
What is plywood?
Content
Plywood boards or "sheets" consist of three or more thin layers of natural wood glued together.
The layers are known as "layers", hence the name "plywood". As a rule, the thicker the plywood, the more layers it has.
It is a versatile material with a huge range of applications, from wall and floor coverings to concrete molds, designer furniture and packaging.
Plywood is significantly stronger than some other wood-based sheet materials such as medium density fibreboard (MDF).
See our page What is MDF?, for more information on Medium Density Fibreboard.
The strength of plywood is due to the fact that the direction of the fibers of each layer alternates with respect to adjacent layers.

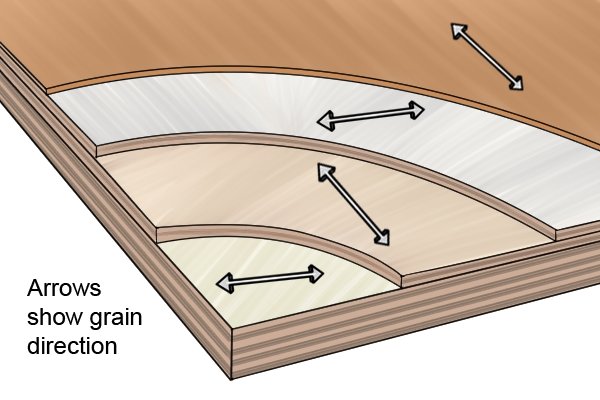
The rotation of the grain direction of each layer, called cross grain, is often 90 degrees (right angle). This means that the grain of each other layer is oriented in the same direction, and the layer is oriented at a 90 degree angle between them. However, the angle of rotation can be as low as 30 degrees. In some thicker plywoods, seven layers may be arranged in sequence at angles of 0, 30, 60, 90, 120, 150, and 180 degrees).

Rotating grain has a number of advantages. This:
Reduces the chance of splitting when sheets are nailed to the edges
Reduces expansion and shrinkage for better dimensional stability
Gives plywood a consistent strength in all directions throughout the board.
A Brief History of Plywood
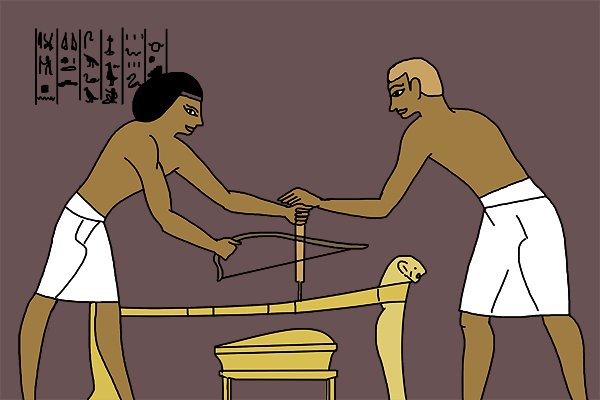
Ancient Egypt
Wooden products made in ancient Egypt around 3500 BC are the earliest known examples of the use of plywood. They were made from sawn veneer glued crosswise, much like modern plywood.

China, England and France
About 1,000 years ago, The Chinese planed wood and glued it to make furniture.
The British and French made panels on a common basis from plywood in the 17th and 18th centuries.

From home to construction
Early examples of plywood, usually made from decorative hardwoods, were most commonly used in the production of household items such as cabinets, chests, countertops, and doors.
Softwood plywood for use in construction appeared in the 20th century.
What is it used for?

Huge range of applications
The range of uses for plywood, both indoors and outdoors, seems endless. In construction, it can be used in walls, floors, roofs and stairs; as a formwork (type of form) to hold concrete during setting; and in a temporary frame for shaping for laying brick or stone when arranging arched openings.

Furniture
Plywood is also still widely used in furniture manufacturing.
Packaging, modeling and art surfaces
Other applications include secure packaging, sports and play equipment, and even the bodies of some vehicles and light aircraft.
Thinner plywood is often used in model making, and some artists paint on it after coating it with plaster, a sealant that provides a slightly rough surface that holds paint well.
Designed for Special Purposes
Different types of plywood are designed for specific purposes. For example, high strength plywood made from mahogany and/or birch was used in the construction of some World War II aircraft, while marine plywood made from strong face and inside veneers with few defects performs better in wet and humid conditions.
Features

