
Toyota Rush engines
Content
Toyota Rush is the same Daihatsu Terios, but with additional features and an updated engine. The compact class SUVs differ only in emblems and are sold by both Japanese automakers.
First generation (J200/F700; 2006-2008)
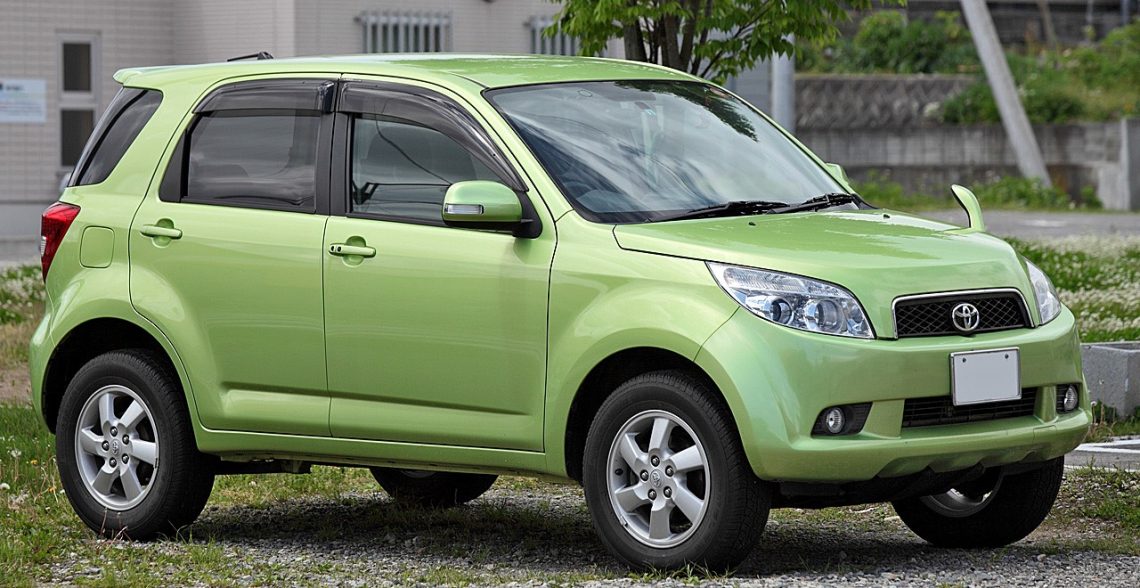
In early 2006, Toyota released its first compact crossover Rush with a body on a powerful semi-frame. In the Japanese market, this model replaced the first generation Terios. In fact, the car was a slightly improved version of the Daihatsu Terios.
The 3SZ-VE gasoline engine was offered as a power unit in Rush. The engine is in-line, 4-cylinder, with two camshafts, a 16-valve gas distribution mechanism and a DVVT system.

With a working volume of 1495 cm3, the 3SZ-VE power unit is capable of developing a maximum of 109 hp. power. The maximum torque of the unit is 141 Nm at 4400 rpm. The motor provides sufficient traction, while remaining quite dynamic. Fuel consumption on average varies from 7.2 to 8.1 liters per hundred kilometers.
In November 2008, a minor Rush update was made for Japan that resulted in a 5% improvement in fuel efficiency (for the automatic 2WD model).
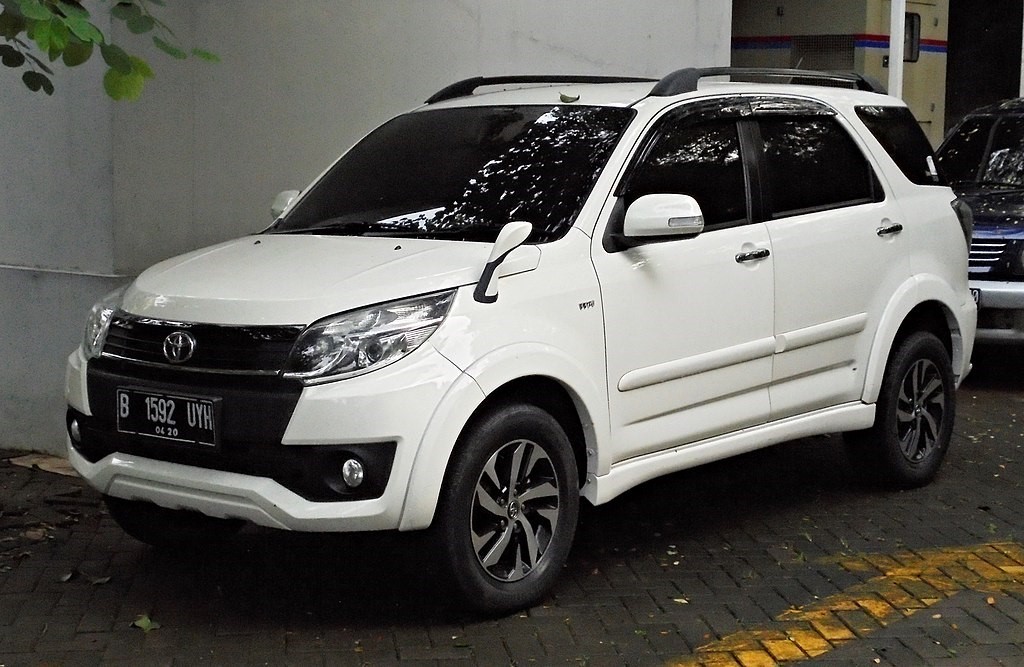

In the fall of 2008, sales of the Daihatsu Be-Go twin, a restyled version of Toyota Rush, produced under an OEM agreement, began on the Japanese market. The power plant of the car remained the same.
