
Toyota F, 2F, 3F, 3F-E engines
Content
The first Toyota F-series engine was developed in December 1948. Serial production began in November 1949. The power unit was produced for forty-three years, and is one of the leaders in terms of production duration among power units.
The history of the creation of the Toyota F ICE
The engine was developed in December 1948. It was a modified version of the earlier Type B engine. The power plant was first installed on a 1949 Toyota BM truck. With this version of the engine, the car was called Toyota FM. The trucks were originally delivered to Brazil. Then the motor began to be installed on various light commercial vehicles, fire engines, ambulances, police patrol cars.
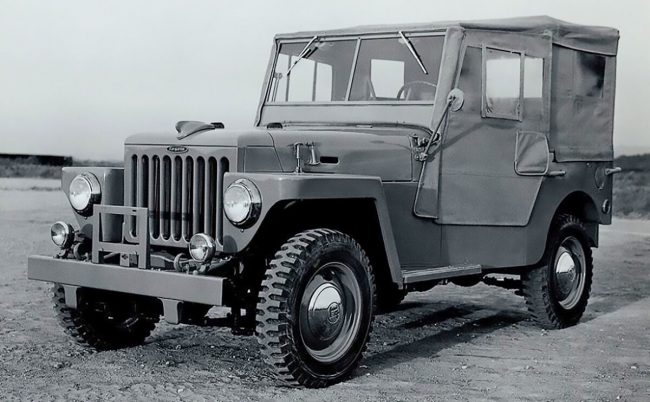
On August 1, 1950, Toyota Corporation launched the Toyota Jeep BJ SUV, the progenitor of the legendary Toyota Land Cruiser.

The car received the name Land Cruiser in 1955, and under this name it began to be exported to other countries. The first export cars were equipped with F-series engines, which made them popular.
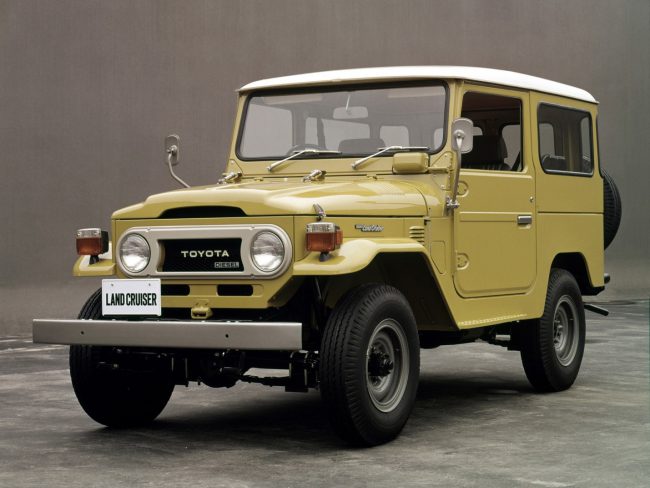