Energy
Plywood is strong, generally fairly resistant to impact damage, relatively light, and relatively easy to cut and “work” with tools.
It is excellent as a sheet material for forming or covering large, flat, sloping or even shapes such as walls, floors, some types of roofs and large containers.
Useful for complex work
Some types of plywood are suitable for more complex work, such as making models, wooden puzzles, and small boxes.
Large panels quickly cover large areas
Because plywood is available in large panels, large areas can be covered with minimal edge jointing, and the wide choice of thicknesses makes it suitable for a wide range of applications from thick shelving to thin cladding.
How is plywood made?
The production of plywood typically requires logs called "hullers" that are larger in diameter and straighter than the average log from which the wood is cut.
The bark is removed before the peeler is heated and soaked for 12 to 40 hours before slicing.
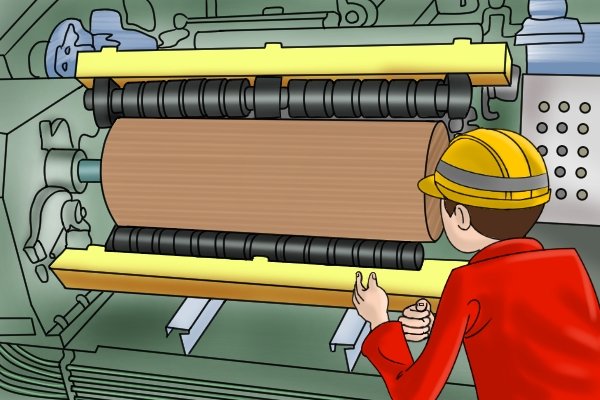
Then it is placed in a large peeling machine and rotated around its long axis ...
 … while a long blade separates a continuous sheet or layer from the log.
… while a long blade separates a continuous sheet or layer from the log. 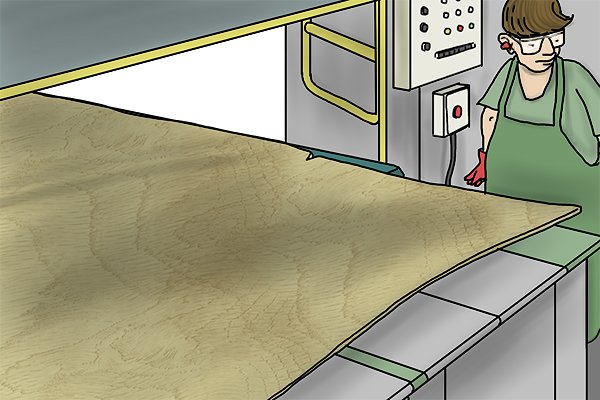 The long sheet is cut into parts of the original length and width, and the surfaces are scanned for defects.
The long sheet is cut into parts of the original length and width, and the surfaces are scanned for defects. 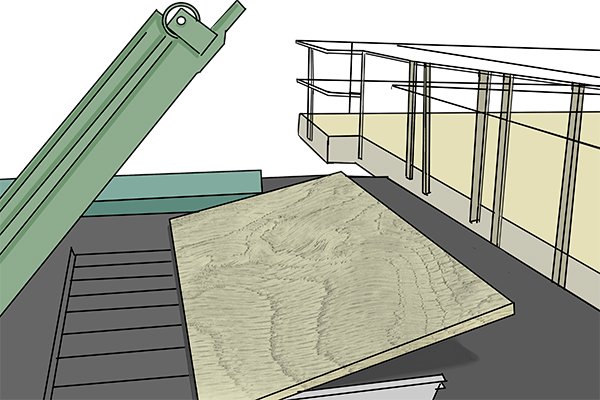
The layers are then pressed and glued together, and the resulting boards are cut to their final dimensions.
The final operation is usually grinding - leveling - boards. Some boards are coated (such as melamine or acrylic) and their edges are sealed.
What are the types of plywood?

The range of plywood is very large. Following are some of the main types available. Talk to your builders salesperson or look online if you are looking for something very specific to meet a specific need.
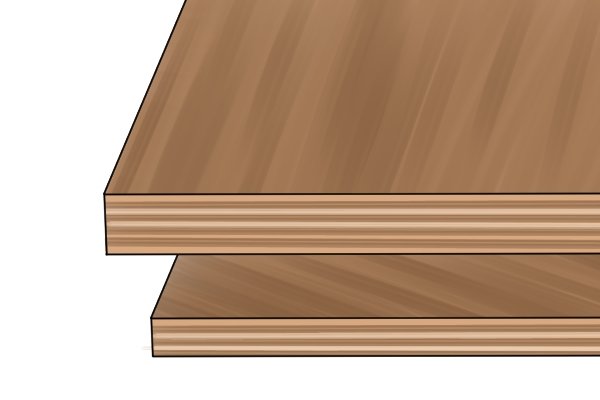
Coniferous plywood
This is a very common type of plywood used mainly in construction and industrial applications.
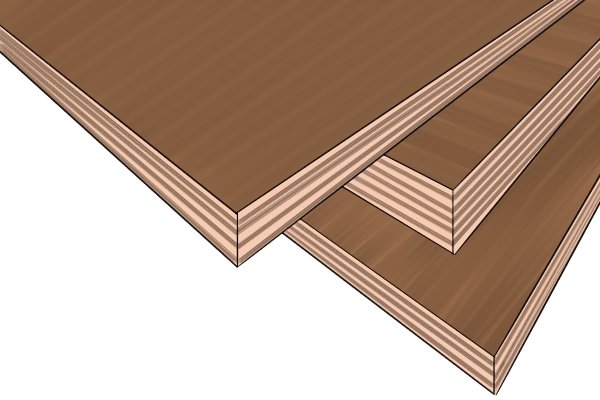
Hardwood plywood
This type has more strength and rigidity. Its resistance to damage and wear makes it suitable for harsh environments including floors and walls.
tropical plywood
Made from Asian, African and South American tropical woods, this plywood outperforms softwood plywood due to its increased strength and flatness of plies. It is the preferred choice of many in the construction industry. Some specimens have a very attractive texture and coloration, making them suitable for use in some types of furniture.

