Active Body Control - active wheel suspension
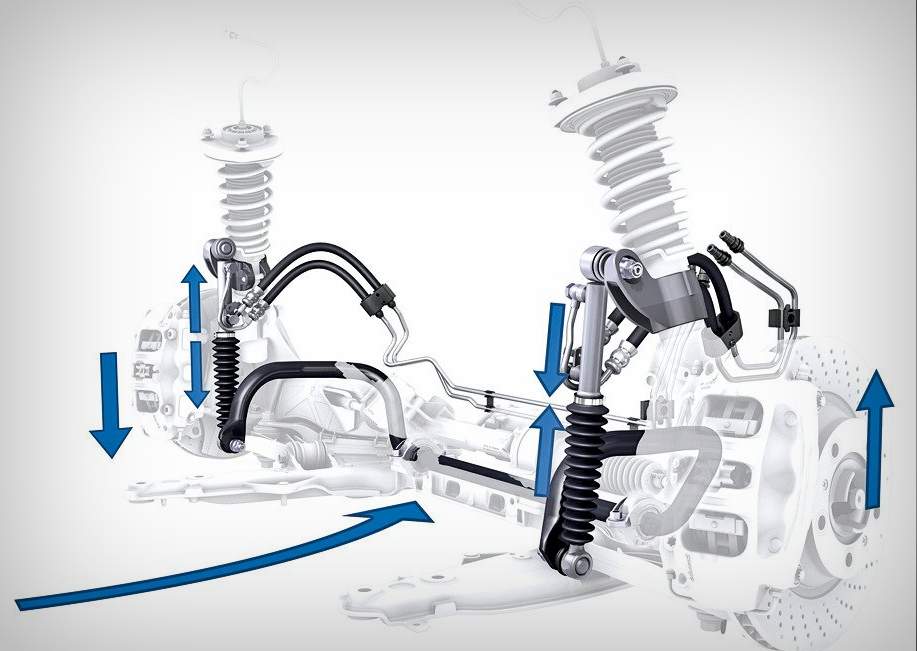
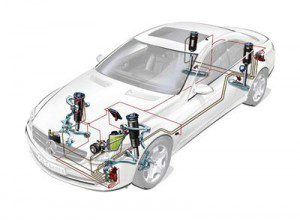 ABC (Active Body Control) is an abbreviation for actively controlled chassis. The system allows electronically controlled hydraulic cylinders to maintain a constant ride height regardless of load, additionally compensate for body tilt when braking or accelerating, when cornering, and also compensate for the influence of crosswinds. The system also dampens vehicle vibrations down to 6 Hz.
ABC (Active Body Control) is an abbreviation for actively controlled chassis. The system allows electronically controlled hydraulic cylinders to maintain a constant ride height regardless of load, additionally compensate for body tilt when braking or accelerating, when cornering, and also compensate for the influence of crosswinds. The system also dampens vehicle vibrations down to 6 Hz.
The ABC system was the first Mercedes-Benz introduced in its Mercedes Coupé CL in 1999. The system pushed the boundaries of the eternal struggle between comfortable and agile driving, in other words, pushed the boundaries of active safety while maintaining high controllability. comfort. The active suspension adapts to the current road conditions in a fraction of a second. Thus, Active Body Control significantly reduces the amount of body movement when starting, cornering and braking. At the same time, a car equipped with this system provides almost comparable comfort to cars equipped with Airmatic air suspension. During dynamic driving, the chassis control system reacts by decreasing the ground clearance depending on the speed, for example v at 60 km / h will reduce the coupe to 10 millimeters. This reduces air resistance and reduces fuel consumption. The system also replaces the role of the lateral stabilizers.
To respond as quickly as possible, the system is equipped with a range of sensors, powerful hydraulics and electronics. Each wheel has its own electronically controlled hydraulic cylinder located directly in the damping and suspension unit. This hydraulic cylinder generates a precisely defined force based on commands from the control unit and, by its generated force, influences the action of the helical spring. The control unit performs this control every 10 ms.
In addition, the ABC system can effectively filter vertical body movements vibrating at a frequency of up to 6 Hz. These are vibrations that affect driving comfort and usually occur, for example, when driving over bumps, when braking or when cornering. The rest, more high-frequency vibrations of the wheels are filtered out in the classical way, that is, with the help of gas-liquid shock absorbers and coil springs.
The driver can choose from two programs, which he simply changes using a button on the instrument panel. The Comfort program gives the car the comfort of driving a limousine. Conversely, the selector in the "Sport" position adjusts the chassis to match the characteristics of a sports car.