
Glossary of files
Content
| The following terms refer either to how the teeth of the file are placed, how they were cut, or whether they were cut at all. | |
Abrasive | |
| This term refers to a rough surface that removes material from another surface when they rub against each other. | |
 | An example of a commonly encountered abrasive is the rough side of a sponge, which can be used to remove stubborn bits of food from a plate when washing dishes. |
Bit | |
 | As you might expect, this term describes how the teeth of the file were cut. With this type of file, the teeth are sheared by a series of chisel blows, either by hand or on a machine. |
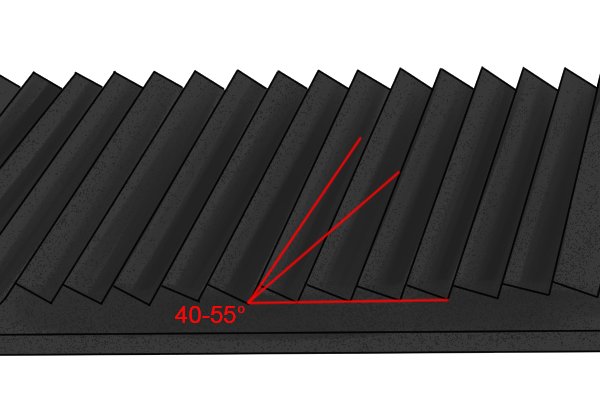
Coarseness | |
 | This describes how rough or smooth the file is. Coarse files have farther apart teeth and they quickly remove material from the workpiece, but leave a rough surface. |
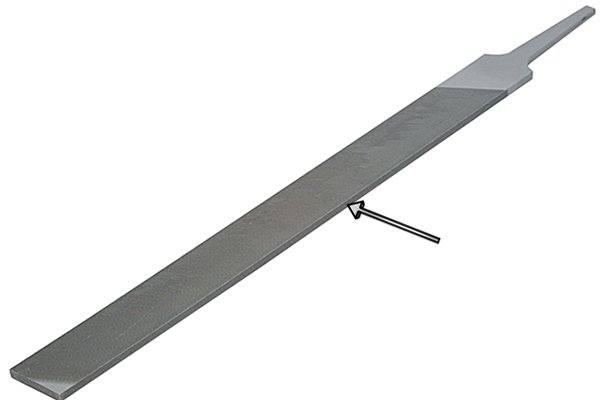 | Smooth files have closely spaced teeth. They run much slower but leave a smoother finish. |
Deburring | |
 | It is the process of removing unwanted chips from the edge of a piece of material that have been created by cutting, drilling, or a similar process. |
