car intake system
Content
Your vehicle's air intake system draws air from outside into the engine. But do you know exactly how it works? Here's what you need to know.
There are a handful of car owners who aren't entirely sure what an air intake system does, how it works, and how important it is to a car. In the 1980s, the first air intake systems were offered, which consisted of molded plastic intake tubes and a cone-shaped cotton gauze air filter. Ten years later, foreign manufacturers began to import popular Japanese air intake system designs for the compact sports car market. Now, thanks to technological advances and engineering ingenuity, intake systems are available as metal tubes, allowing for a greater degree of customization. The pipes are usually powder-coated or painted to match the color of the car. Now that modern engines aren't equipped with carburetors, we're concerned about fuel-injected engines. So the question is, what exactly do we need to know about this?
Air intake system and how it works
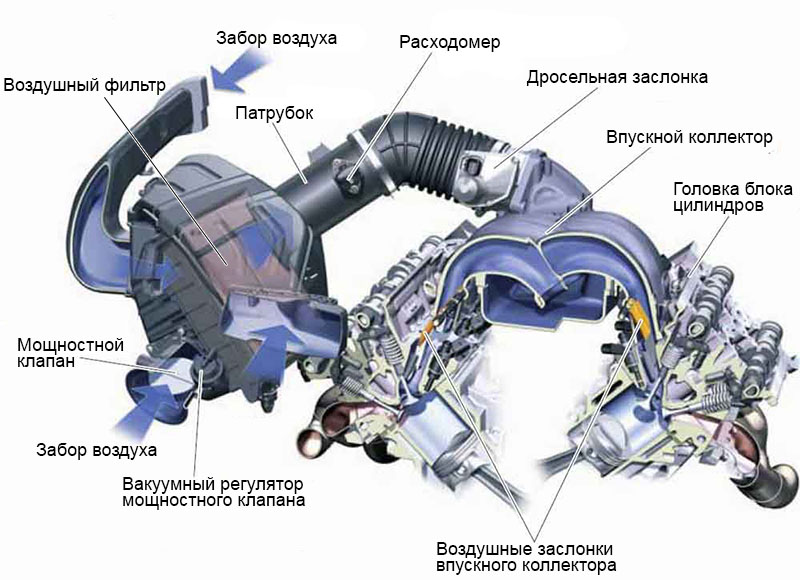
The function of the air intake system is to provide air to the vehicle's engine. Oxygen in the air is one of the necessary components for the combustion process in an engine. A good air intake system ensures a clean and continuous flow of air into the engine, thus increasing the power and mileage of your car.
A good air intake system ensures a clean and continuous flow of air into the engine. The air intake system of a modern car consists of three main parts - the air filter, the mass air flow sensor and the throttle body. Located right behind the front grille, the air intake system draws in air through a long plastic tube that goes into the air filter housing, which will be mixed with automotive fuel. Only then will air enter the intake manifold, which supplies the fuel-air mixture to the engine cylinders.
Air filter
The air filter is an important part of the car's intake system, since it is through the air filter that the engine "breathes". This is usually a plastic or metal box that houses the air filter. The engine requires a precise mixture of fuel and air to run, and all air enters the system through the air filter first. The job of an air filter is to filter out dirt and other foreign particles in the air, preventing them from entering the system and possibly damaging the engine.
The air filter prevents dirt and other foreign particles from the air from entering the system. The air filter is usually located in the air stream to the throttle body and intake manifold. It is located in a compartment in the air duct to the throttle assembly under the hood of your vehicle.
Mass flow sensor
air mass The mass air flow sensor is used to determine the mass of air entering the internal combustion engine with fuel injection. So it goes from the mass flow sensor to the throttle valve. Two common types of mass air flow sensors are used in automotive engines. These are the impeller and the hot wire. The vane type has a damper that is pushed by the incoming air. The more air enters, the more the damper moves back. There is also a second vane behind the main one that goes into a closed bend that dampens the movement of the vane for a more accurate measurement. Hot wire uses a series of wires strung in the air stream. The electrical resistance of a wire increases as the temperature of the wire increases, which limits the electrical current flowing through the circuit. As air passes the wire, it cools, reducing its resistance, which in turn allows more current to flow through the circuit. However, as more current flows, the temperature of the wire increases until the resistance reaches equilibrium again.
The two most common types of mass air flow sensors are vane meters and hot wire.
Cold air intake and how it works
The cold air intake is used to bring cooler air into the car's engine to increase its power and efficiency. The most efficient intake systems use an airbox that is sized to match the engine and extends the engine's powerband. The intake pipe or air inlet to the system must be large enough to ensure that sufficient air enters the engine under all conditions from idle to full throttle. Cold air intakes work on the principle of increasing the amount of oxygen available for combustion with the fuel. Because cooler air has a higher density (higher mass per unit volume), air intakes typically work by bringing in colder air from outside a hot engine bay. The simplest cold air intake replaces the standard air box with a short metal or plastic tube leading to conical air filter, called short pressure air intake. The power produced by this method can vary depending on how limited the factory airbox is. Well-designed air intakes use heat shields to isolate the air filter from the rest of the engine bay, providing cooler air to the front or side of the engine bay. Some systems called "wing mounts" move the filter into the wing wall, this system draws air through the wing wall, which provides even more insulation and even cooler air.
Throttle valve
The throttle body is the part of the air intake system that regulates the amount of air entering the engine's combustion chamber. It consists of a drilled housing that houses a butterfly valve that rotates on a shaft.
Throttle body The amount of air entering the engine's combustion chamber. When the accelerator pedal is depressed, the throttle valve opens and lets air into the engine. When the accelerator is released, the throttle valve closes and effectively cuts off the flow of air into the combustion chamber. This process effectively controls the rate of combustion and ultimately the speed of the vehicle. The throttle body is usually located between the air filter housing and the intake manifold, and it is usually located near the mass air flow sensor.
How it improves your air intake system
Some of the benefits of having a cold air intake include increased power and torque. Because a cold air intake draws in a larger volume of air that can be much colder, your engine can breathe more easily than with a restrictive stock system. When your combustion chamber is filled with cooler, oxygen-rich air, the fuel burns on a more efficient mixture. You get more power and torque from every drop of fuel when combined with the right amount of air. Another benefit of cold air intake is improved throttle response and fuel economy in most cases. Stock air intakes often deliver warmer, more fuel-rich combustion mixtures, causing your engine to lose power and throttle response, running hotter and slower. Cool air intakes can help you save fuel by improving your air-to-fuel ratio.

