Adaptive vehicle suspension
Content
- What is adaptive suspension
- How does the adaptive suspension of the car
- How adaptive car suspension works
- Pros and cons of adaptive car suspension
- The main differences of the adaptive suspension
- Which cars are equipped with adaptive suspension
- Scheme of the device of the adaptive suspension of the car
- The main breakdown options and the price of suspension parts
The article describes the principle of operation of the adaptive suspension of a car, the pros and cons, as well as the device. The main models of machines in which the mechanism and the cost of repairs are found are indicated. At the end of the article, a video review of the principle of operation of the adaptive suspension The article describes the principle of operation of the adaptive suspension of a car, the pros and cons, as well as the device. The main models of machines in which the mechanism and the cost of repairs are found are indicated. At the end of the article there is a video review of the principle of operation of the adaptive suspension.
The suspension of a car is considered one of the main components responsible for comfort and the ability to move. As a rule, this is a combination of various elements, nodes and elements, each of which plays an important role. Before that, we have already considered MacPherson struts, a multi-link and a torsion beam, so there is something to compare with and understand how much comfort is better or worse, cheap or expensive repairs, as well as how adaptive the suspension and the principle of operation are fixed.
What is adaptive suspension

From the name itself, that the suspension is adaptive, it becomes clear that the system can automatically or on-board computer commands change certain characteristics, parameters and adapt to the requirements of the driver or road surface. For some manufacturers, this version of the mechanism is also called semi-active.
The main characteristic of the whole mechanism is the degree of damping of the shock absorbers (speed of vibration damping and minimization of shock transmission to the body). The first mention of the adaptive mechanism has been known since the 50s of the 20th century. Manufacturers then began using hydropneumatic struts instead of traditional dampers and springs. The basis was hydraulic cylinders and hydraulic accumulators in the form of spheres. The principle of operation was quite simple, due to a change in fluid pressure, the parameters of the base and chassis of the car changed.
The first car in which a hydropneumatic strut was discovered was a Citroen, released in 1954.
Later, the same mechanism was used for DS cars, and starting from the 90s, the Hydractive suspension appeared, which is used and improved by engineers to this day. By adding electronic and automatic control systems, the mechanism itself can be adapted to the road surface or the driver's driving style. Thus, it is clear that the main part of the current adaptive mechanism are electronics and hydropneumatic racks that can change characteristics based on various sensors and analysis of the on-board computer.
How does the adaptive suspension of the car
Depending on the manufacturer, the suspension and components may change, but there are also elements that will be standard for all options. Typically, this set includes:
- electronic control unit;
- active racks (adjustable car racks);
- anti-roll bars with adjustable function;
- a variety of sensors (road roughness, body roll, clearance, and others).
Each of the listed items has a significant responsibility for the functionality of the adaptive automation system. The heart of the mechanism is the electronic suspension control unit of the car, it is he who is responsible for selecting the mode and setting up individual mechanisms. As a rule, it analyzes information collected from various sensors, or receives a command from a manual unit (selector controlled by the driver). Depending on the type of signal received, the stiffness adjustment will be automatic (in the case of collecting information from sensors) or forced (by the driver).

The essence of an electronically adjustable stabilizer bar is the same as in a conventional anti-roll bar, the only difference is the ability to adjust the degree of rigidity based on a command from the control unit. It often works at the moment of maneuvering the car, thereby reducing body roll. The control unit is able to calculate signals in milliseconds, which allows you to instantly respond to road bumps and various situations.
Vehicle adaptive base sensors are usually special devices whose purpose is to measure and collect information and transfer it to the central control unit. For example, a car acceleration sensor collects data on the quality of expensive cars, and at the moment of body roll it works and transmits information to the control unit.
The second sensor is a road bump sensor, it reacts to bumps and transmits information about the vertical vibrations of the car body. Many consider him the main one, as he is responsible for the subsequent adjustment of the racks. No less important is the body position sensor, it is responsible for the horizontal position and during maneuvers transmits data on the inclination of the body (when braking or accelerating). Often in this situation, the car body leans forward during hard braking or backwards during hard acceleration.
As shown, adjustable adaptive suspension struts
The last detail of the adaptive system is adjustable (active) racks. These elements quickly react to the road surface, as well as the style of the car. By changing the pressure of the fluid inside, the stiffness of the suspension as a whole also changes. Experts distinguish two main types of active lightning: with magnetic rheological fluid and with an electromagnetic valve.