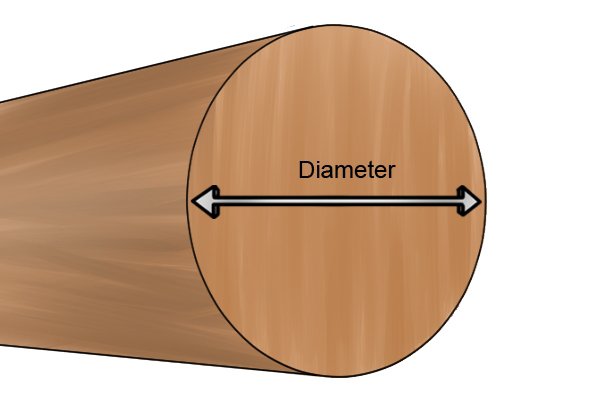
Diameter | |
 | The maximum possible measurement of a circle through its center point. Chainsaw files are usually measured by diameter so that they can be matched to the right size chainsaw blade. |
Draw Stroke | |
 | Pulling the file back towards you. Usually the file does not come into contact with the workpiece during the draw stroke unless you are filing. Cm.: What is lottery registration? |
Edge | |
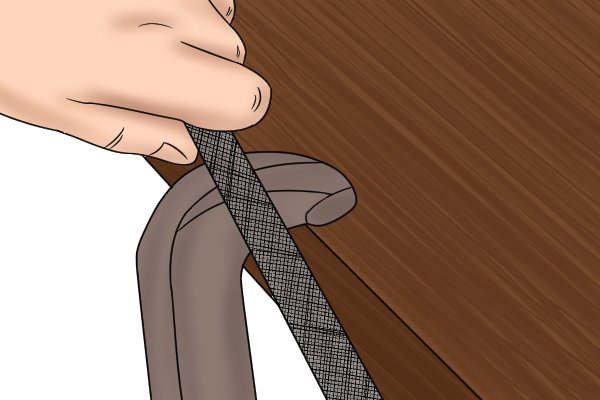 | The angle between two file edges that may or may not be cut with teeth. Cm.: What are the main parts of a file? |
engraved cut | |
 | This type of file has teeth engraved. This means that it was immersed in a specially prepared acid, which eroded the tooth pattern on its surface. This process is commonly used to re-sharpen files. |
Face | |
 | A large file surface that is usually toothed and is used to remove material from the workpiece. Cm.: What are the main parts of a file? |
Finish | |
 | Work on the piece of material until it feels smooth to the touch. |
Foil | |
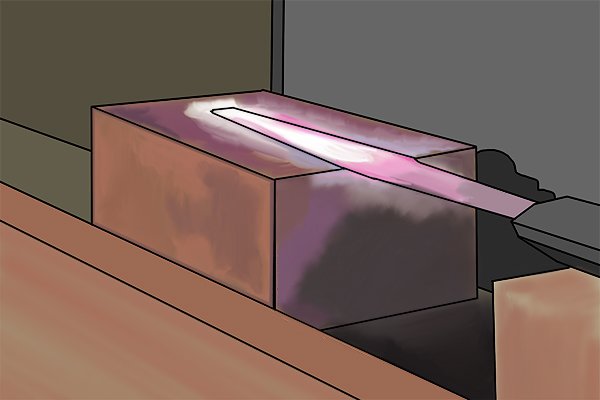 | A thin elongated burr that is formed when sharpening a knife with a file. The foil is the same thickness as the cutting edge of the knife and resembles a piece of kitchen foil. |
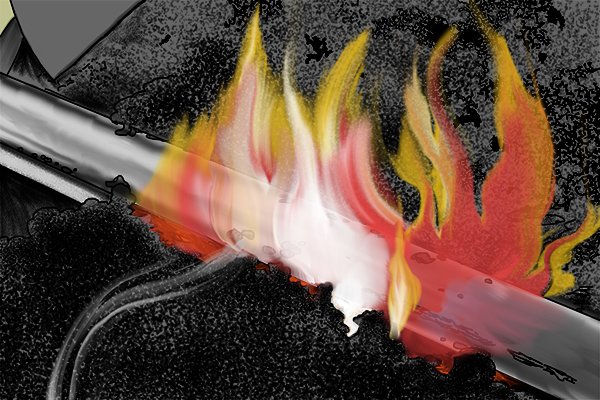 | It can be removed from the edge of the blade by simply pulling gently on it. Cutting with a knife with foil attached will cause it to coat the edge of the blade and make it dull. |
hard metal | |
 | A metal with a high Mohs score, such as steel (5.5), chromium (8), or boron (9). Cm.: What is hardness? |
heel | |
 | The part of the file between the shank and face where the teeth are not cut. Cm.: What are the main parts of a file? |
Driver File | |
 | A file designed to shape an object by removing material by abrasion. Cm.: What is a typist file |
nest | |
 | A rectangular slot partially carved in a piece of wood to connect or install a locking mechanism. |
plain | |
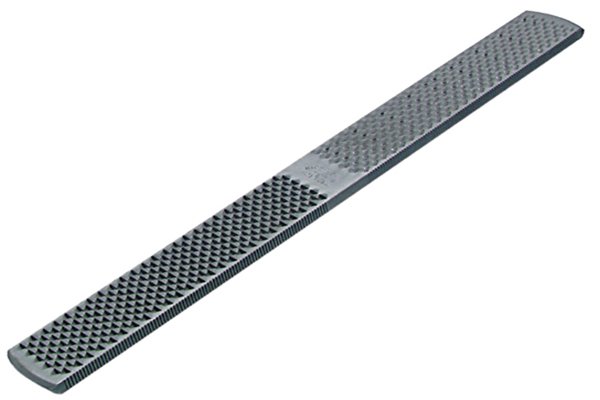 | A file made without a shank. |
Pneumatic | |
 | The term refers to an air-powered tool or device, such as an air file. |
Point | |
 | End of file. It can be easy to remember this name because it is the part of the tool that points to your workpiece. |
push move | |
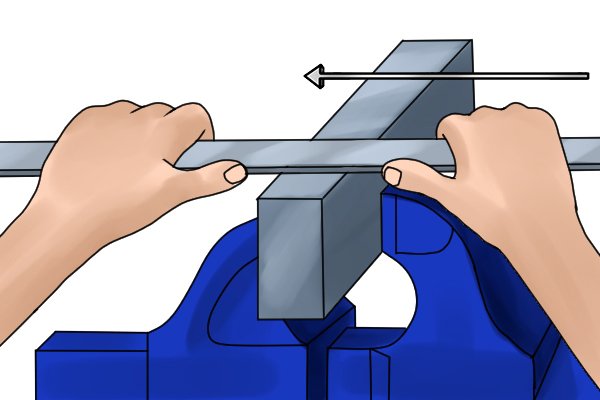 | Pushing the file away from itself, which will cause the teeth to abrade the material from the workpiece. |
Rake | |
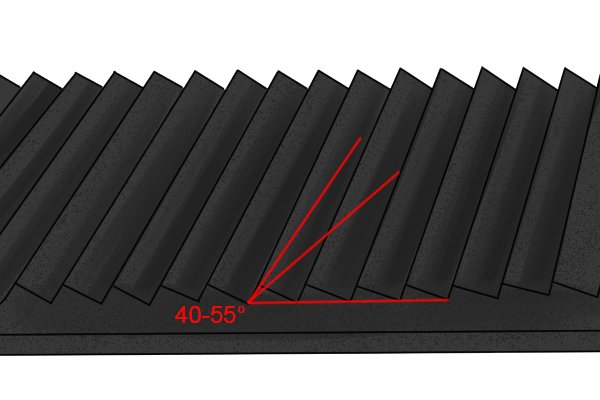 | The front file is the angle at which the teeth connect to its body. |
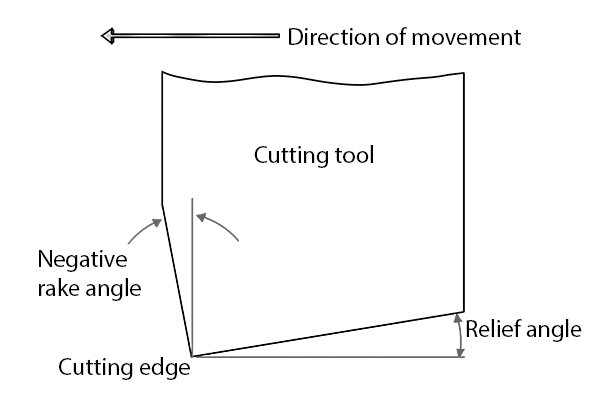 | A positive rake angle means the teeth are pointing in the same direction as the tool is moving. Negative rake means they are pointing in the opposite direction. |
cut | |
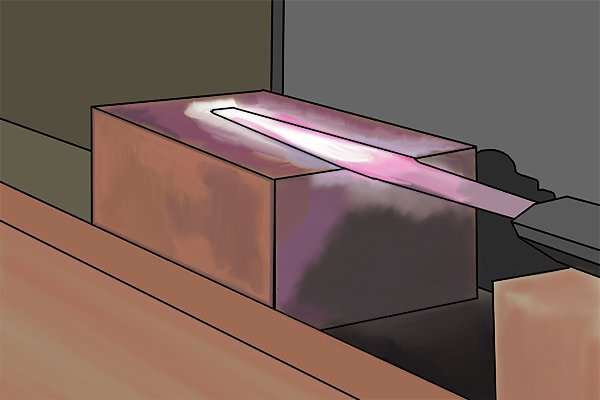 | Reslicing is the best way to recycle dull files. The file is refired (annealed) which makes the steel soft enough to be machined again. |
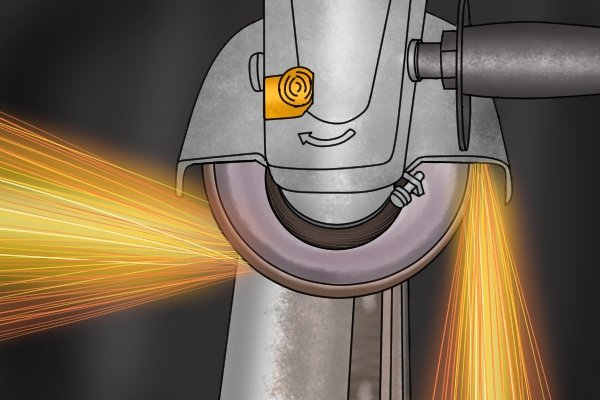 | Then the old teeth are ground down, and the new ones are cut out. |
 | The file then goes through the heat treatment process again so that it can be re-hardened for use. |
 | This is not something a home tinker can usually do at home, and it can be more expensive to send a file in for re-cutting than it is to buy a new file. For more information see How to sharpen a file |
Safely | |
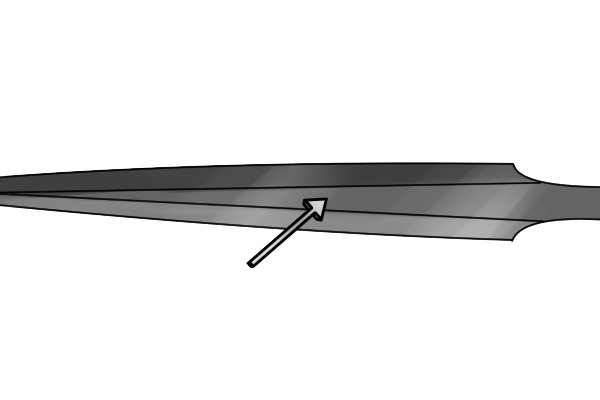 | A surface or edge that does not have cut teeth is called safe. |
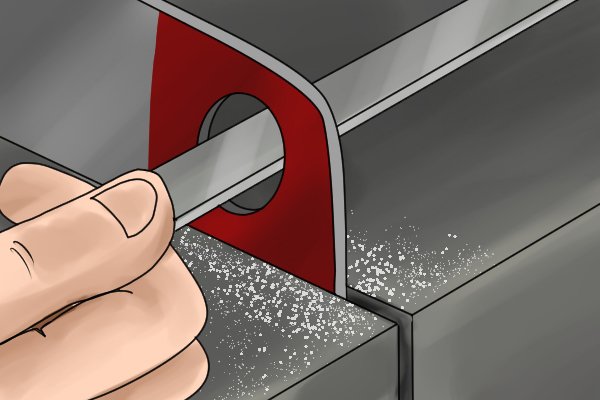 | Safety edges allow the craftsman to lean the tool against one surface of the workpiece while turning the other without damaging the material on which the safety edge rests. This is especially useful when creating square holes. |
saw file | |
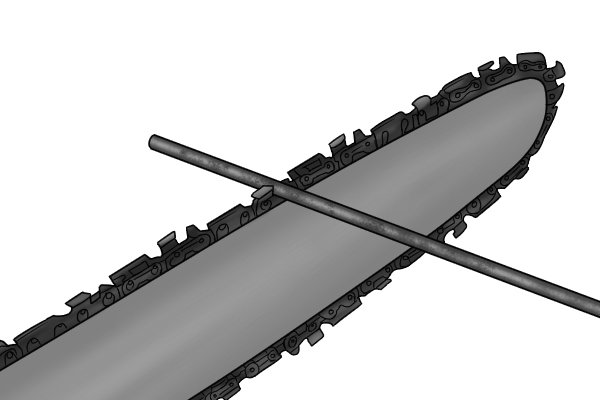 | A file designed for sharpening blades or other cutting or drilling tools. Cm.: What are saw files? |
Stitching | |
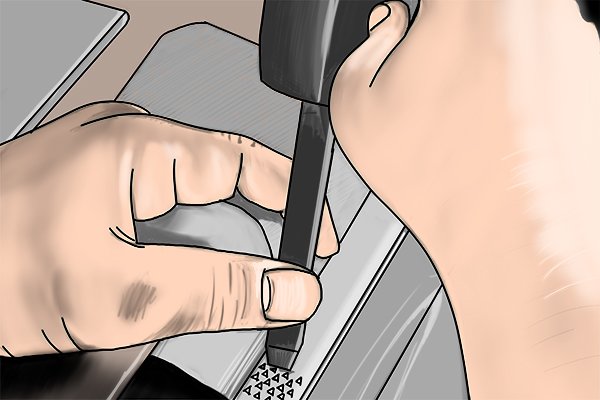 | The process of cutting teeth into a rasp using a triangular punch. Cm.: How are files created? |
Put the | |
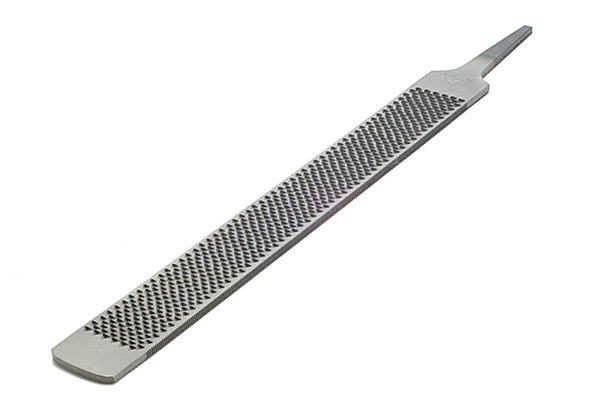 | The term "set" refers to files with teeth that do not reach the entire surface. |
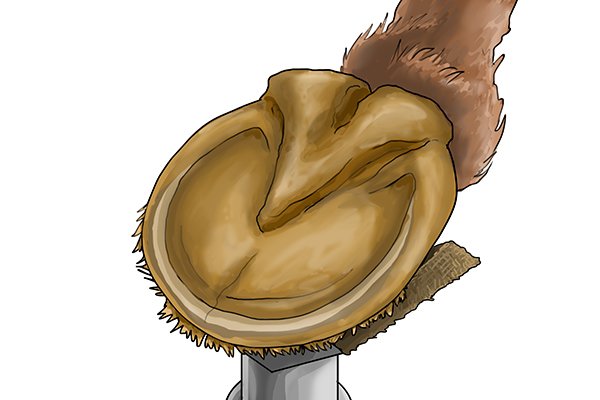 | Some files are designed to be even more secure than just leaving the edges safe. This is well suited for work that requires a great deal of control, such as trimming a horse's hoof. |
soft metal | |
 | Metals that score low on the Mohs scale, such as lead (1.5), gold (2.5), silver (2.5), aluminum (2.75) or copper (3). Nail hardness 2.5. Cm.: What is hardness |

