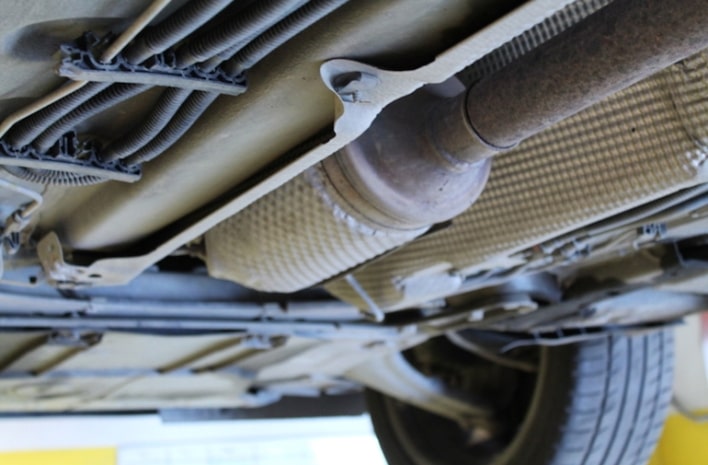

What is a particulate filter and why you need to know it
Content
Cars make a significant contribution to environmental pollution. This is especially true of the air we breathe in big cities. The aggravation of environmental problems forces us to take increasingly stringent measures to clean up automotive exhaust gases.
So, since 2011, in cars running on diesel fuel, the presence of a particulate filter is mandatory (you can often find the English abbreviation DPF - diesel particulate filter). This filter is quite expensive and can cause problems in some cases, so it is useful to have an idea about it.
The purpose of the particulate filter
Even the most advanced internal combustion engine does not provide one hundred percent combustion of fuel. As a result, we have to deal with exhaust gases, which contain a number of substances harmful to humans and the environment.
In vehicles with a gasoline engine, the catalytic converter is responsible for cleaning the exhaust. Its task is to neutralize carbon monoxide (carbon monoxide), volatile hydrocarbons that contribute to the formation of smog, toxic nitrogen compounds and other products of fuel combustion.
Platinum, palladium and rhodium usually act as direct catalysts. As a result, at the outlet of the neutralizer, toxic substances turn into harmless ones - oxygen, nitrogen, carbon dioxide. The catalytic converter works effectively at a temperature of 400-800 °C. Such heating is provided when it is installed directly behind the exhaust manifold or in front of the muffler.
The diesel unit has its own characteristics of functioning, it has a lower temperature regime and a different principle of fuel ignition. Accordingly, the composition of the exhaust gases also differs. One of the products of incomplete combustion of diesel fuel is soot, which has carcinogenic properties.
The catalytic converter can't handle it. Small particles of soot contained in the air are not filtered by the human respiratory system. When inhaled, they easily penetrate the lungs and settle there. To prevent soot from entering the air in diesel cars, a diesel particulate filter (SF) is installed.
The diesel engine catalyst (DOC - diesel oxidation catalyst) has its own characteristics and is installed in front of the particulate filter or integrated into it.
The device and principle of operation of the "soot"
Typically, the filter is a ceramic block placed in a stainless steel housing with square through channels. The channels are open on one side and have a staggered plug on the other.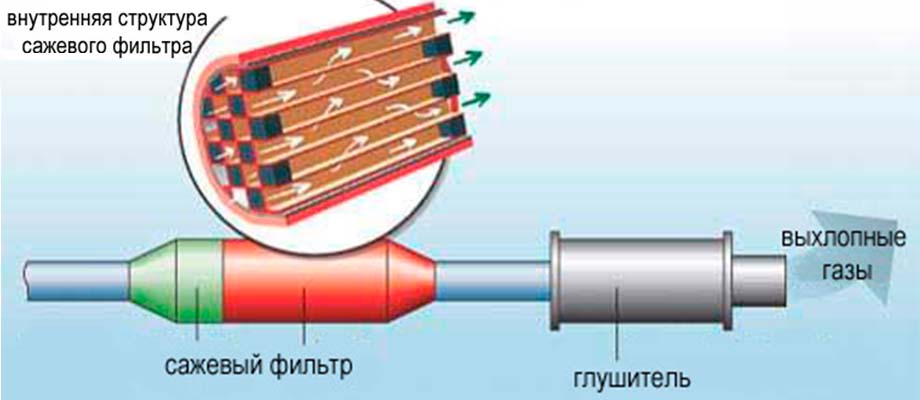 Exhaust gases pass almost unhindered through the porous walls of the channels, and soot particles settle in the blind ends and do not enter the air. Additionally, a layer of a catalyst substance can be applied to the metal walls of the housing, which oxidizes and neutralizes carbon monoxide and volatile hydrocarbon compounds contained in the exhaust.
Exhaust gases pass almost unhindered through the porous walls of the channels, and soot particles settle in the blind ends and do not enter the air. Additionally, a layer of a catalyst substance can be applied to the metal walls of the housing, which oxidizes and neutralizes carbon monoxide and volatile hydrocarbon compounds contained in the exhaust.
Most particulate filters also have sensors for temperature, pressure and residual oxygen (lambda probe).