The first version of active racks is filled with a special liquid. The viscosity of a liquid can vary depending on the strength of the electromagnetic field. The greater the resistance of the fluid to passage through the valve, the stiffer the base of the car will be. Such struts are used in Cadillac and Chevrolet (MagneRide) or Audi (Magnetic Ride) cars. Solenoid valve struts change their stiffness by opening or closing a valve (variable section valve). Depending on the command from the control unit, the section changes, and the rigidity of the racks changes accordingly. This type of mechanism can be found in the suspension of Volkswagen (DCC), Mercedes-Benz (ADS), Toyota (AVS), Opel (CDS) and BMW (EDC) vehicles.
How adaptive car suspension works
It's one thing to understand the basics of adaptive suspension, and quite another to understand how it works. After all, it is the very principle of operation that will give an idea of the possibilities and use cases. To begin with, consider the option of automatic suspension control, when the on-board computer and the electronic control unit are responsible for the level of stiffness and settings. In such a situation, the system collects all information from the clearance, acceleration and other sensors, and then transfers everything to the control unit.
The video shows the principle of operation of the Volkswagen adaptive suspension
The latter analyzes the information and draws conclusions about the condition of the road surface, the driver's driving style and other characteristics of the car. According to the conclusions, the block transmits commands to adjust the stiffness of the struts, control the anti-roll bar, as well as other elements responsible for comfort in the cabin and linked to the work of the vehicle's adaptive base. It should be understood that all elements and details are interconnected and work not only to receive commands, but also to respond to status, resolved commands, and the need to correct certain nodes. It turns out that the system, in addition to transmitting programmed commands, also learns (adapts) to the requirements of the driver or to the unevenness of the road.
Unlike automatic control of the adaptive suspension of the machine, manual control differs in the principle of operation. Experts distinguish two main directions: the first, when the stiffness is set by the driver forcibly by adjusting the racks (using the regulators on the car). The second option is semi-manual or semi-automatic, since initially the modes are connected to a special block, and the driver only has to choose the driving mode. Therefore, the adaptive suspension electronics sends commands to the mechanisms to set the stiffness of the mechanism. At the same time, information from the sensors is read minimally, most often used to adjust the available parameters so that the base is as comfortable as possible for certain road conditions. Among the most common setting modes are: normal, sporty, comfortable for off-road driving.
Pros and cons of adaptive car suspension
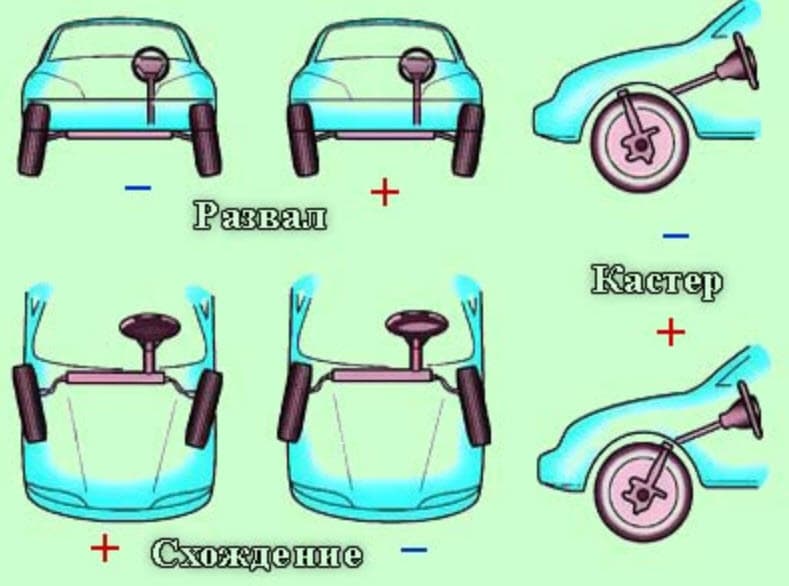
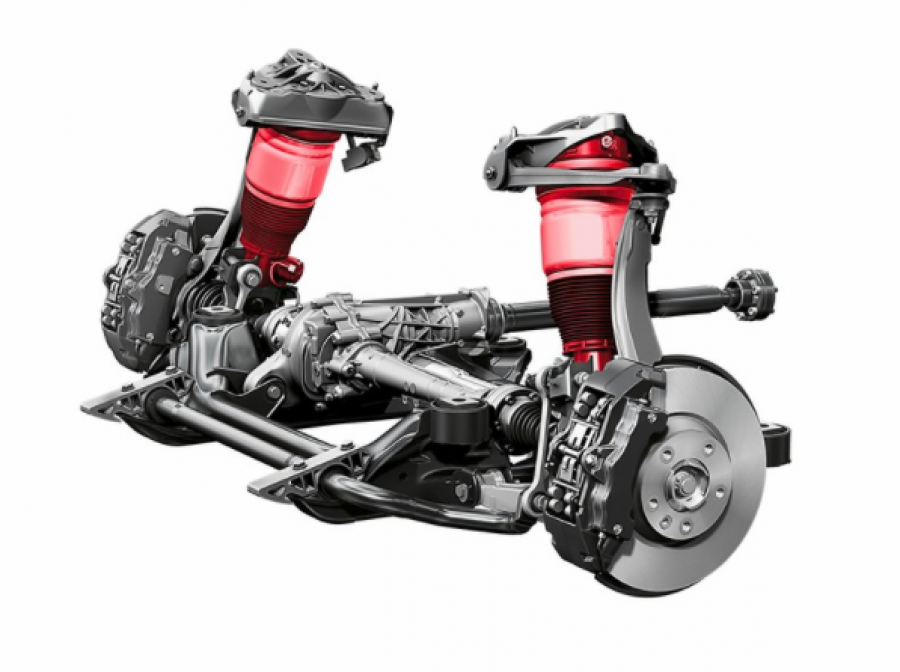
No matter how ideally the mechanism is arranged, there will always be positive and negative sides (plus and minus). The adaptive suspension of a car is no exception, despite the fact that many experts talk only about the advantages of mechanisms.
