Citroën Advanced Comfort damping: principle and function

To compensate for the disappearance of hydropneumatic suspension while maintaining a solid reputation for suspension comfort, Citroën has developed special shock absorbers inspired by its competitors. Thus, there is no technological revolution here, as hydropneumatics was in its day, even if Citroën did file a patent.
Therefore, it should be understood that we are far from hydropneumatic suspension, which combines air cushions with specific integrated hydraulic damping (see here). Here it is still a combination of a hydraulic shock absorber and a coil spring.
However, here we will focus only on shocks and forget about the rest, because only they are new. However, it should be noted that the installation of these shock absorbers will require adjusting the springs and anti-roll bars, but this is obvious and only a trifle here.
It should also be noted that Citroën Advanced Comfort is a global program aimed at improving the comfort of Citroëns. This includes getting through the redesigned seats as well as a stiffer chassis design to limit the waves that can go over it (the goal is to avoid shaking the entire car when going over bumps in the road).
Compared to Hydractive?
Technically speaking, the Advanced Comfort cushioning is a straw compared to the Hydractive. Indeed, this new process ultimately only consists of installing slightly better dampers, which are not enough to revolutionize the running gear of our expensive Citroëns… The device is completely passive and only slightly improves the filtering of road bumps. In addition, Hydractive provides even more comfort thanks to the air suspension (airbags replace conventional metal springs), not to mention the fact that it allows you to adjust the height of the ride height and the sharpness of the reaction to the car's imperfections. road (shock absorber calibration). In short, if marketing is doing its best to make the most of its new process, it is in no way equivalent to the famous Hydractive, whose system is much more advanced and sophisticated. One consists of slightly more complex shock absorbers, while the other offers a whole hydraulic and air device designed to enable the running gear (calibration and body height).
How does it work?
The classic shock absorber (more here) consists of damping the speed of the spring to avoid bouncing at the slightest impact: what a spring does after it has been crushed. Thus, the principle is to reduce the speed of the spring during the compression phase and also to relax (to avoid rebound, since the speed at which it returns to its normal position is significantly reduced), thanks to the two pistons filled with oil. the flow rate from one to the other is limited by the size of the holes (by changing the size of the latter, you can then modulate the flow: this is a controlled damping).
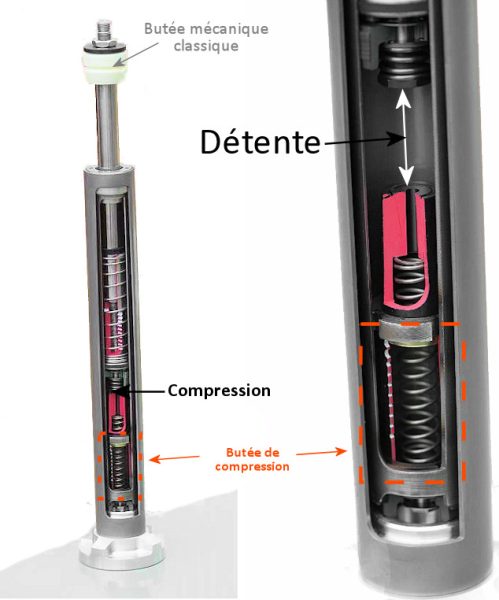
CLASSIC SHOCK ABSORBER:

A COMPRESSION OF THE BUTEE PROTEGE:
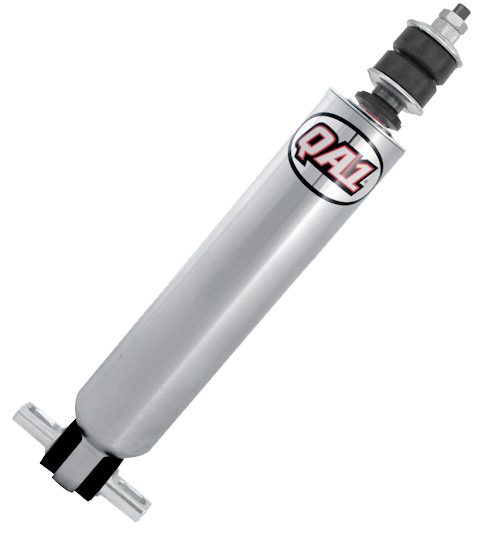

Obviously, there is a limit to travel: when the shock absorber is completely crushed (for example, speed bumps filmed at high speed), we find ourselves at a stop. On "conventional" shock absorbers, this stopper is placed on the pusher. In this case, it acts like a small spring, except that it is made of a kind of rubber (polyurethane).
When this happens, the travel of the shock absorbers and therefore the wheels stops, causing shock and discomfort to passengers. The rubber reacts quite simply by sending the wheel the other way (hence the trigger side), which then causes a slight rebound effect. In short, the car, crushed by the suspension, bounces on a rubber stop. This rebound becomes synonymous with discomfort and possibly loss of control of the vehicle.