In April 2015, Toyota introduced the second facelift of the Rush to the Indonesian market. Exterior changes included a redesigned front bumper, grille and hood. The bumper is trimmed with a two-tone effect, while the grille is trimmed with faux carbon fiber. The engine was left "native Daihatsovsky", cast iron, chain, longitudinal.
3NW-NE
The 3SZ-VE unit belongs to the category of short-stroke internal combustion engines. It differs from other "Toyota" engines of the "third wave" with a cast-iron cylinder block and the presence of pressed valve seats. The gas distribution mechanism is driven by a Morse chain.
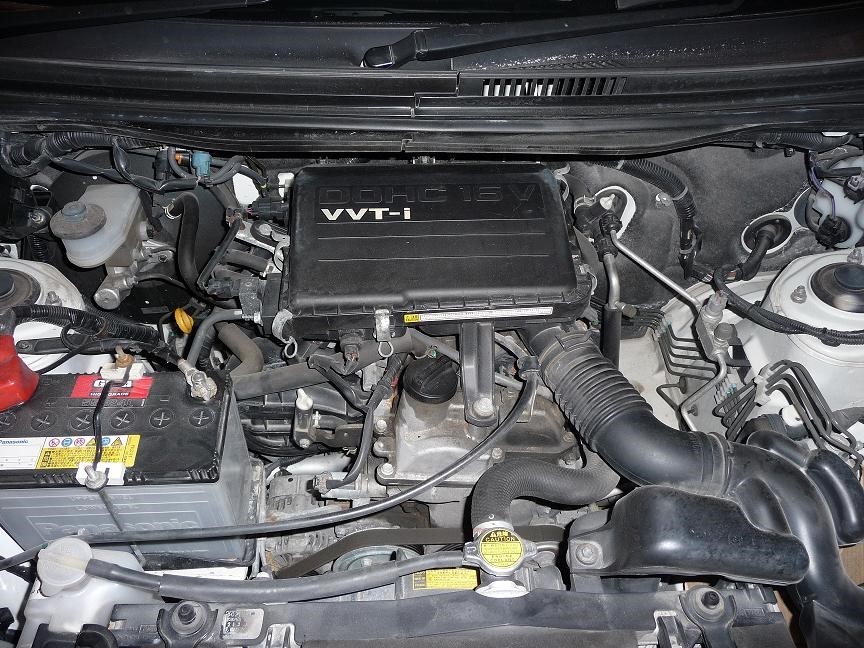

Powertrains in the Rush J200
| Mark | Max power, hp/r/min | Type | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cylinder Ø, mm | Compression ratio | HP, mm | |||
| 3SZ-VE 1.5 | 109/6000 | Inline, 4-cylinder | 72 | 10 | 91.8 |
Second generation (F800; 2017-present)
The second generation of Rush was introduced at the same time as Terios 3 in the fall of 2017. The second crossover was based on a frame body structure. The novelty, unlike its predecessor, is equipped only with rear-wheel drive.
Under the hood of the second generation Rush, a new 4-cylinder 1.5-liter power unit is installed - 2NR-VE (105 hp, 140 Nm), capable of being paired with a 5-speed manual or 4-speed automatic gearboxes. The maximum torque of the motor is 136 Nm at 4200 rpm.