The second version of the engine, called 2F, was introduced in 1975. The third modernization of the power plant was made in 1985 and was called 3F. In 1988, deliveries of Land Cruisers with such an engine began in the United States. Later, the 3F-E version with an injector appeared. F-series engines existed on the assembly line until 1992. Then their production was completely discontinued.
Design features of F engines
The Toyota Jeep BJ was designed according to the patterns of military off-road vehicles. This car was designed to overcome off-road and was not very suitable for driving on asphalt. The F engine was also suitable. In fact, it is a low-speed, low-speed, large-displacement engine for moving goods and driving in difficult road conditions, as well as in areas where there are no roads as such.
The cylinder block and cylinder head are made of cast iron. Six cylinders are arranged in a row. The power system is carburetor. The ignition system is mechanical, with a breaker-distributor.
The OHV scheme is applied when the valves are located in the cylinder head, and the camshaft is located at the bottom of the block, parallel to the crankshaft. The valve is opened with pushers. Camshaft drive - gear. Such a scheme is very reliable, but consists of many massive parts that have a large moment of inertia. Because of this, lower engines do not like high speeds.
Compared to its predecessor, the lubrication system has been improved, lightweight pistons have been installed. The working volume is 3,9 liters. The compression ratio of the engine was 6,8:1. Power varied from 105 to 125 hp, and depended on which country the car was exported to. The maximum torque ranged from 261 to 289 N.m. at 2000 rpm
Structurally, the cylinder block repeats the licensed American-made engine GMC L6 OHV 235, taken as a basis. The cylinder head and combustion chambers are borrowed from the Chevrolet L6 OHV engine, but adapted to the larger displacement. The main components of Toyota F engines are not interchangeable with American counterparts. The calculation was made that car owners will be satisfied with the reliability and unpretentiousness of engines made on the basis of time-tested American analogues that have proven themselves from the best side.
In 1985, the second version of the 2F engine was released. The working volume was increased to 4,2 liters. The changes affected the piston group, one oil scraper ring was removed. The lubrication system has undergone modernization, the oil filter has been installed in front of the engine. Power increased to 140 hp. at 3600 rpm.
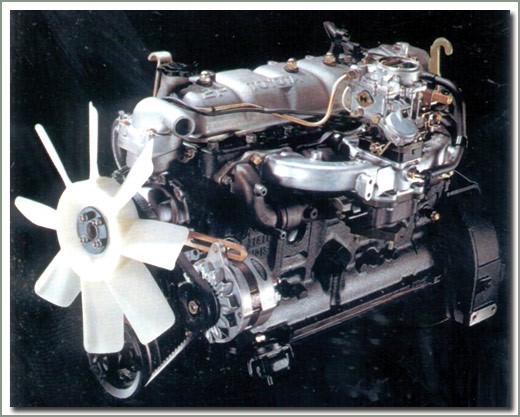
3F was introduced in 1985. Initially, the engines were installed on right-hand drive Land Cruisers for the domestic market, then cars with such engines began to be exported to many countries. Have been modified:
- cylinder block;
- cylinder head;
- intake tract;
- exhaust system.
The camshaft was moved to the cylinder head, the engine became overhead. The drive was carried out by a chain. Subsequently, on the 3F-E version, instead of a carburetor, distributed electronic fuel injection began to be used, which made it possible to increase power and reduce exhaust emissions. The working volume of the engine decreased from 4,2 to 4 liters, due to a shortened piston stroke. Engine power has increased by 15 kW (20 hp) and torque has increased by 14 N.m. As a result of these changes, the maximum rpm is higher, making the engine more suitable for road travel.

Technical specifications
The table shows some of the technical specifications of the F-series engines:
| Engine | F | 2F | 3F-E |
|---|---|---|---|
| Supply system | Carburetor | Carburetor | Distributed Injection |
| Number of cylinders | 6 | 6 | 6 |
| Number of valves per cylinder | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| Compression ratio | 6,8:1 | 7,8:1 | 8,1:1 |
| Working volume, cm3 | 3878 | 4230 | 3955 |
| Power, hp / rpm | TBU | 135/3600 | 155/4200 |
| Torque, N.m / rpm | TBU | 289/2000 | 303/2200 |
| Fuel | A 92 | A 92 | A 92 |
| Resource | 500+ | 500+ | 500+ |
Torque and power varied depending on the country the cars were exported to.
Advantages and disadvantages of motors F
The F-series engines laid the foundation for Toyota's reputation for rugged, reliable powertrains. The F engine is able to pull several tons of cargo, tow a heavy trailer, ideal for off-road. High torque at low revs, low compression make it an unpretentious, omnivorous motor. Although the instructions recommend using A-92 fuel, the internal combustion engine is able to digest any gasoline. Motor advantages:
- simplicity of design;
- reliability and high maintainability;
- insensitivity to stress;
- long resource.
Motors calmly nurse half a million kilometers before overhaul, even if they are operated in difficult conditions. It is important to observe service intervals and fill the engine with high-quality oil.
The biggest drawback of these engines is high fuel consumption. 25 - 30 liters of gasoline per 100 km for these engines is not the limit. Engines, due to low speed, are poorly adapted to movement at high speeds. This applies to a lesser extent to the 3F-E motor, which has slightly higher maximum power and torque revolutions.
Tuning options, contract engines.
It is doubtful that it would occur to anyone to turn a truck engine into a high-speed sports engine. But you can increase the power by applying a turbocharger. Low compression ratio, durable materials allow you to install a turbocharger without interfering with the piston group. But in the end, in any case, significant alterations will be required.
F-series engines have not been produced for almost 30 years, so it is difficult to find a contract engine in good condition. But there are offers, the price starts from 60 thousand rubles.

