Armored personnel carriers M2, M3 / M5 / M9
Content
Armored personnel carriers M2, M3/M5/M9
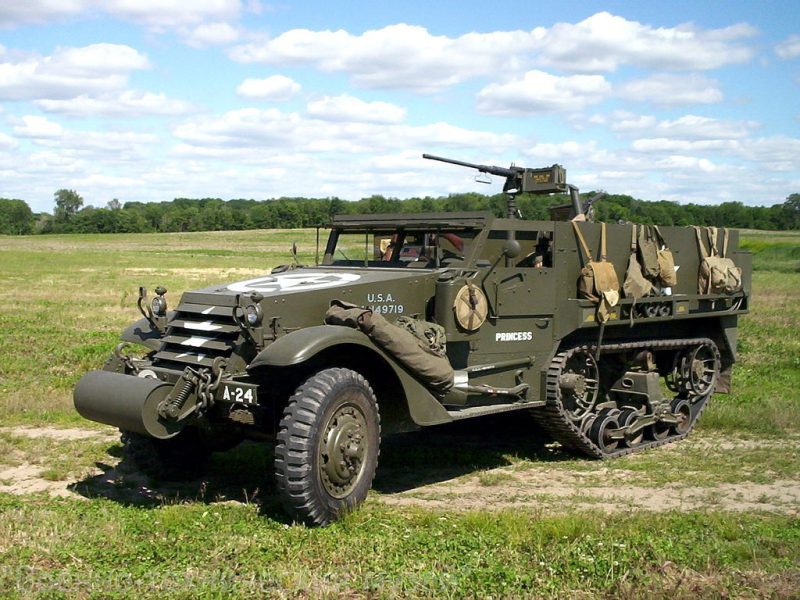
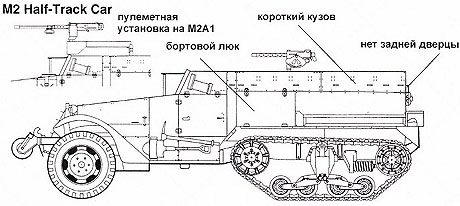
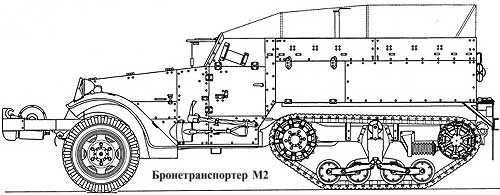
To increase the cross-country ability, they were equipped with self-recovery winches. The winches were driven by the engine. The armored hull was open from above, the armor plates were located without a rational slope. The front armor plate of the cockpit, equipped with viewing slots, as a rule, could be folded up and fixed horizontally on the racks. For the entry and exit of the crew and the landing, there were two doors in the cockpit and one door in the rear armor plate. Armament, as a rule, consisted of one 12,7-mm machine gun mounted on a turret next to the driver's cab, as well as one 7,62-mm machine gun on the rear armor plate. Half-track armored personnel carriers have proven themselves well as simple and reliable vehicles. Their disadvantages were insufficient maneuverability on rough terrain and an unsuccessful configuration of armor protection. M2 semi-tracked conveyorThe M2 armored personnel carrier, which was a development of the T14, was equipped with a White 160AX engine, while the T14 had a White 20A engine with L-shaped heads. The White 160AX engine was selected from the three engine types primarily for its exceptional reliability. In order to simplify the design of the machine, the front axle and steering are made almost the same as on a truck. The transmission has five speeds - four forward and one reverse. The steering wheel is on the left. Rear suspension - Timken 56410-BX-67 with rubber track. The caterpillar is a rubber casting, made on the armature in the form of cables and equipped with metal guides. On the highway, the M2 accelerated to a speed of 72 km / h, although off-road it moved much more slowly.
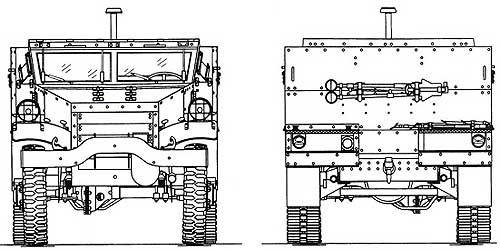
The layout of the semi-tracked vehicle is generally similar to the layout of the wheeled M3A1 Scout Car. Normally ten people are placed in the back - three in front and seven behind. The control compartment has two more seats, the left one for the driver and the right one for the passenger. Between the two extreme front seats, another seat is installed with a shift back. To the right and left of this seat are large luggage boxes. The center seat is set approximately halfway down the length of the machine. The lids of the luggage boxes are made hinged, in addition, access to the trunks can be carried out through hatches in the walls of the hull. Behind the right and left seats are two main fuel tanks. The tanks are made of ordinary structural steel, but equipped with self-tightening rubber when hit by bullets.