| Pros and cons of adaptive car suspension | |
| Advantages | defects |
| Excellent running smoothness | High production cost |
| Good car handling (even on a bad road) | High cost of suspension repair and maintenance |
| Ability to change the free space of the car | Design complexity |
| Adaptation to road conditions | Complexity of repair |
| Driving mode selection | Replacement of pairs of hydropneumoelements on axles |
| Long service life of hydropneumoelements (about 25 km) | — |
We see that the main problem of the adaptive base of the car is the high cost of its maintenance, repair and production. In addition, the design is not the most simple. The failure of one of the sensors will immediately affect the convenience and fit of the mechanism. A big plus is the electronics, which react in a fraction of a second, thus creating ideal conditions for the proper functioning of the car body.
The main differences of the adaptive suspension
Comparing the adaptive suspension device described above and others, such as multi-link or MacPherson struts, differences can be noticed even without special skills in the field of car design. For example, while the MacPherson is comfortable, passengers in the car will experience the intersection of good and bad pavement. The handling of such a suspension on a bad road is lost and is not always the best in the case of off-road driving.
As for adaptability, the driver, in fact, may not understand when the car entered the road in poor condition. The system adjusts with lightning speed, changes the control conditions and the stiffness of the racks. The sensors become more sensitive, and the racks respond faster to commands from the electronic control unit.
Depending on the layout of the mechanism, in addition to specific racks, the system is distinguished by many sensors, the layout of the parts themselves, as well as a bulky appearance that is easy to notice when looking at the steering wheel of a car. It is worth noting that the suspension of such a car is constantly evolving, and it makes no sense to talk about any specific design or differences. Engineers from different manufacturers take into account the shortcomings, reduce the cost of expensive parts, increase the service life and expand the capabilities. If we talk about similarities with other known suspensions, then the adaptive system is most suitable for multi-link or double-link designs.
Which cars are equipped with adaptive suspension
Finding a car with adaptive suspension is much easier today than it was 10 years ago. We can say that many premium cars or SUVs are equipped with a similar mechanism. Of course, this is a plus for the cost of the car, but also a plus for comfort and handling. Among the most popular models:
- Toyota Land Cruiser Prado
- Audi K7;
- BMVH5;
- Mercedes-Benz GL-Class;
- Volkswagen Tuareg;
- Vauxhall Movano;
- BMW 3 series;
- Lexus GX460;
- Volkswagen Caravelle.
Naturally, this is the minimum list of cars that can be found on the street in any city. Thanks to its excellent comfort qualities and ability to adapt to the road, the adaptive base is becoming more and more popular.
