How to learn to understand cars from scratch? Detailed video
The ability to understand machines is a rather broad concept. For some, it is enough to distinguish one model from another. The same people whose profession is connected with cars put a much broader meaning into this concept:
- body type;
- Vehicle class;
- engine type - injector, carburetor, diesel, single or two-stroke, hybrid, electric vehicle;
- transmission - mechanics, automatic, variator, robotic, preselective (dual clutch).
If you work, for example, in a company selling spare parts or in a car shop, then according to the job description, you simply must have broad knowledge of:
- thoroughly know the model range of a particular automaker - that is, they must know what is the difference between different engines, for example VAZ-2104 - VAZ-21073, VAZ-21067, their volume, fuel, features;
- technical features of various units;
- design and device features.
If you have ever had to buy spare parts, then you know that it is enough for a good specialist to show this or that spare part - a working brake cylinder, a second gear, a main or intermediate shaft of a gearbox, a clutch cable, a release bearing, a feredo disk - he will name them without any problems brand, tell what car it is from, and most importantly, tell you exactly what it is. He will also easily select the part you need from the catalog - from the sealing rubber ring or cuff, to the distributor assembly or the backstage of the gearbox.

It is clear that such a skill comes only with experience. We will try to give basic recommendations on our website Vodi.su.
Basic Concepts
Any car consists of seven main systems:
- motor;
- transmission;
- steering;
- chassis or suspension;
- brake system;
- body;
- electrical equipment.
Body - classes and types
The first thing we see when admiring this or that car is the body. We have already talked about this a lot on our website, so we will just repeat.
Body types:
- single-volume - minivans (engine, interior, trunk are combined into one spatial structure);
- two-volume - hatchback, station wagon, SUV, crossover;
- three-volume - sedan, limousine, roadster, pickup.
Also, the class of the car depends on the length of the body - there are a lot of classification methods, the most common is the European one:
- "A" - compact hatchbacks, such as Chevrolet Spark, Daewoo Matiz;
- "B" - small cars - all VAZs, Daewoo Lanos, Geely MK;
- "C" - middle class - Skoda Octavia, Ford Focus, Mitsubishi Lancer.
Well, and so on - on our website Vodi.su there is an article where the classes are described in more detail.

Individual manufacturers also have their own types of classification, for example, BMW, Audi, or Mercedes. It is enough to go to the official website to determine the difference:
- Mercedes A-class - the smallest class, corresponds to the B-class according to the European classification;
- B-class - corresponds to the C-class;
- C-class (Comfort-Klasse);
- CLA - compact prestige lightweight class;
- G, GLA, GLC, GLE, M - Gelendvagen, SUVs and SUV class.
It is easy to understand the classification of Audi:
- A1-A8 - hatchbacks, station wagons with different body lengths;
- Q3, Q5, Q7 - SUVs, crossovers;
- TT - roadsters, coupes;
- R8 - sports car;
- RS - "charged versions" with improved technical characteristics.
BMW has the same classification:
- Series 1-7 - passenger cars such as hatchback, station wagon, sedan;
- X1, X3-X6 - SUVs, crossovers;
- Z4 - roadsters, coupes, convertibles;
- M-series - "charged" versions.
For most buyers, especially women, it is the body type that is critical. However, the bodywork is just the wrapper, and the specs are the most important thing. Let's consider the main ones.

