FSI engine - what is it? The principle of operation, adjustment and differences from other internal combustion engines
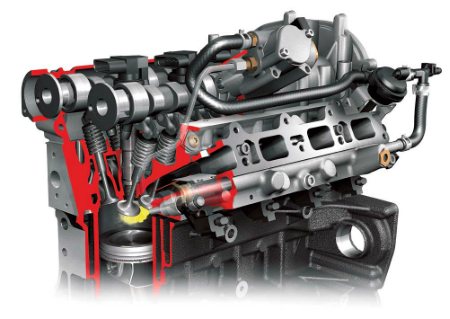
The main difference in the design of FSI power units from other mechanical combustion devices lies in the supply of high-pressure gasoline through the nozzle directly into the combustion chamber.
An automobile engine using FSI technology was developed in the laboratory of the Mitsubishi concern, and today such motors are already installed on many brands of cars from various European, American and Japanese manufacturers. Volkswagen and Audi are rightfully considered leaders in the production of FSI power units, almost all of whose cars are now equipped with these engines. In addition to them, such engines, but in smaller volumes, are installed on their cars: BMW, Ford, Mazda, Infiniti, Hyundai, Mercedes-Benz and General Motors.

The use of FSI engines significantly reduces harmful emissions from cars and reduces fuel consumption by 10-15%.
The main difference from previous designs
An important distinguishing feature of the FSI is the presence of two sequential fuel systems supplying gasoline. The first is a low-pressure constantly circulating fuel return system connecting the gas tank, circulation pump, strainer, control sensor, and gasoline supply pipeline to the second system.
The second circuit supplies fuel to the injector for atomization and supply to the cylinders for combustion and, as a result, mechanical work.
The principle of operation of the contours
The task of the first circulation circuit is to supply fuel to the second one. It provides a constant circulation of fuel between the fuel tank and the gasoline injection device, which is installed as a spray nozzle.
Maintaining the constant circulation mode is provided by a pump located in the gas tank. The installed sensor constantly monitors the pressure level in the circuit and transmits this information to the electronic unit, which, if necessary, can change the operation of the pump for a stable supply of gasoline to the second circuit.
The task of the second circuit is to ensure the supply of the required amount of atomized fuel into the combustion chambers of the engine.
To do this, it includes:
- a plunger-type feed pump to create the necessary fuel pressure when it is supplied to the nozzle;
- a regulator installed in the pump to ensure metered fuel supply;
- pressure change control sensor;
- nozzle for spraying gasoline during injection;
- distribution ramp;
- safety valve, to protect the elements of the system.
Coordination of the work of all elements is provided by a special electronic control device through actuators. To obtain a high-quality combustible mixture, an air flow meter, an air flow regulator and air damper control drives are installed. The control electronic devices provide the ratio of the amount of atomized fuel and the air required for its combustion, specified by the program.
By the way, on our vodi.su portal, there is an article from which you will learn how to use the quick engine start.
Adjustment principle
In the operation of the FSI engine, there are three modes of formation of a combustible mixture, depending on the load on the engine:
- homogeneous stoichiometric, designed for the operation of the power unit at high speeds and heavy loads;
- homogeneous homogeneous, for motor operation in medium modes;
- layered, for engine operation at medium and low speeds.

In the first case, the position of the throttle air damper is determined depending on the position of the accelerator, the intake dampers are fully open, and fuel injection occurs at each engine stroke. The coefficient of excess air for fuel combustion is equal to one and the most efficient combustion is achieved in this mode of operation.
At medium engine speeds, the throttle valve opens fully and the intake valves are closed, as a result, the excess air ratio is maintained at 1,5 and up to 25% of exhaust gases can be mixed into the fuel mixture for efficient operation.
In stratified carburetion, the intake flaps are closed, and the throttle valve is closed and opened depending on the load on the engine. The coefficient of excess air is in the range from 1,5 to 3,0. The remaining excess air in this case plays the role of an effective heat insulator.
As you can see, the principle of operation of the FSI engine is based on changing the amount of air supplied for the preparation of a combustible mixture, provided that fuel is directly supplied to the combustion chamber through a spray nozzle. The fuel and air supply is controlled by sensors, actuators and an electronic engine control unit.
Loading…