Auto cleaning
The soot deposited on the walls of the filter gradually clogs it and creates an obstacle to the exit of exhaust gases. As a result, there is an increased pressure in the exhaust manifold and the power of the internal combustion engine drops. In the end, the internal combustion engine may simply stall. Therefore, an important issue is to ensure the purification of the SF.
Passive cleaning is carried out by oxidizing soot with hot exhaust gases at a temperature of about 500 ° C. This happens automatically while the car is moving.
However, urban conditions are characterized by short distance travel and frequent traffic jams. In this mode, the exhaust gas does not always reach a sufficiently high temperature and then soot will accumulate. The addition of special anti-particulate additives to the fuel can help in this situation. They contribute to the burning of soot at low temperatures - about 300 ° C. In addition, such additives can reduce the formation of carbon deposits in the combustion chamber of the power unit.
Some machines have a forced regeneration function that is triggered when the differential sensor detects too much pressure difference before and after the filter. An additional portion of fuel is injected, which is burned in the catalytic converter, heating the SF to a temperature of approximately 600 ° C. When the soot burns out and the pressure at the inlet and outlet of the filter equalizes, the process will stop.
Other manufacturers, for example, Peugeot, Citroen, Ford, Toyota, use a special additive, which contains cerium, to warm up the soot. The additive is contained in a separate container and is periodically injected into the cylinders. Thanks to it, the SF heats up to 700-900 ° C, and soot at this temperature completely burns out in a set of minutes. The process is fully automatic and occurs without driver intervention.
Why regeneration can fail and how to do a manual cleanup
It happens that automatic cleaning does not work. The reasons may be the following:
- during short trips, the exhaust gases do not have time to heat up to the desired temperature;
- the regeneration process was interrupted (for example, by shutting down the internal combustion engine);
- malfunction of one of the sensors, poor contact or broken wires;
- there is little fuel in the tank or the fuel level sensor gives low readings, in this case regeneration will not start;
- Faulty or clogged exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) valve.
If too much soot has accumulated, you can remove it manually by washing.
To do this, the particulate filter must be dismantled, one of the pipes must be plugged, and a special flushing fluid must be poured into the other. Leave upright and shake occasionally. After about 12 hours, drain the liquid and rinse the filter with running water. If there is a viewing hole or a lift, dismantling and cleaning can be done independently. But it is better to go to the service station, where at the same time they will check and replace the defective elements.
Service technicians can also burn out the accumulated soot using special equipment. To heat the SF, an electric or microwave heater is used, as well as a special fuel injection algorithm.
Causes of increased soot formation
The main reason for increased soot formation in the exhaust is bad fuel. Low-quality diesel fuel may contain a significant amount of sulfur, which not only leads to the formation of acid and corrosion, but also prevents the complete combustion of fuel. Therefore, if you notice that the particulate filter becomes dirty faster than usual, and forced regeneration starts more often, then this is a serious reason to look for another gas station.
An incorrect adjustment of the diesel unit also contributes to an increase in the amount of soot. The result can be a reduced oxygen content in the air-fuel mixture, which occurs in certain areas of the combustion chamber. This will lead to incomplete combustion and the formation of soot.
Service life and replacement of the particulate filter
Like any other part of the car, the SF gradually wears out. The filter matrix begins to break down and loses its ability to effectively regenerate. Under normal conditions, this becomes noticeable after about 200 thousand kilometers.
In Ukraine, operating conditions can hardly be considered normal, and the quality of diesel fuel is not always at the proper level, so it is possible to count on 100-120 thousand. On the other hand, it happens that even after 500 thousand kilometers, the particulate filter is still in working condition.
When the SF, despite all attempts at cleaning and regeneration, begins to clearly degrade, you will notice a significant decrease in the power of the internal combustion engine, an increase in fuel consumption and an increase in exhaust smoke. The ICE oil level may rise and an uncharacteristic sound may appear during the operation of the ICE. And on the dashboard the corresponding warning will light up. All arrived. It's time to change the particulate filter. Pleasure is expensive. Price - from one to several thousand dollars plus installation. Many strongly disagree with this and prefer to simply cut the SF out of the system.
What happens if you remove the particulate filter
Among the advantages of such a solution:
- you will get rid of one of the causes of headache;
- fuel consumption will decrease, although not too much;
- the power of the internal combustion engine will increase slightly;
- you will save a decent amount of money (removing the SF from the system and reprogramming the electronic control unit will cost about $ 200).
Negative consequences:
- if the car is under warranty, you can forget about it;
- an increase in soot emissions in the exhaust will be noticeable to the naked eye;
- since the catalytic converter will also have to be cut out, the harmful emissions of your car will not fit into any standards;
- an unpleasant whistle of the turbine may appear;
- environmental control will not allow you to cross the border of the European Union;
- ECU flashing will be required, it can have unpredictable consequences for the operation of various vehicle systems if the program contains errors or is not fully compatible with this particular model. As a result, getting rid of one problem, you can get another, or even a set of new ones.
In general, the choice is ambiguous. It is probably better to purchase and install a new diesel particulate filter if funds allow. And if not, try to revive the old one, try to burn out the soot in various ways, and wash it by hand. Well, leave the option of physical removal as a last resort, when all other possibilities have been exhausted.