communication between the flywheel and the transmission countershaft. They replace the classic clutch used in manual and robotic gearboxes. By their design, these clutches do not differ from analogues used in automatic gearshift machines.

These elements never work at the same time, because each of them is responsible for its own direction of movement of the car. When the driver moves the selector lever to position D, the forward speed clutch is clamped. Position R disengages this clutch and activates the second clutch responsible for reverse.
Lever position N and P deactivate both clutches and they are in the open state. Such couplings are only used in the configuration with a dual-mass flywheel. The reason is that this disc eliminates torsional vibrations coming from the crankshaft (for more information about why a flywheel is in the car and what modifications of this part of the power unit are, read in another article).
Planetary gear
As stated earlier, this mechanism is only intended to drive the vehicle in R (reverse) mode. When the driver activates forward speed, the friction disc block is clamped, thereby connecting the shaft at the input of the gearbox and the carrier. In this case, the planetary gear is locked and is in free rotation with the drive shaft.
When reverse gear is activated, the ring gear locks onto the body of the mechanism, the front clutch is released and the rear clutch is clamped. This ensures that torque is transmitted in the other direction, and the wheels turn so that the machine begins to move backward.
The gear ratio in this case is equal to one, and the speed of the vehicle is controlled by the ECU, depending on the engine speed, the position of the accelerator pedal and other signals.
CVT transmission
The key mechanism, without which the box will not work, is the variator transmission. Variator in the sense that the mechanism provides a large number of options for the ratio of diameters between the pulleys.
The device of each pulley includes two tapered discs capable of moving relative to the axis of the shaft. Due to this, the central part of the devices on which the circuit is placed increases / decreases in accordance with the required value.
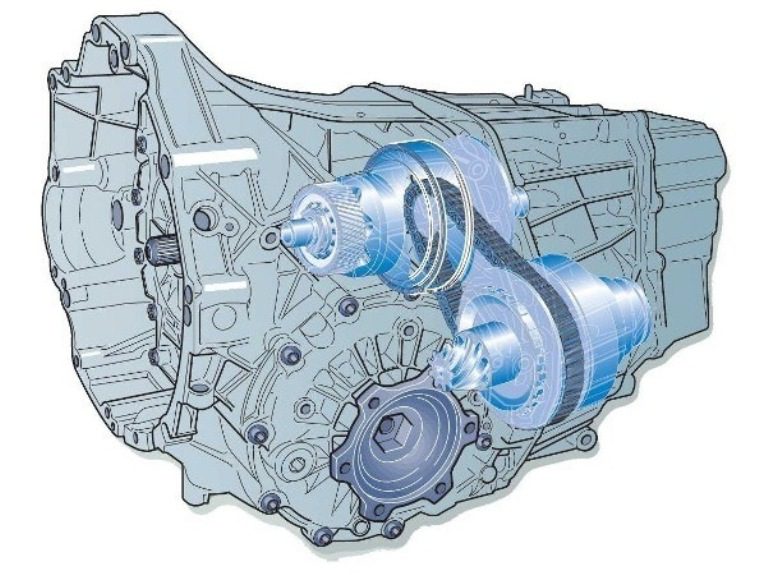
The drive pulley is connected to the crankshaft using an intermediate gear. The main gear is driven by a chain and driven pulley. The peculiarity of this design is that the electronics smoothly changes the diameter of the contact part of the pulley and chain. Thanks to this, the speed change occurs imperceptibly for the driver (there is no turbo lag or power gap when changing gear).
So that the disks of each pulley can move along the shaft, each of them is connected to a hydraulic cylinder. Each mechanism has two hydraulic cylinders. One is responsible for the downforce of the chain to the surface of the pulley, and the other changes the gear ratio by increasing / decreasing the diameter of the pulley.
Management system
The transmission control system includes the following elements:
- Hydraulic block;
- ECU;
- Sensors.
Each of the sensors records different parameters of the transmission and the vehicle. For example, this is the number of revolutions of the drive and driven shafts, how effective the cooling of the lubrication system is, and the pressure of the lubricant. The availability of certain sensors depends on the model year of the transmission and its model.
The task of the electronic control unit is to collect signals from sensors. In the microprocessor, various algorithms are activated that determine what the gear ratio should be at a particular moment of vehicle movement. It is also responsible for engaging the forward or reverse speed clutch.
Despite the fact that this modification of the gearbox does not use a torque converter, hydraulics are still present in it. The valve body is needed to connect / disconnect the corresponding friction clutch. The working fluid in the line changes its direction, and the control unit determines how much force should be on the discs for effective engagement. A solenoid valve is used to change the direction of oil flow.
An additional function of the valve body is to cool the couplings during their operation so that the surfaces of the discs do not overheat, due to which they will lose their properties. The valve body design implies the presence of such elements:
- Zolotnika;
- Hydro valves;
- Solenoid valves responsible for changing the pressure in the system.
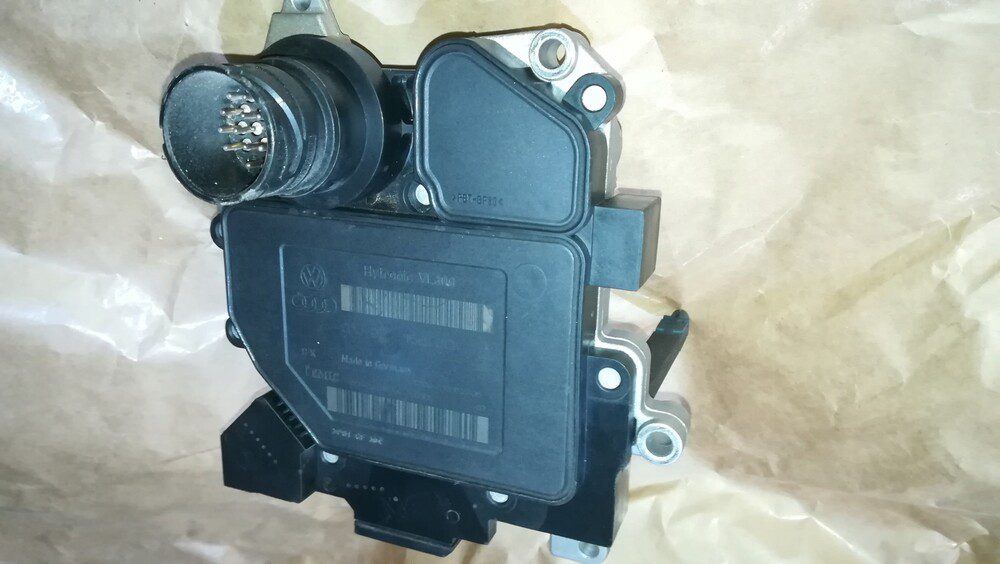

