How to find a leak in a car
Content
Many motorists are familiar with the following situation: you approach your “iron horse” in the morning, turn the ignition key, but the starter does not turn, the engine does not start or starts, but with great difficulty. In an advanced case, even the electromechanical locks do not work, you have to open it manually, since the alarm is turned off ... But after all, last night everything was in order! This is due to the discharge of the battery, which is caused by a large current leakage in electrical equipment. How to check the current leakage on a car with a multimeter, at what values it is worth sounding the alarm, and what can be done - we'll talk about this in the article.
Content
- 1 Causes and consequences
- 2 How to check the leakage current in a car
- 3 How to find the leakage current
Causes and consequences
First you need to understand what a car battery is. Like any other battery, it is a chemical current source that has an electrical capacity, the value of which is usually printed on the battery label. It is measured in ampere-hours (Ah).
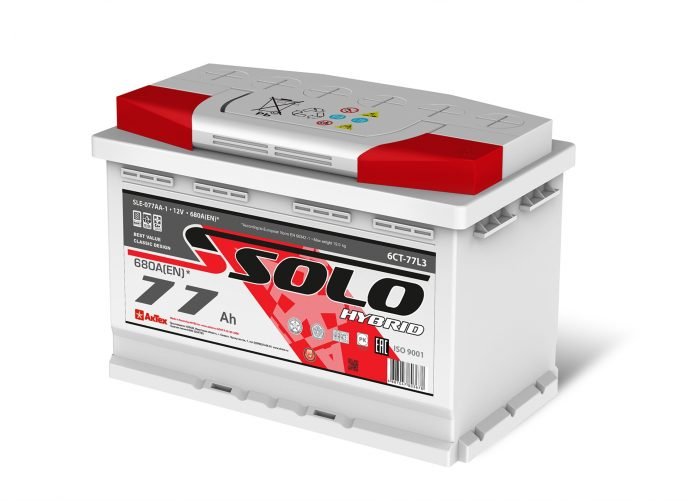

Battery capacity is measured in ampere-hours and shows how much current the car battery will discharge.
In fact, the capacity determines the amount of electrical energy that a fully charged battery can deliver. The leakage current is the current drawn from the battery. Let's say we have a serious short circuit in the auto wiring, and the leakage current is 1 A. Then the 77 Ah battery given as an example will be discharged in 77 hours. During use, the battery life and its effective capacity decrease, so the starter may not have enough starting current even when the battery is half discharged (up to 75% in cold weather). With such a leak, we can assume that in a day it will become almost impossible to start a car with a key.
The main trouble is the deep discharge of the battery. When receiving energy from a battery, sulfuric acid, which is part of the electrolyte, is gradually converted into lead salts. Up to a certain point, this process is reversible, since this happens when the battery is charged. But if the voltage in the cells falls below a certain level, the electrolyte forms insoluble compounds that settle on the plates in the form of crystals. These crystals will never recover, but will reduce the working surface of the plates, leading to an increase in the internal resistance of the battery, and, therefore, to a decrease in its capacity. In the end, you have to buy a new battery. A dangerous discharge is considered to be a voltage below 10,5 V at the battery terminals. If you brought your car battery home to charge and saw a lower voltage, it's time to sound the alarm and deal with the leak urgently!
In addition, leaks caused by short circuits or melted wire insulation at high enough currents can lead not only to damage to the battery, but also to fire. Indeed, a new car battery is capable of delivering hundreds of amps for a short period of time, which, according to the laws of physics, can lead to melting and ignition in a few minutes. Old batteries can boil over or explode under constant stress. Even worse, all this can happen quite by accident at any time, for example, at night in a parking lot.
