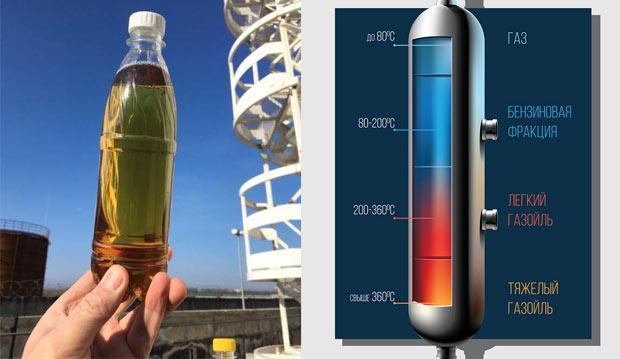
Gasoil. What is this fuel?
Content
Gas oil, sometimes referred to as "red diesel", is a type of automotive fuel. It can be included as a component of conventional diesel fuel (up to 20%), and is also used in the petrochemical industry as an intermediate product of hydrocarbon catalytic cracking processes. It turns out that gas oil is mainly an additive or a semi-finished product?
Physical and chemical properties of gas oil
In domestic oil refining, the resulting gas oil must comply with the technical requirements of GOST R 52755-2007, and is not an independent, but a composite fuel, which is obtained by mixing gas condensates or oil. Such gas oil is recommended to be used only as additives.
GOST stipulates the following gas oil parameters:
- Density at external temperature 15°C, t/m3 - 750… 1000.
- Kinematic viscosity at 50°C, mm2/s, not higher - 200.
- Boiling temperature, °C - 270… 500.
- The content of sulfur compounds in the finished product,% - up to 20.
- Acid number, in terms of KOH - up to 4.
- The presence of mechanical impurities,% - up to 10;
- The presence of water,% - up to 5.
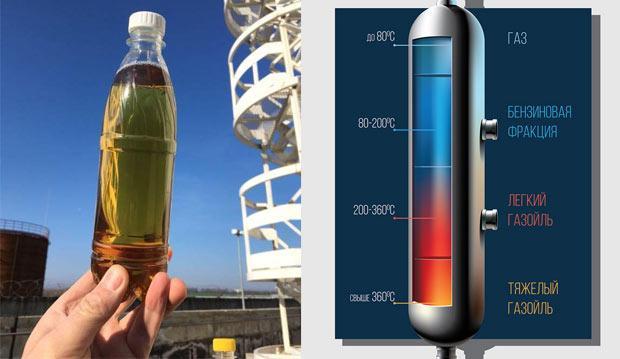

There are no other characteristics in this standard regarding gas oil, and a significant data interval allows us to conclude that, in fact, gas oil does not represent an integral class of hydrocarbons, but is divided into several groups. There are two main types of gas oil - atmospheric gas oil (or light) and vacuum gas oil (or heavy).
Physical properties of atmospheric gas oil
This type of hydrocarbon is obtained at atmospheric (or slightly higher, up to 15 kPa) pressure, when fractions with a temperature of 270 to 360°C.
Light gas oil has fairly high fluidity, relatively low viscosity, and in high concentrations it can act as a thickener. This significantly reduces the usefulness of this type of gas oil as a fuel for vehicles, so some oil traders sell not light gas oil, but its condensate, which is actually a waste product of continuous petrochemical production.
Atmospheric gas oil can be distinguished by its color - it is either pure yellow or yellow-green. The uncertainty of gas oil characteristics, given in the previous paragraph, also indicates a rather unstable behavior of this type of fuel, which is aggravated by the presence of a significant amount of nitrogen and especially sulfur, which pollutes engines.


Physical properties of vacuum gas oil
Heavy gas oil boils at higher temperatures, in the range of 350…560°C, and under vacuum inside the catalyst vessel. Its viscosity is higher, therefore, the flash point increases accordingly (up to 120 ... 150°C) and the thickening temperature, on the contrary, decreases, and does not exceed -22 ... -30°C. The color of such gas oil is slightly yellow, and sometimes almost transparent.
Although the external consumer characteristics of heavy gas oil are very close to the properties of the corresponding diesel fuel, they are not stable and are highly dependent on external conditions. This is explained by the processing modes implemented to obtain gas oil. Therefore, it, being an intermediate fraction of the chemical processes of oil refining, cannot have any permanent performance characteristics.


Application of gas oil
As an independent type of fuel for vehicles, gas oil is not recommended. However, it finds application in the following areas of economic activity:
- Furnace equipment used for heating residential and industrial premises.
- River and sea vessels equipped with low power diesel engines.
- Diesel generators.
- Agricultural or road construction machines, from lawn mowers and grain dryers to excavators and scrapers.
Often, gas oil is recommended as a backup fuel for hospitals, data centers and other organizations using liquid petroleum products. This is explained not so much by the value of gas oil as a fuel, but by its cheapness.


Gas oil and diesel fuel: differences
Let's start with the fact that NO type of gas oil can be recommended as a diesel fuel for cars: it heavily pollutes the moving parts of the engine, due to which the stability of the torque values drops, and the consumption of such "fuel" increases dramatically. But for less delicate power drives (which are used in hoisting and transport equipment, combines, tractors, etc.), the instability of the physicochemical characteristics of gas oil is of no particular importance, and the use of engines of such equipment is shorter in time.
The concept of "red diesel", more common abroad, means only the addition of a special dye to gas oil. This helps to track unscrupulous fuel distributors, since such a color change, detected at a gas station, entails large fines.
The chemical composition of gas oil and diesel fuel is almost identical, so it is worth pointing out that from this point of view, gas oil is a red-tinted diesel fuel. Which will inevitably cause significant damage to your car.


Watch this video on YouTube

