5 things to know before buying an electric car.
Content
Are you thinking about buying an electric car? Are you confused about what a hybrid is, what a plug-in hybrid is, and how does it differ from an electric vehicle? Or maybe you are afraid of the too low mileage offered by electric vehicles? This post should explain many things to you in the world of electromobility.
1. Different types of electric vehicles (EV - Electric Vechicle)
Hybrid = Internal combustion engine + Electric motor.
Hybrid cars use both engines interchangeably, and it is up to the car to decide when to use an electric motor, when to use an internal combustion engine, and when to use an electric motor to support an internal combustion engine - especially in urban traffic. In some vehicles, it is possible to enable the electric driving mode, however, the range that can be obtained is small at 2-4 km, and for electric motors there is a maximum speed limit, usually 40-50 km /. hour The batteries of these vehicles are charged during braking when electricity is restored, but the batteries cannot be charged in any other way. The advantages of hybrid vehicles are manifested in the city, where fuel consumption is much lower than that of internal combustion vehicles.
Plug-in hybrid = Combustion engine + electric motor + battery.
PHEV vehicles or Plug-in Hybrids (Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vechicle). It is always a car that has an internal combustion engine (gasoline or diesel) and an electric one, but there are different modes of operation of these engines. There are PHEV vehicles in which an electric motor drives the rear axle and an internal combustion engine drives the front axle. These engines can work separately, for example, only an internal combustion engine or only an electric motor, but they can also work together, and the electric motor supports the internal combustion engine. An example of a vehicle is the Volvo V60 plug-in.
A continuation of this idea is a car with two engines, but the internal combustion engine while driving can additionally recharge the batteries while driving. This hybrid model was presented by Mitsubishi Outlander PHEV.
Another idea for a hybrid is to install an internal combustion engine and an electric motor, but it is the electric motor that transfers power to the wheels, and the combustion engine works as a generator. Thus, when the energy stored in the batteries is depleted, the combustion engine starts, but does not generate power to the wheels. This will be a means of generating electricity to power the electric motor and partly the batteries. It should be noted that this is the most economical use of an internal combustion engine. An example of such a car is the Opel Ampera.
Of course, in plug-in hybrids, we can charge the batteries from the external power supply of the charger. Some plug-in cars even allow DC fast chargers!
Electric range varies by vehicle and driving style. It usually ranges from 30 to 80 km using an electric motor.
Electric vehicle = Electric motor + battery
Electric vehicles or electric vehicles (or BEV - Battery Electric Vechicle) are vehicles that do not have electric motors. Their range depends on the capacity of the batteries, expressed in kWh (kilowatt-hours), less often in Ah (ampere-hours), although both forms are correct, the former is more user-friendly. However, these vehicles provide a completely different driving experience compared to combustion vehicles. I recommend that you try it yourself and use car sharing first.
2. Range of electric vehicles.
This is the deciding factor, but also the biggest fear if you are faced with buying an electric vehicle. It all depends on how much and how you plan to ride per day. According to Joint Research Center , more than 80% of drivers in the European Union drive less than 65 km during the day. Don't ditch the electric car right away looking for a one-off trip from Zakopane to Gdansk or a vacation to Croatia. However, if you cover long distances during the day, or often have to travel further, consider a plug-in hybrid.
Remember that the range of electric vehicles is influenced by:
- Battery capacity depends on the vehicle and sometimes on the model version.
- Weather - Extremely low or high temperatures can limit the range of an electric vehicle. Just heating and cooling a car consumes a lot of electricity. Don't worry, your batteries won't overheat. Electric vehicles are being cooled.
- Driving style - How you drive affects how far you drive. It is best to drive without sudden acceleration or deceleration. Remember that an electric vehicle recovers energy during braking, so simply releasing the accelerator pedal will cause quite a lot of braking.
How much mileage can I get by driving an electric car normally?
Below I will present to you several popular electric vehicle models and their mileage. The days when an electric car drove only 100 km and had to look for a charging point are long gone.
Electric car mileage
- Tesla Model S85d - 440km - but okay, this is Tesla, and Tesla is known to be the leader in the electric vehicle world, so let's touch the ground a little.