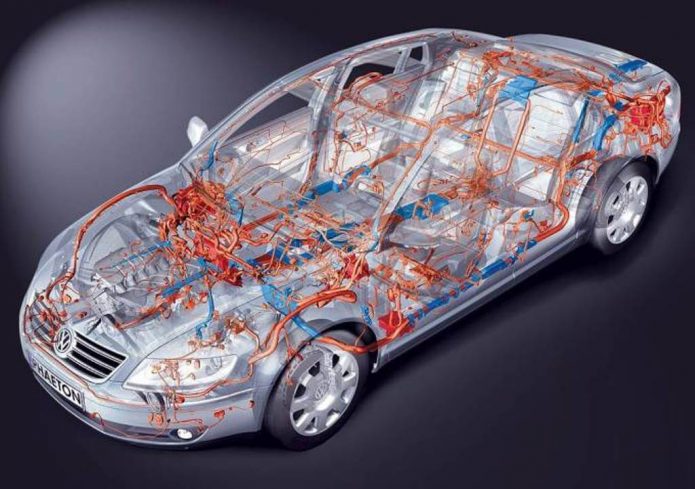
The electrical system of a car is a complex of complex electronic systems interconnected
After considering all the unpleasant consequences of the leakage current, it is worth understanding its causes. Previously, in the days of carbureted cars with a minimum of electronics, its complete absence was considered normal leakage current. In those cars, there was simply nothing to draw current from the battery when the ignition was turned off. Today, everything has changed: any car is simply crammed with various electronics. These can be both standard devices and subsequently installed by the driver. And although all modern electronics support special “sleep” modes or standby modes with very low power consumption, a certain amount of current is consumed by standby circuits, under the friendly procession of environmentalists with slogans about energy saving. Therefore, small leakage currents (up to 70 mA) are normal.
Of the factory equipment in the car, the following devices normally constantly consume a certain amount of energy:
- Diodes in the generator rectifier (20-45 mA);
- Radio tape recorder (up to 5 mA);
- Alarm (10-50 mA);
- Various switching devices based on relays or semiconductors, on-board engine computer (up to 10 mA).
In parentheses are the maximum allowable current values for serviceable equipment. Malfunctioning components can dramatically increase their consumption. We will talk about identifying and eliminating such components in the last part, but for now we will give a list of additional devices installed by drivers, which can often add another good hundred milliamps to the leak:
- Non-standard radio;
- Additional amplifiers and active subwoofers;
- Anti-theft or second alarm;
- DVR or radar detector;
- GPS navigator;
- Any USB powered equipment connected to the cigarette lighter.
How to check the leakage current in a car
Checking the total current leakage along the 12 V line of the car is very simple: you need to turn on the multimeter in ammeter mode in the gap between the battery and the rest of the car network. At the same time, the engine must be turned off and no manipulations with the ignition can be made. The huge starting currents of the starter will definitely lead to damage to the multimeter and burns.
It is important! Before you start working with the multimeter, it is recommended that you read the training article on working with the device.
Let's consider the process in more detail:
- Turn off the ignition and all additional consumers.
- We get to the battery and, using a suitable wrench, unscrew the negative terminal from it.
- Set the multimeter to DC ammeter mode. We set the maximum measurement limit. On most typical meters, this is either 10 or 20 A. We connect the probes to the appropriately marked sockets. Please note that in the ammeter mode, the resistance of the "tester" is zero, so if you habitually touch two battery terminals with the probes, you will get a short circuit.
