ESP in the car
Very often, happy owners of new and modern cars have a question: what is ESP, what is it for and is it needed? It is worth understanding this in detail, which, in fact, we will do below.
Contrary to popular belief, driving is not always easy. In particular, this statement is relevant for situations where the path of movement is hampered by various external factors, whether it be difficult turns or difficult weather conditions. And many times together. The main danger in these cases is skidding, which can cause difficulties in driving, and in some moments even uncontrolled and unpredictable movement of the car, which can cause an accident. In addition, difficulties can arise both for beginners and for already quite experienced drivers. To solve this problem, a special system is used, abbreviated as ESP.
How to decrypt ESP

ESP system logo
ESP or Electronic Stability Program - this name in the Russian version means the electronic dynamic stabilization system of the car or, in other words, the exchange rate stability system. In other words, ESP is an active safety system component that can control the moment of force of one or even several wheels at the same time using a computer, thereby eliminating lateral movement and leveling the vehicle's position.
Various companies produce similar electronic devices, but the largest and most recognized manufacturer of ESP (and under this brand) is Robert Bosch GmbH.
The abbreviation ESP is the most common and generally accepted for most European and American cars, but not the only one. For different cars on which the exchange rate stability system is installed, their designations may differ, but this does not change the essence and principle of operation.
See also: What is the difference between rear-wheel drive and front-wheel drive and how does this affect the stability of the car.
An example of ESP analogues for some car brands:
- ESC (Electronic Stability Control) — for Hyundai, Kia, Honda;
- DSC (Dynamic Stability Control) — для Rover, Jaguar, BMW;
- DTSC (Dynamic Stability Traction Control) — для Volvo;
- VSA (Vehicle Stability Assist) — for Acura and Honda;
- VSC (Vehicle Stability Control) — для Toyota;
- VDC (Vehicle Dynamic Control) — for Subaru, Nissan and Infiniti.
Surprisingly, ESP gained wide popularity not when it was created, but somewhat later. Yes, and thanks to the scandal of 1997, associated with serious shortcomings, then developed by the Mercedes-Benz A-class. This compact car, for the sake of comfort, received a rather high body, but at the same time a high center of gravity. Because of this, the vehicle had a tendency to roll over violently and was also in danger of tipping over when performing the "reorder" maneuver. The problem was solved by installing a stability control system on compact Mercedes models. This is how ESP got its name.
How the ESP system works