The main armament is mounted on a guide rail that runs along the edge of the inner surface of the body walls. Officially, the vehicle was armed with one 12,7 mm machine gun and one 7,62 mm machine gun. At the front, the crews armed armored personnel carriers to the best of their own strengths and capabilities. In addition to the rails, the machine gun was mounted on a turret mounted in front of the middle front seat. The body of the vehicle is made of rolled armor plates with a thickness of 6,3 mm. The armor plates are bolted to the steel frame with oval-headed bolts. The thickness of the flaps in the frontal armor plate of the body is 12,5 mm.
For access to the car in the sides of the body, in the area of \u2b\u1941bthe control compartment, automobile-type doors are made. Landing and excavation is also carried out through the top of the body walls. Doors in the stern of the hull could not be made due to the presence of a guide rail for machine guns. In the frontal armor plate of the body, there are a network of two armored doors that recline on hinges to improve visibility from the cab. Narrow viewing slots are arranged in the hatches, which, in turn, are closed with valves. The upper parts of the doors are made folding to improve visibility. The radiator is covered with armored blinds installed in the front wall of the hood. The blinds are swivel. Serial production of M1943 armored personnel carriers began in the spring of 11415 and continued until the end of 2. A total of 2 M8423 armored personnel carriers were manufactured. White Motors and Autocar, two firms, were engaged in the serial construction of M2992 half-track armored personnel carriers. The White company delivered XNUMX cars to the customer, the Autocar company - XNUMX.
Initially, the M2 vehicles were planned to be used as artillery tractors and ammunition transporters. The limited capacity of the vehicle - ten people - did not allow one armored personnel carrier to carry an entire infantry squad. With the advent of armored personnel carriers, changes were made to the tactics of the actions of the American “armored infantry”, M2 vehicles began to be used to transport a machine gun squad, and before the advent of M8 armored vehicles, in reconnaissance units. M2A1 semi-tracked armored personnel carrierThe rails-guides under armament in combat conditions turned out to be inconvenient. On the M2E6 prototype, instead of rails, the M32 annular turret was mounted, which was used on military trucks. The turret was placed above the right front seat in the control compartment. Then came the improved ring machine gun turret M49, which finally removed the problem of guide rails. Two machine guns were installed on the M49 turret at once - one 12,7-mm caliber and one 7,62-mm caliber.
The armored personnel carrier with an annular machine-gun turret was designated M2A1. Serial production of М2А1 machines was carried out from the end of 1943 to the end of 1944. White and Avtokar supplied 1643 М2А1 half-track vehicles. In the M2A1 version, about 5000 previously built M2s were modified. Half-track armored personnel carrier MZThe M3 armored personnel carrier looks very similar to its predecessor M2. The front ends of these machines, including the control compartments, are simply identical. The M3 is slightly longer than the M2. In the sides of the M3 body there are no luggage compartment hatches, as was the case with the M2. Inside, the M3 is quite different from the M2. In the control compartment, the center seat is moved forward, in line with the driver and passenger seats. The fuel tanks are also shifted forward to where the luggage compartments were on the M2.
The middle, turned back, the seat in the back is eliminated. Instead of the seat, a pedestal was built for a machine-gun turret; the turret is provided for the installation of one machine gun of 12,7 mm or 7,62 mm caliber. In the body, on each side, there are five seats, facing the longitudinal axis of the machine. Luggage compartments are organized under the seats.
Since the M3 was originally designed as an infantry carrier, a door was made in the rear wall of the body. Behind the three rear seats on each side is a storage space for rifles.
To improve cross-country ability to cross very rough terrain, a roller is attached to the bumper of the M3 armored vehicle. Instead of a roller, it is possible to mount a winch, designed primarily for self-pulling of the machine.
