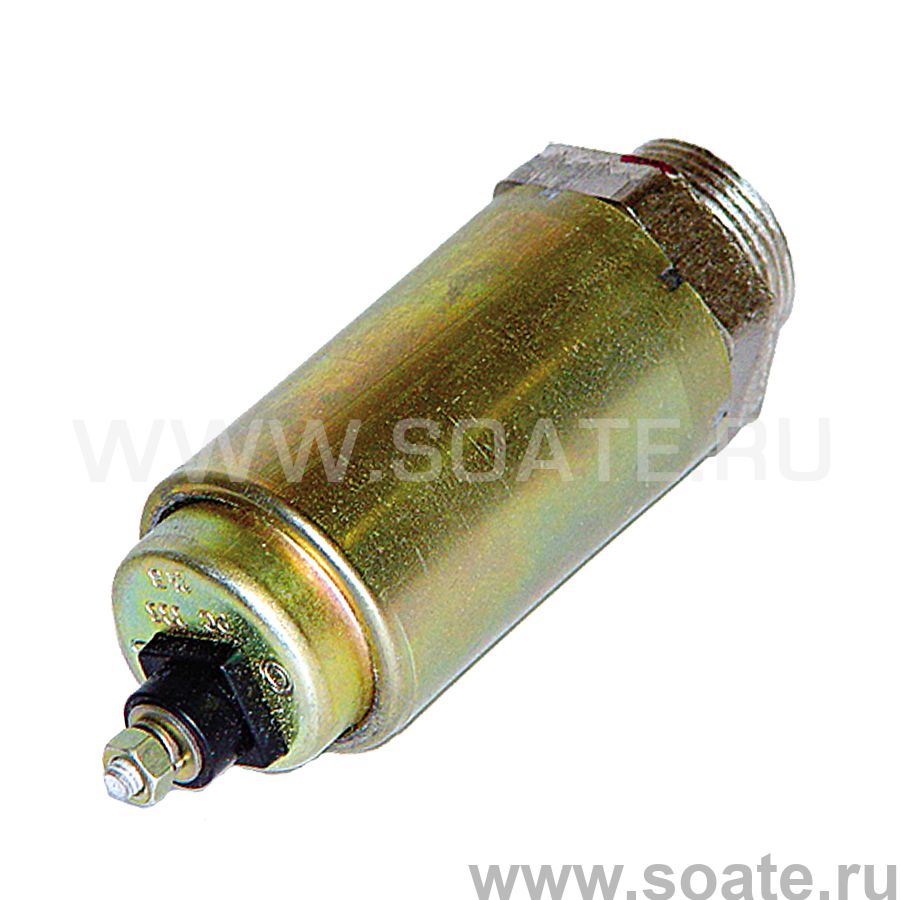
Electromagnet under the hood
The title of this article refers to small and seemingly inconspicuous elements in the electrical circuit of automobiles, called electrical relays. Their main task is to ensure the correct supply of electricity from the battery to the receiver, thanks to which not only the turn signals, dipped, high and fog lights function, but also the power windows and central locking.
With movable armature
The principle of operation of electrical relays used in automobiles can be compared with a well-known electromagnet, for example, from physics lessons. In practice, it looks like this: after turning on the receiving device, current begins to flow through the relay winding. In turn, the magnetic field thus created in its ferromagnetic core attracts a special movable plate, professionally referred to as an anchor. The latter has a contact, which, together with the plate, is attracted to the second (fixed) contact. When both contacts are closed, current can flow from the battery to the receiver. However, when the receiving device is turned off, the current through the electromagnet winding stops flowing. As a result, the movable armature is pulled back by the spring and the contacts open.
Thin instead of thick
When getting acquainted with the principle of operation of electrical relays, it is worth asking about their practical application. It is important to know that it is thanks to these subtle elements that thin electrical wires can be used to conduct electricity, including high currents. It is easy to imagine that if we excluded electrical relays, then we would have to use thick cables, i.e. professionally speaking: with a large section. In addition, in many cases this would have to be done at a relatively large distance, on the line battery - receiver switch - fuse box - receiver. In addition, the distance between a particular button and the receiver will also be an additional difficulty. The latter, which, of course, the vast majority of car users do not know about, in some cases even reaches several meters. Thick bundles of electrical wires would take up so much space that it would be difficult to place them, for example, under the hood (in modern cars this space is already almost completely filled). Another problem will be the high cost of producing such cables.
in three ways
What electrical relays are used in cars? In general, they can be divided into three types. Most often we meet relays with the so-called. open contacts. The name of the latter comes from the principle of their action, which boils down to connecting contacts when current flows through the winding of an electromagnet. Relays can be found, among other things, in the circuits of all types of lights (high beam, low beam and fog), as well as for turning on the horn and heating the rear window (optionally also the windshield). The second type of electrical relay, the so-called closed contacts, is used in alarm and immobilizer installations. Unlike their open counterparts, opening them and activating a specific receiver causes current to flow. In turn, relays of the third type are installed in the circuits of the central lock or power windows. They are neither "open" nor "closed". These relays have fixed upper and lower contacts, and a jumper moving between them is responsible for changing the voltage supplied to the receiver.
Beware of… short circuits!
Compared to many other automotive components, electrical relays are relatively reliable devices. However, in some cases they are also damaged. What are the most common causes of relay failure? They can be damaged both mechanically, for example, after various kinds of shocks (road collisions, etc.), and electrically (short circuits on a certain battery-receiver line). A damaged electrical relay must be replaced immediately. However, there is good news: this activity should not present any particular difficulties. However, be careful! When replacing, be sure to replace the damaged relay with one of the same type, in other words: open-open, closed-closed, and fixed. However, it is much more important to pay attention to the fact that the so-called. Plug-in legs of relays of different types can have the same location and in this case fit into different sockets. As a result, we can easily insert the relay into the socket, but after turning on the power, a very unpleasant surprise awaits us in the form of ... a short circuit in the electrical installation of a particular receiver. The situation is even worse with the so-called. multifunctional devices (including those with a delay switch-off). To avoid unexpected and costly breakdowns, a damaged relay should be replaced by a specialist workshop equipped with specialized diagnostic equipment.