what is it in the car? Principle of operation, device and purpose
ESP or Elektronisches Stabilitätsprogramm is one of the modifications of the car's stability control system, which was first installed on cars of the Volkswagen concern and all its divisions: VW, Audi, Seat, Skoda, Bentley, Bugatti, Lamborghini.
Today, such programs are installed on almost all cars manufactured in Europe, the USA, and even many Chinese models:
- European - Mercedes-Benz, Opel, Peugeot, Chevrolet, Citroen, Renault, Saab, Scania, Vauxhall, Jaguar, Land Rover, Fiat;
- American - Dodge, Chrysler, Jeep;
- Korean - Hyundai, SsangYong, Kia;
- Japanese - Nissan;
- Chinese - Chery;
- Malaysian - Proton and others.
Today, this system is recognized as mandatory in almost all European countries, in the USA, Israel, New Zealand, Australia and Canada. In Russia, this requirement has not yet been put forward for automakers, however, the new LADA XRAY is also equipped with a course stabilization system, although the price of this crossover is much higher than that of more budget cars, such as Lada Kalina or Niva 4x4.

It is worth recalling that we have already considered other modifications of the stabilization system - ESC on Vodi.su. In principle, they all work according to more or less the same schemes, although there are certain differences.
Let's try to understand in more detail.
The device and the principle of operation
The principle of operation is quite simple - numerous sensors analyze various parameters of the movement of the car and the operation of its systems. Information is sent to the electronic control unit, which operates according to specified algorithms.
If, as a result of movement, any situations are observed when the car can, for example, sharply go into a skid, roll over, drive out of its lane, etc., the electronic unit sends signals to the actuators - the hydraulic valves of the brake system, due to which all or one of the wheels, and emergencies are avoided.
In addition, the ECU is associated with ignition systems. So, if the engine is not working efficiently (for example, the car is in a traffic jam, and all cylinders are working at full power), the spark supply to one of the candles may stop. In the same way, the ECU interacts with the engine if it is necessary to slow down the speed of the car.

Certain sensors (steering wheel angle, gas pedal, throttle position) monitor the actions of the engine in a given situation. And if the driver's actions do not correspond to the traffic situation (for example, the steering wheel needs to be turned not so sharply, or the brake pedal needs to be squeezed harder), the corresponding commands are again sent to the actuators to correct the situation.
The main components of ESP are:
- the actual control unit;
- valve body;
- sensors for speed, wheel speed, steering wheel angle, brake pressure.
Also, if necessary, the computer receives information from the throttle sensor and the position of the crankshaft.
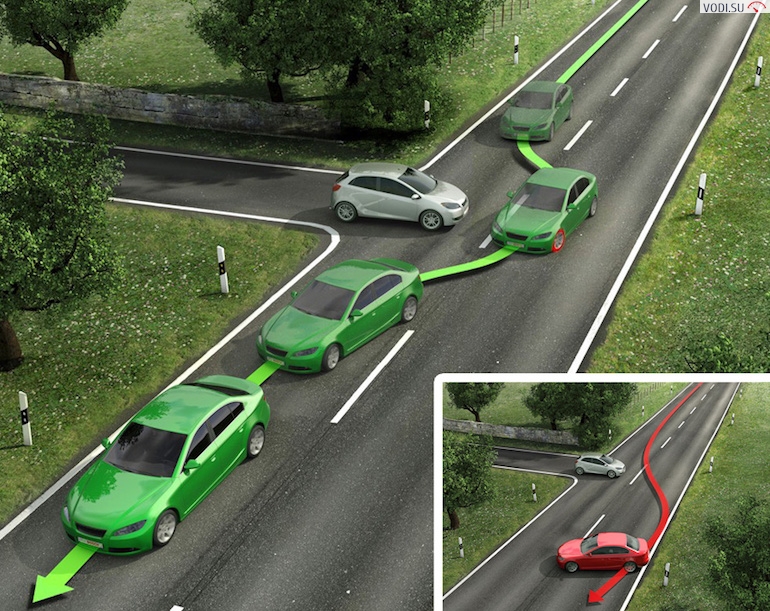
It is clear that complex algorithms are used to analyze all incoming data, while decisions are made in a fraction of a second. So, the following commands can be received from the control unit:
- braking the inner or outer wheels to avoid skidding or increasing the turning radius when driving at high speeds;
- shutdown of one or more engine cylinders to reduce torque;
- change the degree of suspension damping - this option is available only on cars with adaptive suspension;
- changing the angle of rotation of the front wheels.
Thanks to this approach, the number of accidents in countries where ESP is recognized as mandatory has decreased by a third. Agree that the computer thinks much faster and makes the right decisions, unlike the driver, who can be tired, inexperienced, or even intoxicated.
On the other hand, the presence of the ESP system makes the car less responsive to drive, since all driver actions are carefully checked. Therefore, it is possible to disable the stability control system, although this is not recommended.

Today, thanks to the installation of ESP and other auxiliary systems - parking sensors, anti-lock brakes, brake force distribution system, Traction Control (TRC) and others - the driving process has become easier.
However, do not forget about the basic safety rules and traffic rules.


Watch this video on YouTube
Loading…