Hybrid car. The principle of operation, types of hybrids, car examples
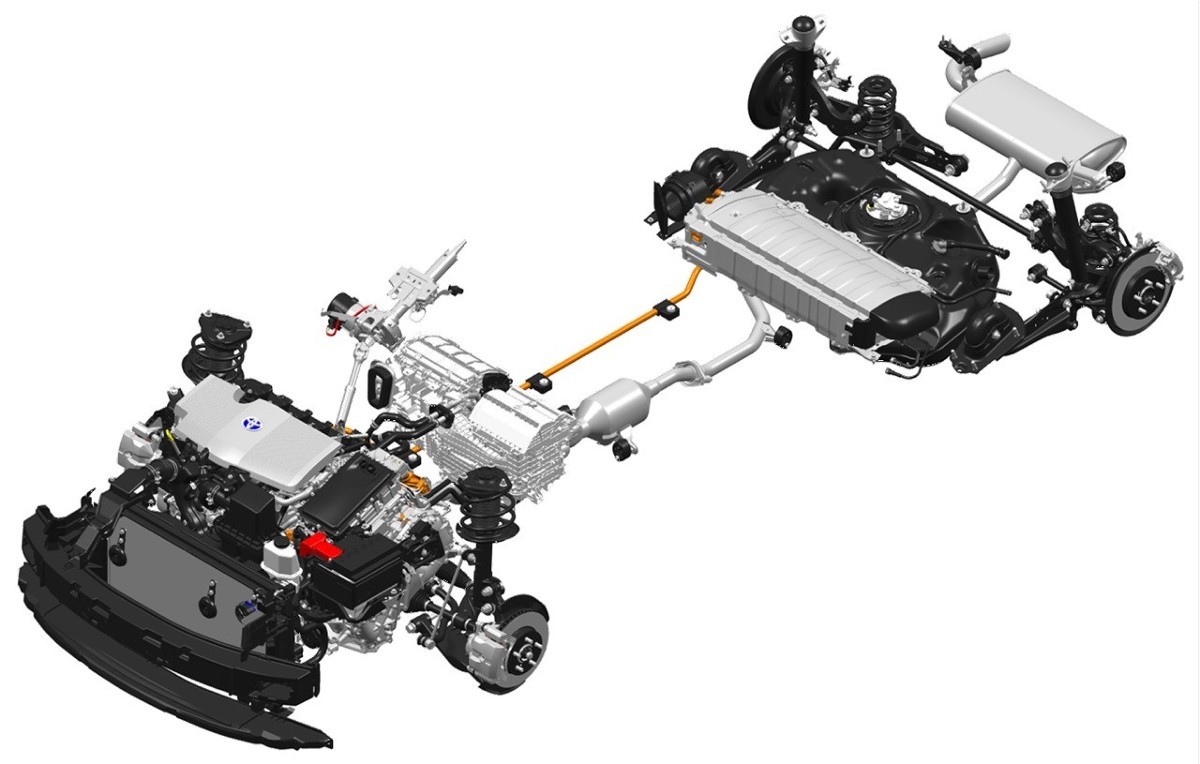 Toyota Prius - you don't have to be a car enthusiast to know this model. It is the world's most popular hybrid and has revolutionized the automotive market in a way. Let's take a look at how hybrids work, along with the types and use cases.
Toyota Prius - you don't have to be a car enthusiast to know this model. It is the world's most popular hybrid and has revolutionized the automotive market in a way. Let's take a look at how hybrids work, along with the types and use cases.