An individual oil pump is required to operate the hydraulic unit. In this case, a gear modification is used, which has a mechanical connection with the input shaft of the gearbox. As an additional pump, the manufacturer has equipped the system with an ejection pump (it provides circulation due to the rarefaction of the working fluid in one cavity). Its task is to cool the working fluid, ensuring its circulation along the line.
To prevent the oil in the line from overheating, a separate radiator is used in the transmission (in more detail, the device and principle of operation of this component is considered separately).
What is the problem with the Audi Multitronic s tronic transmission?
So, if the Multitronic is an improved version of the classic CVT, what is wrong with it, which is why many motorists are hesitant to consider purchasing a car with such a box?
First of all, it is worth paying attention to the fact that the variator is offered as an option that increases driving comfort. The automaker assumes that a comfortable ride is a measured ride without harsh acceleration. It looks more like a quiet stroll in a scenic area than a sprint race in a competition. For this reason, this transmission is not designed for sporty driving.
Early multitronic models were capable of transmitting in the 300 Nm range. torque. Later developments have a slightly increased value - up to 400 Newtons. The multi-strand chain simply won't hold up anymore. For this reason, the unit is set to steadily increase the drive power. Chain wear depends on how often the driver puts the gearbox under maximum stress.
The ideal pair for a continuously variable transmission is a gasoline engine. It can have a high torque, but it rises in a wide range, which ensures smooth acceleration of the transport, and the maximum Newtons is available almost at the peak of the revs.
Much worse multitronic tolerates work paired with a productive diesel engine. In addition to the fact that the maximum torque is already available at medium engine speeds, it changes dramatically. Because of this, the chain wears out faster.
Another problem is that the gear oil change must be approached with special attention, and not to exceed the replacement schedule. Read about what kind of oil is poured into the box. here... Scheduled maintenance of the box must be carried out after approximately 60 thousand km. mileage. A more precise interval is indicated by the car manufacturer.
Symptoms that indicate a Multitronic breakdown include:
- Illumination of all modes on the gearbox selector comes on, regardless of the position of the lever;
- The car lost the smoothness of acceleration - it began to twitch;
- After switching to mode D, the motor stalls;
- When the reverse speed is turned on, traction on the wheels is partially or completely lost;
- Switching to neutral speed N does not interrupt the power take-off and the machine continues to move;
- At speeds up to 50 km / h, an arbitrary change in the gear ratio is observed with the same position of the gas pedal.
How much does a multitronic contract transmission cost? - repair of multitronic audi
Although many service stations provide repair services for multitronic boxes, many motorists are faced with a choice: is it worth repairing it or is it better to buy a used unit in the secondary market, for example, at disassembly. The reason is that the cost of repairing this transmission is almost twice as much as buying a working device.
Another guideline is for what purpose the box needs to be replaced or repaired. If the car is dear to the car owner, and he does not plan to sell it in the near future, then perhaps there is a reason to invest serious funds in the repair of the unit. In the case of a planned sale of a vehicle, it will be cheaper to buy a working box for disassembly. In this case, it will be possible to sell the car at a reasonable price.
Fortunately, the market for used spare parts, mechanisms and assemblies offers a large assortment, including for the repair of this type of box. The main reason is that this is a drivetrain from legendary cars - Audi, which are known for their high quality.
Should you be afraid of the Multitronic gearbox?
The Multitronic automatic transmission was more often installed on front-wheel drive Audi. But this rule does not apply to models with a non-standard body, for example, convertibles (read about the features of this body type separately).
In many cases, the multitronic began to be capricious after one or two hundred thousand kilometers. But most often this is not due to wear of the unit parts, but to a breakdown or malfunction of the control unit. In this case, the problem is solved by purchasing a new controller.
As for the installation on a car equipped with a diesel engine, this does not always automatically mean a quick breakdown of the box. There are cases when a car in such a configuration departed 300 thousand, and the transmission in it was never repaired.