Engine
The topic is vast, let's name the main points:
- by type of fuel - gasoline, diesel, gas, gas-fuel, hybrids, electric vehicles;
- by the number of cylinders - three-cylinder or more (for example, there are engines for 8 and 16 cylinders);
- according to the location of the cylinders - in-line (cylinders just stand in a row), opposed (cylinders against each other), V-shaped;
- by location under the hood - longitudinal, transverse.
In most passenger cars, in-line 3-4-cylinder engines are used with a longitudinal (along the axis of movement) or transverse installation. If we are talking about trucks or cars above the average class, then power is achieved by adding cylinders.
In addition, an integral element of the engine is the cooling system, which can be:
- liquid - cooling is carried out with antifreeze, antifreeze, plain water;
- air - a vivid example of "Zaporozhets", in which the engine was at the back, and the air was sucked in thanks to the fan, the same system is used on motorcycles;
- combined - cooling with antifreeze, a fan is used for additional airflow.
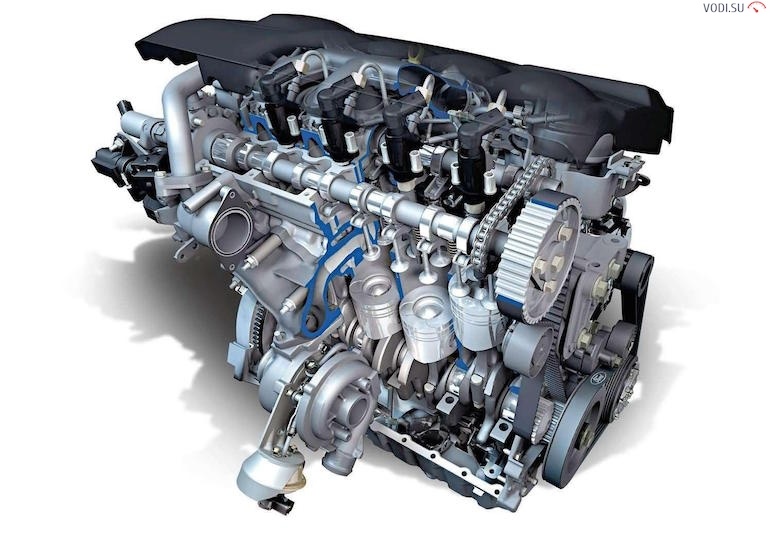
Also important points:
- injection system - carburetor, injector;
- ignition system - contact (using a distributor), non-contact (Hall sensor, switch), electronic (the process is controlled by a control unit);
- gas distribution mechanism;
- lubrication system and so on.
Трансмиссия
The main task of the transmission is to transmit torque from the motor to the wheels.
Transmission elements:
- clutch - connects or separates the transmission from the engine;
- gearbox - driving mode selection;
- cardan, cardan transmission - transfers the moment of movement to the drive axle;
- differential - the distribution of torque between the wheels of the drive axle.
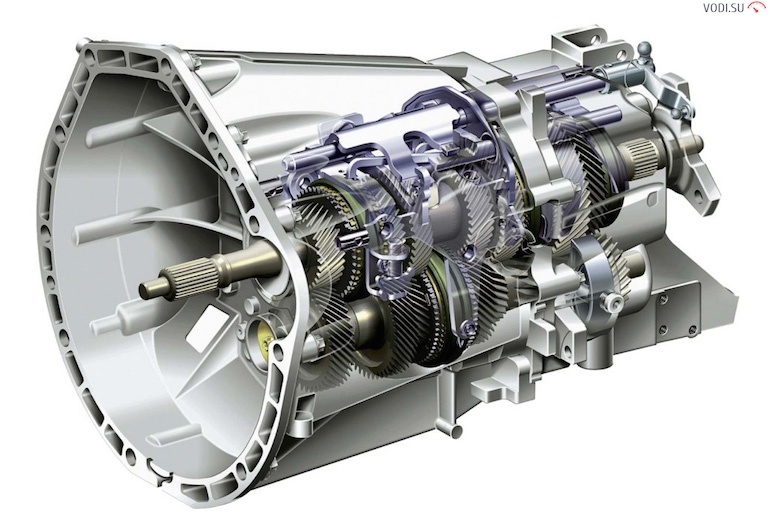
Most modern cars use a single- or double-disk dry clutch, paired with a manual or robotic (semi-automatic, preselective) gearbox, or a torque converter - a hydrostatic system in which engine energy sets the oil flow in motion - automatic transmissions or CVT (variator checkpoint).
That's just the type of gearbox is crucial for many. From our own experience, let's say that mechanics is the best option, since the driver himself chooses the optimal mode and thus consumes less fuel. In addition, manual transmission is simple and cheap to maintain. Automatic and CVT - greatly simplify the driving process, but if they break, then prepare serious amounts of money.
The transmission also includes such a concept as the type of drive:
- front or rear - the moment of rotation falls on one axis;
- full - both axes are leading, however, the drive can be either permanent or plug-in.
The transfer box is used to distribute torque on the vehicle axle. It is installed in all-wheel drive cars, such as UAZ-469 or VAZ-2121 Niva.

As you can see, a car is a rather complicated mechanism. However, for most, it is enough to be able to operate it and perform simple operations, such as changing a wheel. Maintenance is best left to professionals.
Video: device and car selection


Watch this video on YouTube
Loading…