- Kia Niro EV 64 kWh - 445 km
- Kia Niro EV 39,2 kWh - 289 km
- Peugeot e-208 50 kWh - approx. 300 km
- Nissan Leaf 40 kWh - up to 270 km
- Nissan Lead e + 62 kWh - up to 385 km
- BMW i3 - 260 km.
- Smart EQ For Four — 153 км.
As you can see, it all depends on the battery capacity and your driving style. For example, the Peugeot e-208 has an interesting mileage simulator on its configuration page. When driving slowly up to 70 km / h at 20 o C the car is capable of driving 354 km, and with dynamic movement, sharp acceleration to 130 km / h and sharp braking at a temperature of -10 o C the mileage of the car will be only 122 km.
How to quickly calculate the approximate mileage that can be done with an electric vehicle? As in vehicles with an internal combustion engine, the average consumption of gasoline is assumed to be 8 l / 100 km, while in the case of electric vehicles, the average consumption of electricity can be assumed to be 20 kWh / 100 km. Thus, the mileage that you can easily do with, for example, a Kia Niro with a 64 kWh battery is 64 * 0,2 = 320 km. It's about a quiet ride without eco-driving. The Polish YouTuber ran a long distance test and drove a Kia Niro from Warsaw to Zakopane, that is, 418,5 km on a single charge, with an average energy consumption of 14,3 kWh / 100 km.
3. Charging stations.
Of course, you are probably wondering where and how you will charge such a car and what kind of connectors there are in general.
Relax, this has already been said. Visit previous posts:
Summing up? - there are many chargers.
Some are paid, some are free. Types of connectors? No problem. AC charging uses Type 2 or less commonly Type 1. Most charging stations have a built-in Type 2 socket or Type 2 cable, so if you buy a car with a Type 1 socket, you should get a Type 1 - Type 2 adapter. for DC charging, in Europe we will find CSS COMBO 2 or CHAdeMO connectors. Many fast charging stations are equipped with two of these attachments. No worries.
If I drive my car under a 100 kWh charger, will my 50 kWh battery charge from 0 to 100% in 30 minutes?
Unfortunately not.
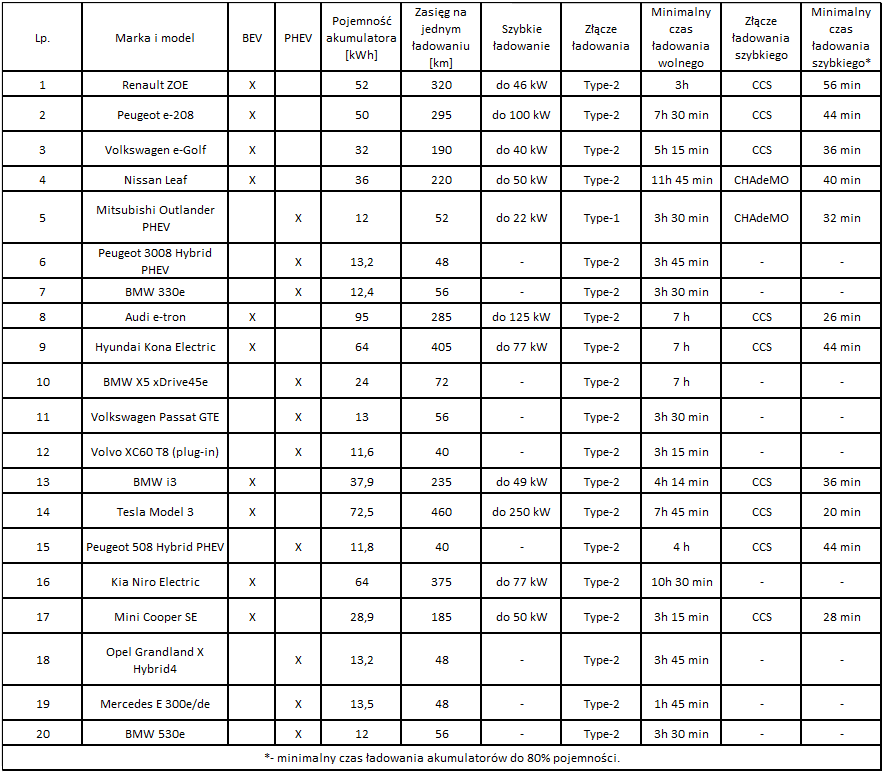
Below is a table of the top 20 most-bought EVs in the EU in 2020.