The C4 Picasso 2 is one of the first models to feature the Citroën Advanced Confort damping system.
To improve the situation, Citroën has fitted its shock absorbers with two internal hydraulic stops. Therefore, these stops are not visible from the outside, as with conventional polyurethane.
When you reach the stop, that is, when you reach the limits of the possible wheel travel, the compression stop takes effect. The principle of its operation is the same as that of the shock absorber itself: we are talking about slowing down the movement due to playing with oil, or, rather, about the speed of oil passage from one compartment to another.
Thus, the stop will damp the travel more smoothly than the rubber, and above all, it will prevent the rebound effect! Indeed, these specific stops do not try to send everything back (like a spring) when they are compressed, but the polyurethane stop, on the contrary, does.
CITROËN ADVANCE COMFORT SHOCK ABSORBER
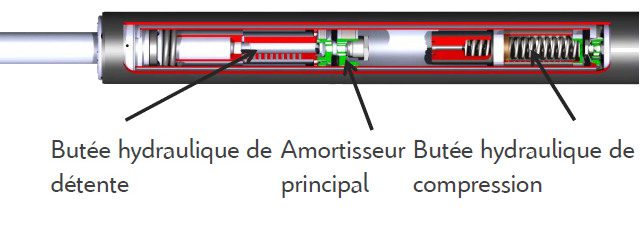
The classic rubber stopper is still present, but its size has been reduced (see the chapter on advantages and disadvantages below)
And if the systems available in competition (see here, for example) include (typically) only a hydraulic compression stop, Citroën added a second rebound stop (when the suspension returns to its normal position when the wheel returns to the down position.). to make the end of the rebound more progressive: the goal is to prevent the shock absorber pistons from hitting each other after reaching maximum travel (because if there is a limit of compression travel, it is also on rebound, the wheel should remain attached to the car even if this link is made not only by the shock absorber).

The oil passes through the holes of the hydraulic stops, so the principle is the same as for the shock absorber: movement is slowed down due to the time it takes for the fluid to move from one container to another (not through the rubber).

To summarize and simplify, this is a shock absorber that works in a classic way when road bumps are limited. Thus, the difference arises mainly when we reach the limits of compression and relaxation, in which case “smart” feet start to work. These two additional stops are small shock absorbers replacing the base rubber, so we can see the Citroën Advanced Comfort damping as a set of shock absorbers: one large and two small ones at the ends (in the stops), which only act in cases of extreme compression and relaxation.
Advantages and disadvantages ?

Unlike rubbers, these feet do not react harshly, so there is a benefit in comfort and behavior in borderline situations: because you have to ride very hard to engage the feet.
In addition, the reaction of these stops also depends on the compression / expansion rate, which is not accounted for by conventional polyurethane stops (which therefore will react the same regardless of the arrival speed of the lower piston of the shock absorber.). Their way of working is more subtle and complex, which allows them to maintain good stability even when driving fast on very uneven roads (which is often found in rural areas). But again, for implementation, you have to really beat. And then, if the dampers and springs are set too flexible, the car will not have very interesting dynamic driving performance despite using these progressive bumpers.

One advantage is cost containment too: this type of shock would be ten times cheaper than controlled damping, which requires a whole electromechanical gearbox, so it will be present on most models, not just the highest. ... However, you won't be able to change the damping setting, so here it is passive and fixed ... So the steering suspension is more advanced because it also allows the computer to control it (several adjustments per second possible) in order. to improve behavior.
In addition, even if it is cheaper than adjustable damping, it will logically remain more expensive than conventional dampers ... But given the group's significant sales potential, economies of scale should close the gap.
Finally, these progressive stops allowed for a smaller rubber stop, which in turn allowed for more clearance. This allows for a slight improvement in damping comfort as we leave more amplitude for wheel deflection.
Citroen sheets
All comments and reactions
Dernier comment posted:
Artist (Date: 2020, 08:20:11)
Since the main function of the suspension springs (or air cylinder) is to absorb shock by compression (of course, the bump should be softened if the compression is too much), and the function of the shock absorbers is to slow down the vibration of the suspension, shouldn't the shock absorbers only brake the tension of the suspension springs? Argument: Compression braking is tantamount to "hardening" the suspension, since the spring does not absorb the impact energy as efficiently as possible. The lack of compression braking undoubtedly leads to a greater displacement of the body compared to the wheel, but if you give preference to comfort ...
Il I. 2 reaction (s) to this comment:
- Administrator SITE ADMINISTRATOR (2020-08-21 08:50:13): A priori, "leaving compression alone" by removing damping from it is likely to cause too many jolts at the final stop. If we slow down the relaxation, but not the contraction, we run the risk of stalling if we associate too many flaws in a row.
The spring itself is also not ideal if you want to achieve proper handling. A single spring (in a relaxed or compressed state) is a little "wild", it must be accompanied by a shock absorber in order to have more subtle and subtle reactions.
Without a compression brake, we will also have a more compressed spring, and therefore have more energy to release, then relaxation will be more intense despite the shock absorber.
However, it is true that I would like to feel and see what relaxation-limited shock absorbers do.
- papun (2021-01-31 19:16:31): Привет,
The opinion of a former mechanic at Alfa Romeo, Ferrari, Jaguar for 10 years and Citroen for 10 years.
Your shock will simply snap into place when relaxing if it is no longer controlled or controlled by the passage of fluid in its designated holes, resulting in a rear click when exiting the rear à ¢, which means the shock is defective. good afternoon papun
(Your post will be visible under the comment after verification)
Write a comment
Do you think PSA succeeded in taking over the Fiat group?