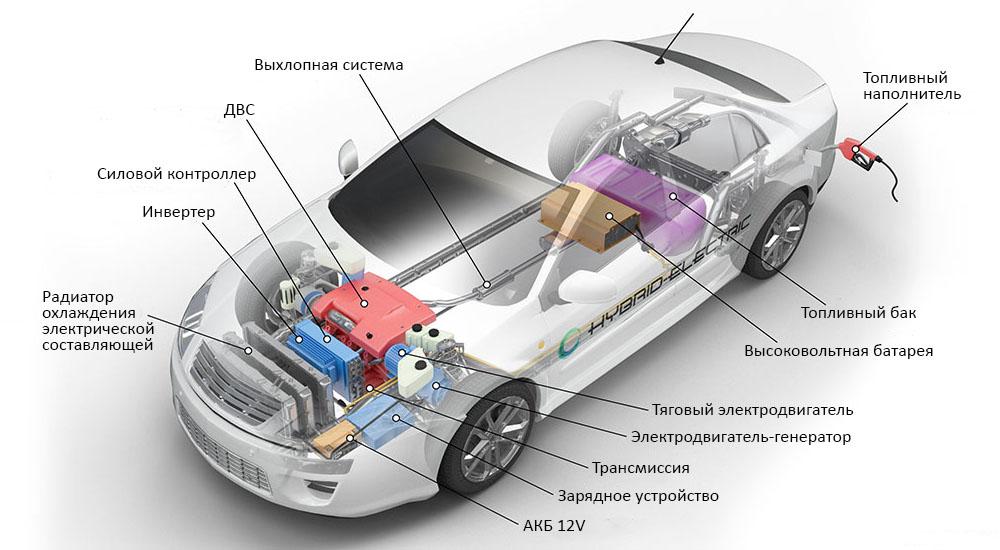
In a nutshell, a hybrid drive can be described as a combination of an electric motor and an internal combustion engine, but due to the several types of this drive, a generalized description does not exist. The very level of development of the hybrid drive introduces a division into micro-hybrids, mild hybrids and full hybrids.
- Micro hybrids (micro hybrids)
 In the case of a micro-hybrid, the electric motor is not used to power the vehicle. It acts as an alternator and starter, it can turn the crankshaft when the driver wants to start the engine, while driving it turns into a generator that recovers energy when the driver slows down or brakes and converts it into electricity to charge the engine. battery.
In the case of a micro-hybrid, the electric motor is not used to power the vehicle. It acts as an alternator and starter, it can turn the crankshaft when the driver wants to start the engine, while driving it turns into a generator that recovers energy when the driver slows down or brakes and converts it into electricity to charge the engine. battery.
- Soft hybrid
A mild hybrid has a slightly more complex design, but still, the electric motor cannot propel the car on its own. It serves only as an assistant to the internal combustion engine, and its task is primarily to recover energy during braking and support the internal combustion engine during vehicle acceleration.
- Full hybrid
This is the most advanced solution in which the electric motor plays many roles. It can both drive a car and support an internal combustion engine and recover energy when braking.
Hybrid drives also differ in how the combustion engine and electric motor are connected to each other. I'm talking about serial, parallel and mixed hybrids.
- serial hybrid
In the serial hybrid we find an internal combustion engine, but it is not connected in any way with the drive wheels. Its role is to drive an electric current generator - this is the so-called range extender. The electricity generated in this way is used by the electric motor, which is responsible for driving the car. In short, an internal combustion engine produces electricity that is sent to an electric motor that drives the wheels.
See also: Dacia Sandero 1.0 SCe. Budget car with economical engine
The editors recommend:
Driver's license. The driver will not lose the right to demerit points
How about OC and AC when selling a car?
Alfa Romeo Giulia Veloce in our test
This type of drive system requires two electrical units to operate, one acting as a power generator and the other acting as a source of propulsion. Due to the fact that the internal combustion engine is not mechanically connected to the wheels, it can operate under optimal conditions, i.e. in the appropriate speed range and with low load. This reduces fuel consumption and combustion installations.
While driving, when the batteries that power the electric motor are being charged, the internal combustion engine is switched off. When the accumulated energy resources are exhausted, the incineration plant starts up and drives a generator that feeds the electrical installation. This solution allows us to keep moving without having to charge the batteries from the socket, but on the other hand, nothing prevents you from using the power cable after arriving at your destination and recharging the batteries using the mains.
advantages:
– Possibility of movement in electric mode without the use of internal combustion engines (silence, ecology, etc.).
Disadvantages:
– High construction cost.
– Large dimensions and weight of the drive.