Plywood Aircraft
Made from mahogany or birch, and often both, this high-strength plywood has plies glued together with an adhesive that is highly resistant to heat and moisture. It was used for some aircraft during World War II and is used today in a variety of applications requiring similar strength and durability.
Decorative plywood
This plywood has an attractive hardwood outer layer for use in furniture, wallboard and other "high quality" applications. Other types of decorative outer layer include mold and resin impregnated paper.

Flexible plywood
Flexible plywood, sometimes referred to as "hat plywood" due to its use in "chimney" hats in Victorian times, was used to create curved shapes.

marine plywood
Marine plywood, as its name suggests, is the choice for boats and many other applications where wet and wet conditions are encountered. It is resistant to fungal attack and delamination - when the layers begin to delaminate, usually due to exposure to dampness. The downside is that it is much more expensive than many other types of plywood.

Fireproof plywood
This is plywood treated with chemicals to increase fire resistance.
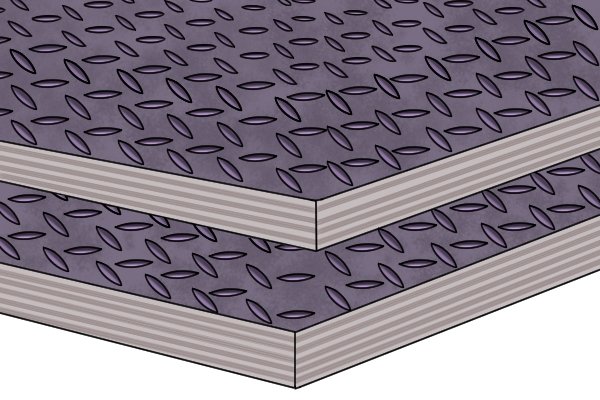
Plywood laminated with phenol
Hot laminate is melted onto the surface of this plywood. The surface can then be left smooth for formwork—for example, a mold for concrete structures or a temporary structure to hold brick arches and other forms in place until the mortar sets—or patterns can be pressed into it for a non-slip or decorative finish. Applications.
What sizes are available?
The maximum and minimum sheet sizes often depend on the particular type of plywood, but the most common standard size is 4ft by 8ft (1220mm x 2440mm). Larger and smaller sheets are often available, usually in 1 foot (300 mm) increments.

Plywood thickness varies from 1/16" (1.4mm) to 1" (25mm), although thicker sheets are available for some special applications.
How is plywood sorted?
Different types of plywood are classified differently, depending on the type of wood they are made from or the country of origin. The evaluation refers to the quality of the wood used, whether one or both outer layers or surfaces have very few or many defects, and whether any defects have been removed during the manufacturing process.
For example, brands of birch plywood:
S class (highest) - only minor components and characteristics
Grade BB (medium) - inserted oval patches replace any large knots and defects.
Grade WG (lower) - open defects on smaller knots with some repaired larger knots.
Class C (lowest) - open defects allowed
There are also Brazilian, Chilean, Finnish, Russian, Swedish and several other varieties. Before buying, check the plywood grade to make sure the plywood meets the requirements for the particular job.
What are the standards for plywood?
There are different standards - European and BS (British Standards) - for plywood used in a wide variety of applications.
For example, in the construction sector, the European standard for wood-based panels EN 13986 requires plywood used in the construction sector to meet one of the three performance classes within EN 636, and suppliers must provide proof of this.
The performance classes are based on the moisture resistance of plywood used in various parts of buildings such as roofs, partitions, floors, and timber-framed exterior walls.
Some types combine excellent weather resistance and outdoor strength properties to meet specific standards such as BS 1088 (plywood for marine use), while the structural standard code BS 5268-2:2002 applies to plywood strength, used in construction work. It is a good idea to check if the plywood you are buying is of the correct standard for the intended use.