Security Systems
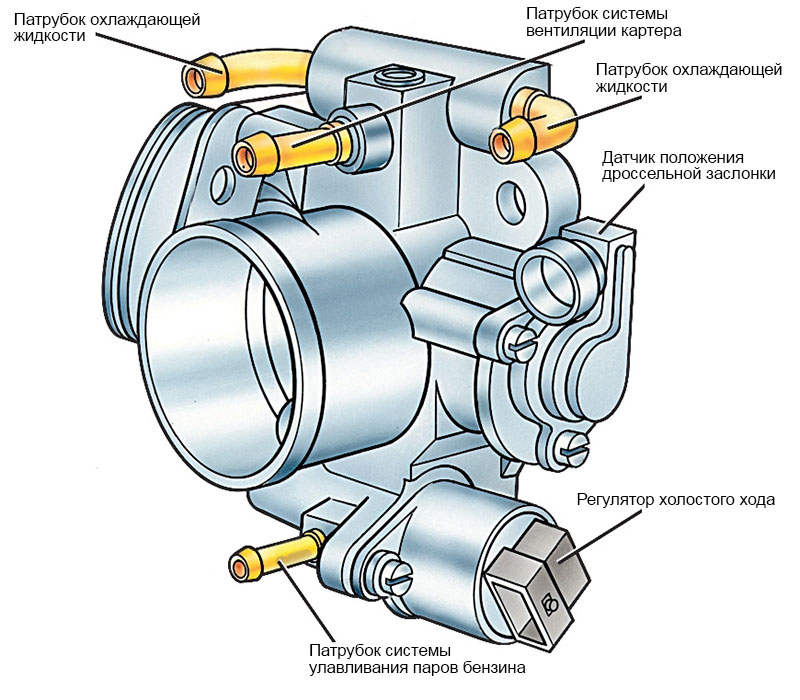
It consists of a special control unit, external measuring devices that control various parameters, and an actuator (valve unit). If we consider the ESP device directly, then it can perform its functions only in combination with other components of the vehicle's active safety system, such as:
- Wheel lock prevention systems during braking (ABS);
- Brake force distribution (EBD) systems;
- Electronic differential lock system (EDS);
- Anti-slip system (ASR).
The purpose of the external sensors is to monitor the measurement of the steering angle, the operation of the brake system, the position of the throttle (in fact, the behavior of the driver behind the wheel) and the driving characteristics of the car. The received data is read and sent to the control unit, which, if necessary, activates the actuator associated with other elements of the active safety system.
In addition, the control unit for the stability control system is connected to the engine and automatic transmission and can affect their operation in emergency situations.
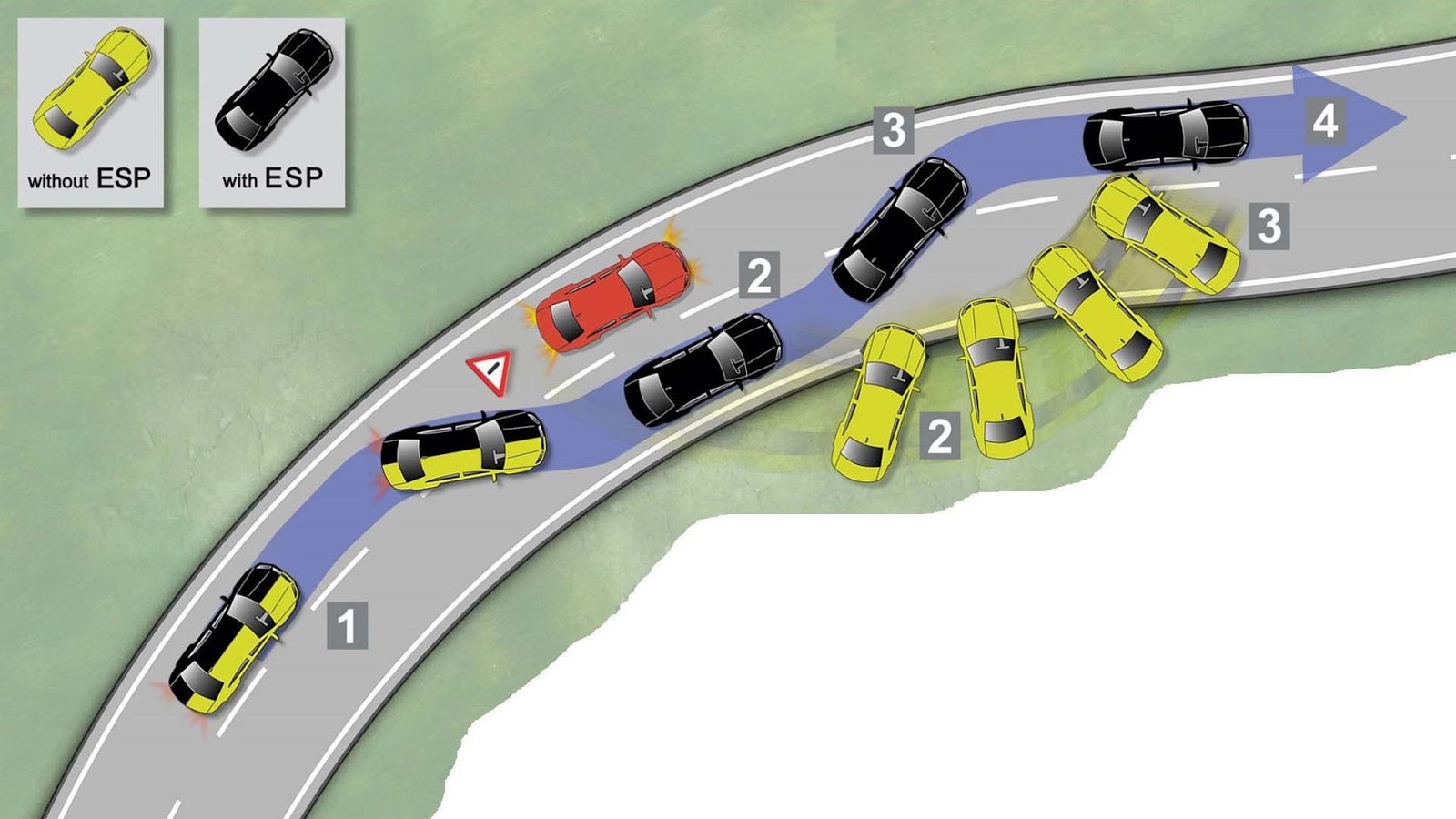
How does ESP work

Vehicle trajectory without ESP

Vehicle trajectory with ESP
The Electronic Stability Program constantly analyzes incoming data about the actions of the driver and compares them with the actual movement of the car. If the ESP thinks the driver is losing control of the car, it will intervene.
Vehicle course correction can be achieved:
- Braking certain wheels;
- Change in engine speed.
Which wheels to brake is determined by the control unit depending on the situation. For example, when the car is skidding, ESP can brake with the outer front wheel and change the engine speed at the same time. The latter is achieved by adjusting the fuel supply.
Drivers' attitude towards ESP

ESP off button
It is not always clear. Many experienced drivers are not satisfied that in some situations, contrary to the desire of the person behind the wheel, pressing the accelerator pedal does not work. ESP cannot assess the driver's qualifications or his desire to "drive the car", his prerogative is to ensure the safe movement of the car in certain situations.
For such drivers, manufacturers usually provide the ability to disable the ESP system; moreover, under certain conditions, it is even recommended to turn it off (for example, on loose soil).
In other cases, this system is really needed. And not just for novice drivers. In winter, it is especially difficult without it. And considering that thanks to the spread of this system, the accident rate has decreased by almost 30%, its “necessity” is beyond doubt. However, we must not forget that no matter how effective such assistance is, it will not provide 100% protection.