Serial production of half-track MZ was carried out in 1941 -1943 by White, Avtokar and Diamond T. A total of 12499 vehicles were built, some of which were upgraded to the M3A1 version. Although the M3 armored personnel carrier was intended to transport an infantry squad, it was used in a variety of ways. Like the M2, the M3s served as artillery tractors and ammunition transporters, while the M3s were used as ambulances, command-staff and repair vehicles. In addition, on the basis of the original version of the M3, a number of highly specialized options were developed. М3А1As with the M2, the weapon mounting system proved to be inadequate. As a result of "front-line requirements", an experimental M2E6 machine appeared, equipped with an M49 turret, the same as on the M2A1. It is logical that the M3 armored personnel carrier with the M49 ring turret began to be designated M3A1. Serial production continued in 1943-1944 by White, Autocar and Diamond T, a total of 2862 cars were built. A large number of previously built M3s were upgraded to the M1A2 level.
М3А2By the beginning of 1943, the Armaments Directorate tried to unify the M2 and M3 machines into a single version. The prototype was designated T29. The vehicle was prepared for testing in the spring of 1943. In October, it was recommended for serial production under the designation M3A2. However, by this time the need for half-tracked armored vehicles had lost its urgency, so the serial production of the M3A2 was never started. The main external difference between the M3A2 and the M3A1 was the presence of an armored shield of an annular bullet turret. It was possible to quickly dismantle the seats from the body.
M9 semi-tracked armored car and M5 semi-tracked armored personnel carrierAfter the US entered the war, the formal reason for which was the Japanese attack on Pearl Harbor, Washington began implementing the “Arsenal of Democracy” program in order to provide US allies with weapons and military equipment. specialized in the production of exclusively peaceful products. Three firms engaged in the production of half-track armored personnel carriers were not able to provide all US allies with equipment of this type. It was decided to involve the International Harvester Company in production, at the same time it was decided to soften the requirements for the “sameness” of armored personnel carriers manufactured by different companies. The main design change was the replacement of the hardened armor plates used on the M2 / M3 armored personnel carriers with homogeneous armor plates. These 5/16-inch thick armor plates had worse bullet resistance than quarter-inch-thick hardened armor plates.
The International Harvester Company was allowed to use a number of original components and assemblies, including the engine, on the machines of its construction. Two variants were approved for serial production - M2E5 and M3E2, respectively, received the designation M9 and M5. There were a number of external differences between the M9 and M5 machines from their counterparts M2 and M3. The M9 machine did not differ in length from the M3 and M5 armored personnel carriers and did not have access hatches to the luggage compartments on the sides. Both machines M5 and M9 were equipped in most cases with flat, and not rounded (automotive type), wings. Unlike the M2, the M9 had a door in the rear of the body. Externally, the M5 and M9 are practically indistinguishable, all the differences are in the interior.
Similar to the M2 and M3 machines, the M5 and M9 machines were adapted to install the M49 ring machine gun turret. after which nx began to be designated as M5A1 and M9A1. Due to significant design differences from the M2 and M3 vehicles adopted by the US Army, the M5 and M9 vehicles were supplied to the allies as part of the Lend-Lease, although some of them leaked to the US troops. Firm International Harvester Company in 1942-1944 manufactured 11017 machines M5 and M9, including M9 - 2026, M9A1 - 1407, M5 - 4625 and M5A1 - 2959. М5А2In 1943, the Armaments Directorate attempted to unify the US Army's armored personnel carrier fleet. The prototype M31, which was a hybrid of the M5 and M9, was recommended for mass production under the designation M5A2. Serial production of M5A2 vehicles did not begin due to a decrease in the need for half-track armored personnel carriers. Performance characteristics
Sources:
|


 During the Second World War, the US industry produced a huge number of half-track armored personnel carriers - more than 41 thousand. The armored personnel carriers produced had approximately the same characteristics and belonged to the four main series: M2, M3, M5 and M9. Each series had several modifications. All machines were created with the wide use of automotive units, had a weight of 8-9 tons and a load capacity of about 1,5 tons. Their undercarriage used rubber tracks with metal reinforcement, small-diameter road wheels and a front axle with driving and steering wheels.
During the Second World War, the US industry produced a huge number of half-track armored personnel carriers - more than 41 thousand. The armored personnel carriers produced had approximately the same characteristics and belonged to the four main series: M2, M3, M5 and M9. Each series had several modifications. All machines were created with the wide use of automotive units, had a weight of 8-9 tons and a load capacity of about 1,5 tons. Their undercarriage used rubber tracks with metal reinforcement, small-diameter road wheels and a front axle with driving and steering wheels.