When purchasing a used car, it is necessary to find out in what condition the transport box is. If there are funds for maintenance and minor repairs of the unit, as well as experience in operating such gearboxes, then you can not be afraid to purchase vehicles with a similar transmission. Of course, there are dishonest sellers who assure that the car was properly operated, but in fact the vehicle was only slightly repaired for the upcoming sale. In a separate review we discussed what else to look for when buying a used car.
Not bad Multitronic copes with the city regime. The driver needs to get used to the intricacies of such a transmission. Of course, it's risky enough to buy an Audi with Multitronic in the aftermarket. Compared to a tiptronic or the same mechanics, this box does not withstand so much mileage. But not everything is as dramatic as many motorists paint. If a used car was bought, then there is a high probability that a car with a box that has already worked out its working life. Naturally, such an acquisition will cost a pretty penny to the new owner. But in general, this type of box works reliably.
In which Audi models has the Multitronic transmission been used?
To date, the production of multitronic has already been completed (the last transmission of this type left the assembly line in 2016), so a new car with Multitronic can no longer be found. It was installed mainly in premium cars of the audi company. More often it can be found in the A4 configuration; A5; A6 as well as A8.
Since the Multitronic was mainly used in front-wheel drive cars, it should be expected that such a car with an automatic transmission (manufactured until 2016) will be equipped with this transmission, although there are exceptions.

It is also worth considering that this development was not used in conjunction with the Quattro system. It was extremely rare that there were modifications that were adapted specifically for this drive. But most of the multitronic was not used on it. In which models that are sold in the secondary market, you can find an automatic transmission of a CVT type (Audi models):
- A4 in B6, B7 and B8 bodies;
- A5 in the back of 8T;
- A6 in the bodies of C5, C6 and C7;
- A7 in the back of C7;
- A8 in D3 and D4 bodies.
How do I know if my car has a Multitronic transmission?
Given that automatic transmissions of the same type may look different, it is extremely difficult to visually determine which transmission is equipped with a particular car. How to determine if Multitronic is worth in the model in question?
This can mainly be determined by how the transmission behaves while the vehicle is accelerating. If you feel a clear gear shift, and at this moment the engine speed is decently reduced, then the engine is paired with a dual-clutch box of the Tiptronic type from Audi.
The presence of a niche in the selector to simulate manual switching (+ and -) does not necessarily mean that the manufacturer has equipped the car with anything but multitronic. In this case, options were also proposed with an imitation of manual control of the transition from one speed to another.
When, in the process of measured acceleration of the car, a small transition is felt every 20 km / h, but there are no significant changes in the engine speed, this indicates that the car is equipped with Multitronic. There is no such effect in boxes with a fixed change in gear ratios.
Box Multitronic: its advantages and disadvantages
Due to the design features, the variator gearbox is not capable of transmitting high torque from the motor to the drive wheels. Despite the fact that engineers have been trying to eliminate this deficiency for decades, so far this has not been fully achieved. Although some automakers have managed to create good car models that can delight sports fans. An example of this is the development of Subaru - Limeatronic, which is installed in the Levorg model.

As for the Multitronic box, which was used in some Audi models, the advantages of this transmission include:
- High smoothness of the ride, as well as comfortable dynamics, which is characteristic of all continuously variable transmission types, but the dynamics of the vehicle does not depend solely on the engine speed;
- Due to the fact that there are no gaps between gear changes (the gear ratio changes without breaking the torque), the car accelerates faster than one equipped with another automatic type of box;
- The unit does not use more oil, as is the case with analogs powered by a torque converter, so the design is much lighter. Thanks to this and the higher-quality principle of using the torque, the transmission allows you to save fuel in comparison with analogues equipped with a torque converter;
- The car responds better to pressing the gas pedal.
But, despite its effectiveness, Multitronic has a number of serious disadvantages:
- When the transport stops downhill, the car may roll if the hand brake pads are not pressed well against the disc;
- The automaker does not recommend transporting a broken car by towing - it is better to use a tow truck;
- Parts of this transmission have a small working life;
- If the box fails, its repair is expensive, and there are not so many specialists who understand the device of this transmission.
In another article a comparison of a variator and a robotic box is considered.
Conclusions
So, in comparison with other automatic transmissions, Multitronic has its own advantages, for example, smooth acceleration and good economy. If you take good care of this car unit in a timely manner, then it will work for a long time. But the restoration of the unit after its breakdown will always be associated with serious waste. It so happens that the masters of the service station say that the oil does not change in this box, it is better not to argue, but simply to find another workshop.
In addition, we offer a short video review of common malfunctions of the Audi Multitronic CVT box:
