Mazda MZR LF engine
Content
- Dynamic characteristics of the Mazda LF engine in the diagram
- Specifications of the Mazda LF engine
- Camshaft specifications
- Characteristics of the timing gear drive sprocket
- Types of connecting rod bearing shells
- Drive belt specifications
- Piston characteristics
- Valve characteristics
- Valve lifter specifications
- Characteristics of the oil pump drive sprocket
- Characteristics of the timing chain drive
- Functions of engine elements
- Specifications of the lubrication system
- Recommended engine oil to use
- What cars use the engine
- Engine user reviews
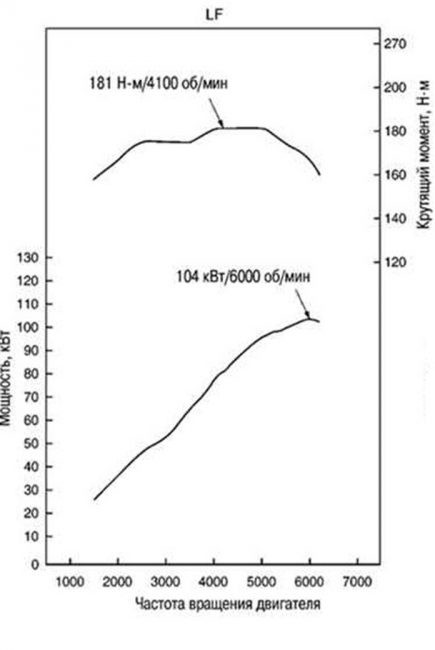
LF class engines are modern new generation units with improved dynamics and repairability. The device has a working volume of 1,8 liters, maximum power - 104 kW (141 hp), maximum torque - 181 Nm / 4100 min-1. The engine allows you to develop a maximum speed of 208 km / h.
Dynamic characteristics of the Mazda LF engine in the diagram
The motors can be supplemented with S-VT turbochargers - Sequential Valve Timing. The turbocharger operates on the principle of operating on the energy of the burnt exhaust gas. Its design includes two axial paddle wheels, which are spun with the help of hot gas entering the part body. The first wheel, working, spins at a speed of 100 minutes -1. With the help of the shaft, the second wheel of the blade is also untwisted, which pumps air into the compressor. Hot air thus enters the combustion chamber, after which it is cooled by an air radiator. Thanks to these processes, a huge increase in engine power is provided.
Mazda produced engines of this series from 2007 to 2012, and during this time it managed to make many technical improvements, both in the design of the unit and in its technical elements. Some engines received new mechanisms for the operation of the gas distribution phases. The new models were equipped with aluminum cylinder blocks. This was done in order to reduce the overall car weight.
Specifications of the Mazda LF engine
| Element | Parameters |
|---|---|
| Type | Petrol, four-stroke |
| Number and arrangement of cylinders | Four-cylinder, in-line |
| The combustion chamber | Wedge |
| Gas distribution mechanism | DOHC (double overhead camshafts in the cylinder head, chain driven, 16-valve) |
| Working volume, ml | 1.999 |
| Cylinder diameter per piston stroke, mm | X 87,5 83,1 |
| Compression ratio | 1,720 (300) |
| Valve opening and closing moment: | |
| inlet | |
| opening before TDC | 4 |
| closing after BMT | 52 |
| high school graduation | |
| opening to BMT | 37 |
| closing after TDC | 4 |
| Valve clearance, mm: | |
| inlet | 0,22-0,28 (on a cold engine) |
| graduations | 0,27-0,33 (on a cold engine) |
Types of liners of main bearings, mm:
| Element | Parameter |
|---|---|
| Outside diameter, mm | 87,465-87,495 |
| Axis displacement, mm | 0.8 |
| Distance from the bottom of the piston to the axis of the piston pin HC, mm | 28.5 |
| Piston height HD | 51 |
The mechanics of the engines also underwent changes, as new ways were developed to rid the vehicles of excessive noise and vibration. For this, the drives of the gas distribution mechanisms in the engines were equipped with silent chains.
Camshaft specifications
| Element | Parameter |
|---|---|
| Outside diameter, mm | Approximately 47 |
| Tooth width, mm | Approximately 6 |
Characteristics of the timing gear drive sprocket
| Element | Parameter |
|---|---|
| Outside diameter, mm | Approximately 47 |
| Tooth width, mm | Approximately 7 |
The cylinder blocks were supplied with a long piston skirt, as well as an integrated type main bearing cap. All engines had a crankshaft pulley with a torsional vibration damper, as well as a pendulum suspension.
Types of connecting rod bearing shells
| Bearing size | Liner thickness |
|---|---|
| Standard | 1,496-1,502 |
| 0,50 oversize | 1,748-1,754 |
| 0,25 oversize | 1,623-1,629 |
The contours of the accessory drive belts have been simplified as much as possible to improve the maintainability of the motors. All engine accessories are now equipped with a single drive belt that automatically adjusts the tension level.
Drive belt specifications
| Element | Parameter |
|---|---|
| Belt length, mm | Approx 2,255 (Approx 2,160) |
| Belt width, mm | About 20,5 |
The front of the engine is equipped with a cover with a hole to improve maintenance. This makes it easier to unlock the chain adjustment ratchet and idler arm lock. The four cylinders of the engine are arranged in one rad. From below, the unit is covered by a pallet, which forms a crankcase. At the same time, this part is a container where the oil is located, with the help of which the complex of engine parts is lubricated, protected and cooled, thus protecting it from wear.
Piston characteristics
| Element | Parameters |
|---|---|
| Outside diameter, mm | 87,465-87,495 |
| Axis displacement, mm | 0.8 |
| Distance from the bottom of the piston to the axis of the piston pins NS, mm | 28.5 |
| Piston height HD, mm | 51 |
The apparatus has sixteen valves. There are four valves per cylinder.
Valve characteristics
| Elements | Parameters |
|---|---|
| Valve length, mm: | |
| inlet valve | about 101,6 |
| Exhaust valve | about 102,6 |
| Diameter of a plate of the inlet valve, mm | About 35,0 |
| Exhaust valve plate diameter, mm | About 30,0 |
| Rod diameter, mm: | |
| inlet valve | about 5,5 |
| Exhaust valve | about 5,5 |
Valve lifter specifications
| Marking | Pusher thickness, mm | Step, mm |
|---|---|---|
| 725-625 | 3,725-3,625 | 0.025 |
| 602-122 | 3,602-3,122 | 0.02 |
| 100-000 | 3,100-3,000 | 0.025 |
Overhead camshafts help the valves to be actuated through special tappets. The engine is lubricated by an oil pump, which is mounted on the end side of the crankcase. The pump works with the help of the crankshaft, which is its drive. The oil is sucked out of the oil pan, passing through various channels, and entering the crankshaft and distribution type shafts, as well as the working surface of the cylinders.
Characteristics of the oil pump drive sprocket
| Element | Parameters |
|---|---|
| Outside diameter, mm | About 47,955 |
| Tooth width, mm | About 6,15 |
Characteristics of the timing chain drive
| Element | Parameters |
|---|---|
| Step, mm | 8 |
| Tooth width, mm | 134 |
The fuel-air mixture is supplied to the engine by an electronic control system, which is automated and does not require mechanical control.
Functions of engine elements
| The actuator for changing the valve timing | Continuously modifies the phases of the exhaust camshaft and crankshaft at the forward end of the intake camshaft using hydraulic pressure from the oil control valve (OCV) |
| Oil Control Valve (OCV) | It is controlled by a current signal from the PCM. Switches the hydraulic oil channels of the variable valve timing actuator |
| Crankshaft position sensor | Sends engine speed signal to PCM |
| Camshaft position sensor | Provides a cylinder identification signal to the PCM |
| Block RSM | Operates the oil control valve (OSV) to provide optimum torque according to engine operating conditions |
Specifications of the lubrication system
| Elements | Parameters |
|---|---|
| Lubrication system | With forced circulation |
| Oil cooler | water cooled |
| Oil pressure, kPa (min -1) | 234-521 (3000) |
| Oil pump | |
| Type | With trachiodal engagement |
| Unloading pressure, kPa | 500-600 |
| The oil filter | |
| Type | Full flow with paper filter element |
| Flow pressure, kPa | 80-120 |
| Filling capacity (approx.) | |
| Total (dry engine), l | 4.6 |
| With oil change, l | 3.9 |
| With oil and filter change, l | 4.3 |
Recommended engine oil to use
| Class | SJ API ACEA A1 or A3 | SL API ILSAC GF-3 | API SG, SH, SJ, SL ILSAC GF-2, GF-3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Viscosity (SAE) | 5W-30 | 5W-20 | 40, 30, 20, 20W-20, 10W-30, 10W-40, 10W-50, 20W-40, 15W-40, 20W-50, 15W-50, 5W-20, 5W-30 |
| Note | Mazda genuine DEXELIA oil | - | - |
What cars use the engine
Mazda LF class engines (including DE, VE and VD modifications) were used in the following vehicles:
- Ford C-Max, 2007-2010;
- Ford Eco Sport, 2004-…;
- Ford Fiesta ST, 2004-2008;
- Ford Focus, 2004-2015;
- Ford Mondeo, 2000-2007;
- Ford Transit Connect, 2010-2012;
- Mazda 3 and Mazda Axela, 2004-2005;
- Mazda 6 for Europe, 2002-2008;
- Mazda 5 and Mazda Premacy, 2006-2007;
- Mazda MX-5, 2006-2010;
- Volvo C30, 2006-2010;
- Volvo S40, 2007-2010;
- Volvo V50, 2007-2010;
- Volvo V70, 2008-2010;
- Volvo S80, 2007-2010;
- Besturn B70, 2006-2012.
Engine user reviews
Viktor Fedorovich, 57 years old, Mazda 3, LF engine: drove a used Mazda of a sports plan. The car has covered over 170 kilometers. I had to replace the oil supply system + fix the block in the service station. The motor is perfectly repairable. In general, I am satisfied with everything, the main thing is to use only the best oil and fuel.