Scheme of the device of the adaptive suspension of the car
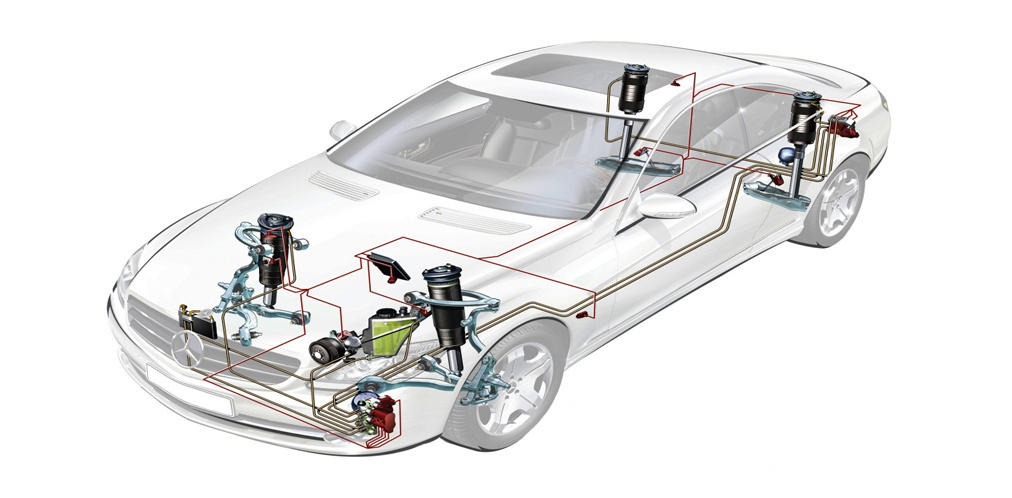
- Front axle sensor;
- Body level sensor (front left);
- Body acceleration sensor (front left);
- Receiver 2;
- Level sensor, rear;
- Rear axle shock absorber;
- Body acceleration sensor, rear;
- Receiver 1;
- Control unit for adaptive suspension;
- Clearance control button in the trunk of the car;
- Air supply unit with valve block;
- Body acceleration sensor, front right;
- Right front level sensor.
The main breakdown options and the price of suspension parts
Like any mechanism, such a suspension fails over time, especially given the careful conditions of its operation. It is very difficult to predict what exactly will fail in such a mechanism, according to various sources, racks, all kinds of connecting elements (hoses, connectors and rubber bushings), as well as sensors responsible for collecting information, wear out faster.
A characteristic failure of the adaptive base of the machine can be various sensor errors. In the cabin you feel discomfort, rumble, and even all the bumps in the road surface. Another characteristic malfunction may be the low clearance of the car, which is not adjustable. In most cases, this is a failure of frames, cylinders or adaptable pressure containers. The car will simply always be underestimated, and there will be no talk of comfort and handling at all.
Depending on the breakdown of the adaptive suspension of the car, the price of spare parts for repairs will also be different. The big disadvantage is that the repair of such a mechanism is urgent, and if a malfunction is detected, it must be fixed as soon as possible. In the classic and most common versions, the failure of shock absorbers or other parts allows you to drive for some time longer without repair. To understand how much repairs will cost, consider the prices for the main parts of the 7 Audi Q2012.
| The cost of adaptive suspension parts Audi Q7 2012 | |
| First name | Price from, rub. |
| Front shock absorbers | 16990 |
| Rear shock absorbers | 17000 |
| ride height sensor | 8029 |
| Rack pressure valve | 1888 g |
Prices are not the lowest, although some parts are said to be repairable. So, before you run out to buy a new part and if you want to save money, look on the Internet to see if you can return it to "combat condition". According to statistics and taking into account the road surface, adaptive shock absorbers and sensors often fail. Shock absorbers due to all kinds of damage and shocks, sensors more often due to operating conditions in mud and frequent jerks, on a bad road.
According to the modern adaptive base of the car, we can say that, on the one hand, this is an ideal choice for comfort and driving. On the other hand, a very expensive pleasure that requires some care and timely repairs. Such a base can be found most often in expensive and premium cars, where comfort is most important. According to many drivers, this mechanism is ideal for off-road trips, long distances or when quietness in the interior of your car is very necessary.
Video review of the principle of operation of the adaptive suspension: