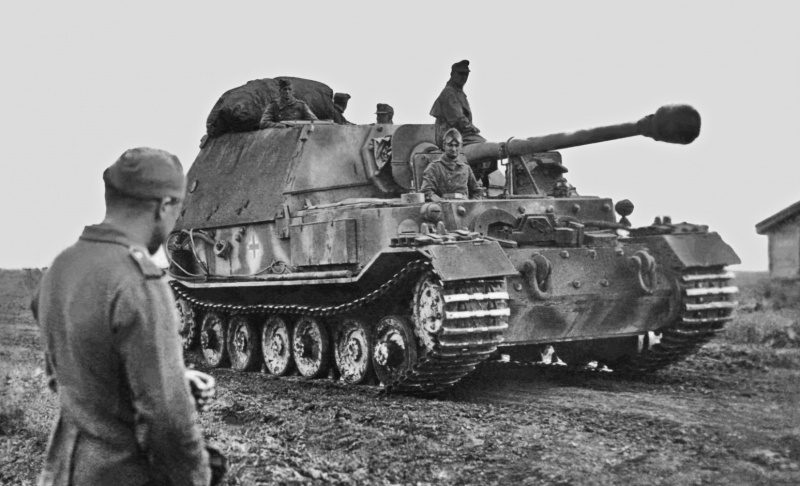
Tank destroyer "Ferdinand" ("Elephant")
Tank destroyer "Ferdinand" ("Elephant") Names:
An electric transmission was used in its undercarriage, which worked according to the following scheme: two carburetor engines powered two electric generators, the electric current of which was used to operate the electric motors that drove the drive wheels of the self-propelled unit. Other distinguishing features of this installation are very strong armor (the thickness of the front plates of the hull and cabin was 200 mm) and heavy weight - 65 tons. The power plant with a capacity of only 640 hp. could provide the maximum speed of this colossus only 30 km / h. On rough terrain, she did not move much faster than a pedestrian. Tank destroyers "Ferdinand" were first used in July 1943 in the Battle of Kursk. They were very dangerous when fighting at long distances (a sub-caliber projectile at a distance of 1000 meters was guaranteed to pierce armor 200 mm thick) there were cases when the T-34 tank was destroyed from a distance of 3000 meters, but in close combat they are more mobile tanks T-34 destroyed them with shots to the side and stern. Used in heavy anti-tank fighter units. In 1942, the Wehrmacht adopted the Tiger tank, designed by the Henschel company. The task to develop the same tank was received earlier by Professor Ferdinand Porsche, who, without waiting for the tests of both samples, launched his tank into production. The Porsche car was equipped with an electric transmission that used a large amount of scarce copper, which was one of the strong arguments against adopting it. In addition, the undercarriage of the Porsche tank was notable for its low reliability and would require increased attention from the maintenance units of tank divisions. Therefore, after preference was given to the Henschel tank, the question arose of using ready-made chassis of Porsche tanks, which they managed to produce in the amount of 90 pieces. Five of them were modified into recovery vehicles, and on the basis of the rest, it was decided to build tank destroyers with a powerful 88-mm PAK43 / 1 gun with a barrel length of 71 calibers, installing it in an armored cabin in the rear of the tank. Work on the conversion of Porsche tanks began in September 1942 at the Alkett plant in St. Valentine and was completed by May 8, 1943. New assault guns were named Panzerjager 8,8 cm Рак43 / 2 (Sd Kfz. 184)
Professor Ferdinand Porsche inspecting one of the prototypes of the VK4501 (P) "Tiger" tank, June 1942
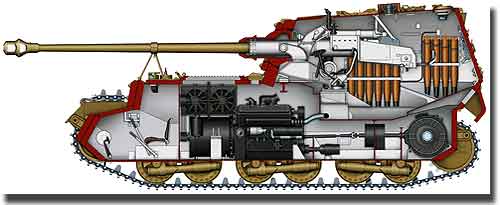
Hitler constantly rushed production, wanting new vehicles to be ready for the start of Operation Citadel, the timing of which was repeatedly postponed due to the insufficient number of new Tiger and Panther tanks produced. The Ferdinand assault guns were equipped with two Maybach HL120TRM carburetor engines with a power of 221 kW (300 hp) each. The engines were located in the central part of the hull, in front of the fighting compartment, behind the driver's seat. The thickness of the frontal armor was 200 mm, the side armor was 80 mm, the bottoms were 60 mm, the roof of the fighting compartment was 40 mm and 42 mm. The driver and radio operator were located in front of the hull, and the commander, gunner and two loaders in the stern. In its design and layout, the Ferdinand assault gun differed from all German tanks and self-propelled guns of the Second World War. In front of the hull there was a control compartment, which housed levers and control pedals, units of a pneumohydraulic braking system, track tensioners, a junction box with switches and rheostats, an instrument panel, fuel filters, starter batteries, a radio station, driver and radio operator seats. The power plant compartment occupied the middle part of the self-propelled gun. It was separated from the control compartment by a metal partition. There were Maybach engines installed in parallel, paired with generators, a ventilation and radiator unit, fuel tanks, a compressor, two fans designed to ventilate the power plant compartment, and traction electric motors. Click on the picture to enlarge (will open in a new window)
Tank destroyer "Elephant" Sd.Kfz.184 In the aft part there was a fighting compartment with an 88-mm StuK43 L / 71 gun installed in it (a variant of the 88-mm Pak43 anti-tank gun, adapted for installation in an assault gun) and ammunition, four crew members were also located here - a commander, a gunner and two loaders . In addition, traction motors were located in the lower rear of the fighting compartment. The fighting compartment was separated from the power plant compartment by a heat-resistant partition, as well as a floor with felt seals. This was done in order to prevent contaminated air from entering the fighting compartment from the power plant compartment and to localize a possible fire in one or another compartment. The partitions between the compartments and, in general, the location of the equipment in the body of the self-propelled gun made it impossible for the driver and radio operator to communicate personally with the crew of the fighting compartment. Communication between them was carried out through a tank phone - a flexible metal hose - and a tank intercom.
For the production of the Ferdinands, the hulls of the Tigers, designed by F. Porsche, made of 80-mm-100-mm armor, were used. At the same time, the side sheets with the frontal and aft ones were connected into a spike, and in the edges of the side sheets there were 20-mm grooves against which the frontal and aft hull sheets abutted. Outside and inside, all joints were welded with austenitic electrodes. When converting tank hulls into Ferdinands, the rear beveled side plates were cut out from the inside - in this way they were lightened by turning into additional stiffeners. In their place, small 80-mm armor plates were welded, which were a continuation of the main side, to which the upper stern sheet was attached to the spike. All these measures were taken in order to bring the upper part of the hull to the same level, which was subsequently necessary to install the cabin. There were also 20 mm grooves in the lower edge of the side sheets, which included bottom sheets with subsequent double-sided welding. The front part of the bottom (at a length of 1350 mm) was reinforced with an additional 30 mm sheet riveted to the main one with 25 rivets arranged in 5 rows. In addition, welding was carried out along the edges without cutting the edges.
The front and frontal hull sheets with a thickness of 100 mm were additionally reinforced with 100 mm screens, which were connected to the main sheet with 12 (front) and 11 (front) bolts with a diameter of 38 mm with bulletproof heads. In addition, welding was carried out from above and from the sides. To prevent the nuts from loosening during shelling, they were also welded to the inside of the base plates. Holes for a viewing device and a machine-gun mount in the frontal hull sheet, inherited from the “Tiger” designed by F. Porsche, were welded from the inside with special armor inserts. The roof sheets of the control compartment and the power plant were placed in 20-mm grooves in the upper edge of the side and frontal sheets, followed by double-sided welding. Two hatches were placed in the roof of the control compartment for landing the driver and radio operator. The driver's hatch had three holes for viewing devices, protected from above by an armored visor. To the right of the radio operator's hatch, an armored cylinder was welded to protect the antenna input, and a stopper was attached between the hatches to secure the gun barrel in the stowed position. In the front beveled side plates of the hull there were viewing slots for observing the driver and radio operator.
Back – Forward >> | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||


 The Elefant fighter tank, also known as the Ferdinand, was designed on the basis of a prototype VK 4501 (P) of the T-VI H Tiger tank. This version of the Tiger tank was developed by the Porsche company, however, preference was given to the Henschel design, and it was decided to convert the manufactured 90 copies of the VK 4501 (P) chassis into tank destroyers. An armored cabin was mounted above the control compartment and the fighting compartment, in which a powerful 88-mm semi-automatic gun with a barrel length of 71 calibers was installed. The gun was directed towards the rear of the chassis, which has now become the front of the self-propelled unit.
The Elefant fighter tank, also known as the Ferdinand, was designed on the basis of a prototype VK 4501 (P) of the T-VI H Tiger tank. This version of the Tiger tank was developed by the Porsche company, however, preference was given to the Henschel design, and it was decided to convert the manufactured 90 copies of the VK 4501 (P) chassis into tank destroyers. An armored cabin was mounted above the control compartment and the fighting compartment, in which a powerful 88-mm semi-automatic gun with a barrel length of 71 calibers was installed. The gun was directed towards the rear of the chassis, which has now become the front of the self-propelled unit.