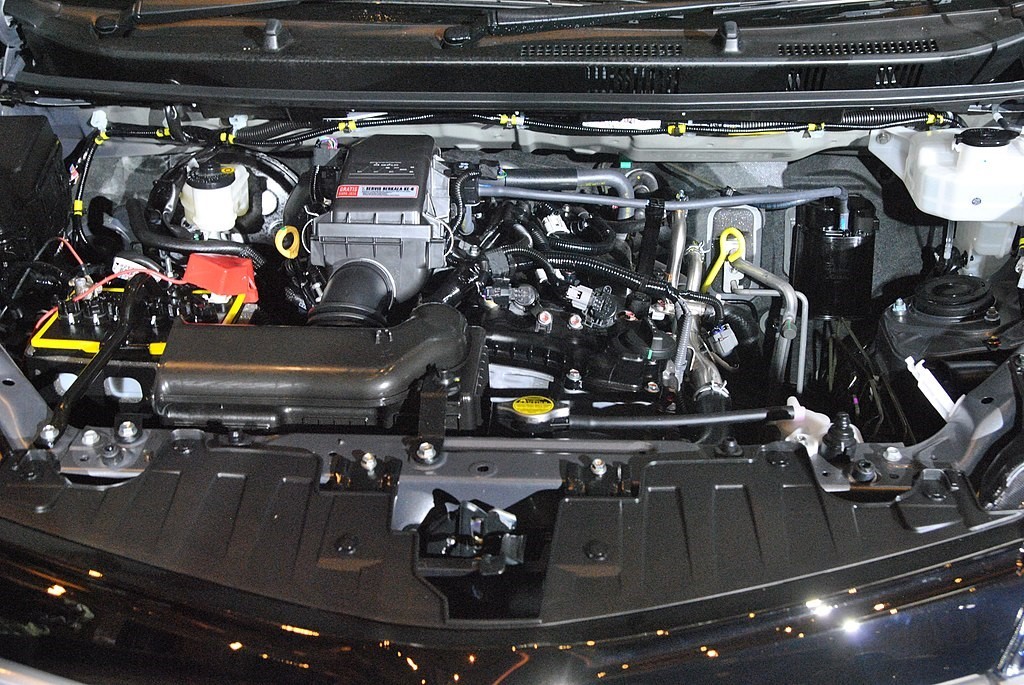
2NR-VE
Initially, the new 2NR-VE engine for the second generation Rush was created by Daihatsu for the 1.5-liter Toyota Avanza models. The 2NR-VE cylinder block still uses high strength steel like its predecessor, the 3SZ-VE engine, and is positioned longitudinally.
2NR-VE is available in two modifications ("sharpened" for environmental standards EURO-3 or EURO-4/5), which differ in the degree of compression. Both versions of the unit are equipped with Dual VVT-i systems.
Powertrains in the Rush F800
| Mark | Max power, hp/r/min | Type | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cylinder Ø, mm | Compression ratio | HP, mm | |||
| 2NR-VE 1.5 | 104/6000 | Inline, 4-cylinder | 72.5 | 10.5-11.5 | 90.6 |
Typical malfunctions of Toyota Rush engines
3NW-NE
For the 3SZ-VE engine, the presence of a cast-iron BC and the preservation of the traditional design determined the ease of operation, making the unit quite reliable. 3SZ-VE is quite repairable.
Unlike fuel quality, the 3SZ-VE engine is very demanding on oil characteristics. Also, when the timing tensioner is loosened, the chain jumps and the valves inevitably hit the pistons. It is important to change the timing chain kit in time.
Another disadvantage of the 3SZ-VE is the accessory drive belt, which wears out quickly and is quite expensive.
2NR-VE
The NR series powerplants use an aluminum engine block and a DOHC head, under which there are 4 valves per cylinder. The units also use distributed or direct fuel injection. The 2NR engine is equipped with a DVVT-i system (when both intake and exhaust valves are controlled).
Specifically, for the 2NR-VE power unit, which is too new today, one can only say that, for obvious reasons, there are no malfunction statistics for it. On the forums, if they complain, it is only about the fragility of the ignition coil and pump, as well as the noisy operation of the unit and excess oil consumption. How much all this corresponds to the truth and how it affects the engine life of the installation, only time will tell.
Conclusion
Offered as a power plant for the first Toyota Rush, the 3SZ-VE gasoline engine is quite reliable in operation. Maintenance is inexpensive, oils are common. Spare parts, consumables, both in price and in assortment - there are no problems. Judging by the numerous reviews, the motor resource of this unit is quite at the level and amounts to up to 300 thousand km.

According to information provided by the Japanese automaker Toyota, the new 2NR-VE gasoline engine, which replaced the 3SZ-VE, is noticeably lower in fuel consumption, by an average of 15-20%. Consumption - 5.1-6.1 liters per 100 km. In power, this atmospheric unit also lost, albeit quite a bit.

