Active and passive safety. How are cars arranged?
 Belts, pretensioners, pillows, curtains, electronics in the chassis, deformation zones - there are more and more guardians of our health and life in the car. For the designers of most modern vehicles, safety is of paramount importance.
Belts, pretensioners, pillows, curtains, electronics in the chassis, deformation zones - there are more and more guardians of our health and life in the car. For the designers of most modern vehicles, safety is of paramount importance.
First of all, it should immediately be noted that the design of a modern car allows it to survive even very serious collisions. And this applies not only to large limousines, but also to small city-class cars. This is great news for any car buyer. We owe this progress mainly to new materials and technologies, but the ingenuity of designers and their ability to introduce valuable innovations is of no small importance.
The first group of automotive elements responsible for improving safety is passive. It remains inactive unless there is a collision or crash. The main role in it is played by the body structure, designed in such a way as to effectively protect the area intended for passengers. The well-designed body of a modern car is a correspondingly rigid form of a cage that protects against the consequences of a collision.
The structure of the front, back and sides is not as rigid as it is geared towards energy absorption. If the entire car were as rigid as possible, delays caused by major crashes would pose a threat to passengers inside. The rigid cabin is designed using high-strength sheets in such a way as to distribute the energy of a possible impact over the largest possible area. Regardless of which side it comes from, both the sills and the pillars, together with the roof lining, must dissipate the compressive forces on the car body.
The front and rear of a modern car are built according to precise calculations based on computer simulations and proven crash tests. The fact is that fragmentation should occur according to the accepted scenario, which provides for the absorption of as much collision energy as possible. Such a scenario is divided into phases, according to which the crushing zone is built. The first is the pedestrian protection zone (not at the rear). It includes a soft bumper, an appropriately shaped front apron and an easily deformable front cover.
The editors recommend: No new speed cameras
The second zone, called the repair zone, serves to absorb the effects of minor collisions. This is done with the help of a special, easily deformable beam immediately behind the bumper and special, small profiles, called "crash boxes", folded into an accordion thanks to special cutouts. Proper beam extension makes headlights well protected. Even if the beam does not hold pressure, the headlights withstand heavy loads thanks to the durable polycarbonate structure.
See also: Volkswagen up! in our test
The third zone, called the deformation zone, is involved in the energy dissipation of the most serious accidents. It includes front belt reinforcement, side members, wheel arches, front hood and in many cases subframe, as well as front suspension and engine with accessories. Airbags are also an important component of passive safety. Not only their number is important, the more the better, but also their location, shape, filling process and accuracy of control.
The front airbag fully deploys only in severe accidents. When the risk is lower, the pillows inflate less, reducing the effects of head contact with the bag. Under the dashboard, there are already knee bolsters, as well as bolsters for rear seat passengers, which are pulled out of the central area of the headlining in the event of a collision.
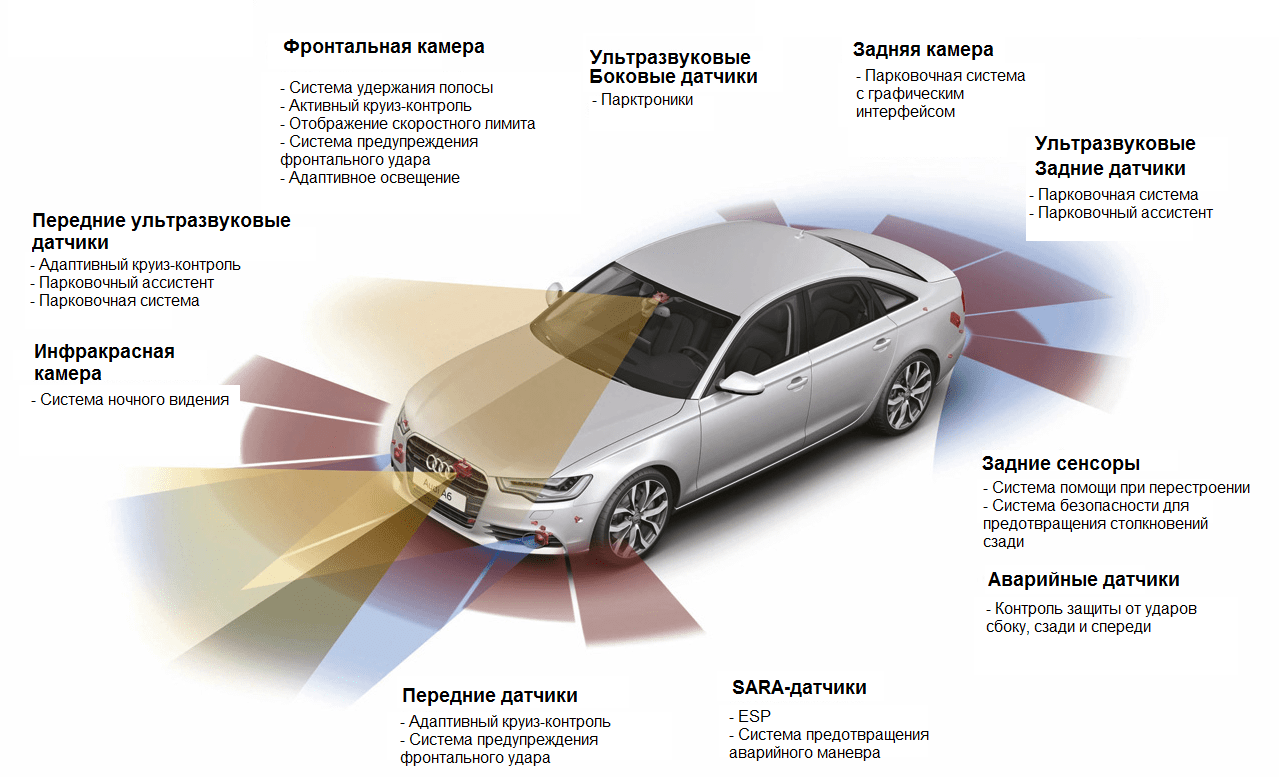
The concept of active safety encompasses all elements that operate while driving and can constantly support or correct the actions of the driver. The main electronic system is still ABS, which prevents the wheels from locking when the car is braking. The optional EBD function, i.e. Electronic Brakeforce Distribution, selects the appropriate braking force for each wheel. In turn, the ESP stabilization system (other names VSC, VSA, DSTC, DSC, VDC) prevents the car from skidding when cornering or in difficult road conditions (puddles, bumps) by braking the corresponding wheel on the right moment. BAS, also known as "Emergency Brake Assist", is designed to maximize brake pedal pressure during emergency braking.