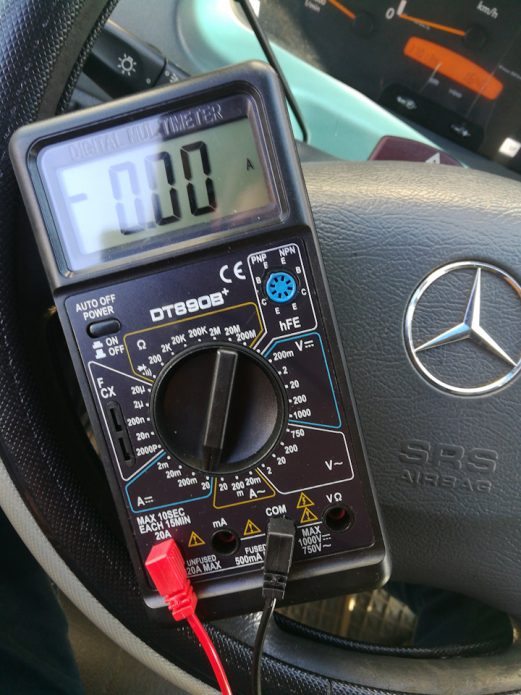

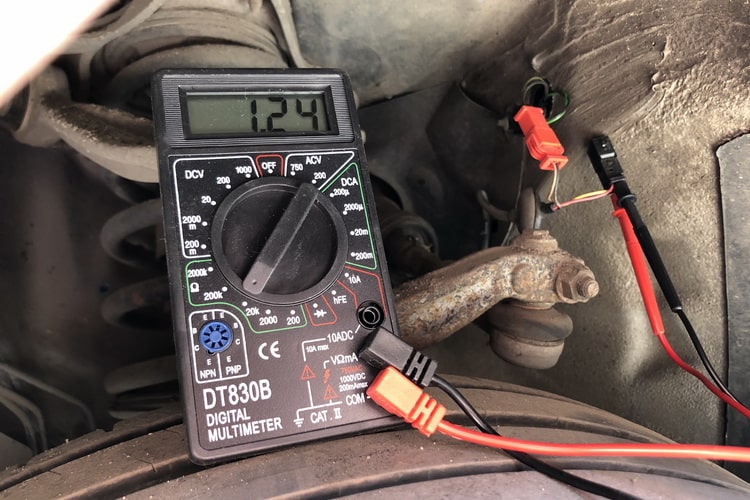
To measure the leakage current, you must turn on the multimeter in DC measurement mode
It is important! Do not use the connector labeled "FUSED". This multimeter input is protected by a fuse, typically 200 or 500 mA. The leakage current is unknown to us in advance and can be much larger, which will lead to the failure of the fuse. The inscription "UNFUSED" indicates the absence of a fuse in this line.
- Now we connect the probes into the gap: black to the minus on the battery, red to the "mass". For some older meters, polarity may be important, but on a digital meter it doesn't matter.
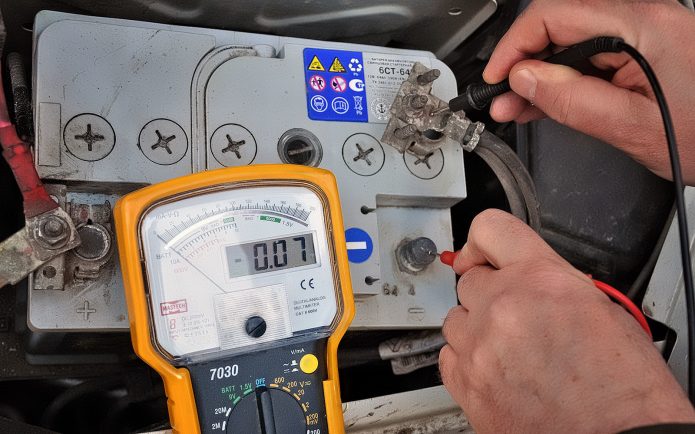

It is most safe to take measurements by disconnecting the negative terminal, but the use of "plus" is also acceptable.
- We look at the readings of the device. In the picture above, we can observe the result of 70 mA, which is quite within the norm. But here it is already worth considering, 230 mA is a lot.

If all electronic equipment is really turned off, then a current value of 230 mA indicates serious problems.
An important subtlety: after closing the on-board circuit with a multimeter, in the first couple of minutes, the leakage current can be very large. This is explained by the fact that de-energized devices have just received power and have not yet entered the power saving mode. Hold the probes firmly on the contacts and wait up to five minutes (you can use the probes with alligator clips to ensure a reliable connection for such a long time). Most likely, the current will gradually drop. If high values remain, then there is definitely an electrical problem.
Normal values of leakage currents vary for different vehicles. Approximately this is 20-70 mA, but for old cars they can be significantly more, as well as for domestic cars. Modern foreign cars can generally consume a few milliamps in the parking lot. Your best bet is to use the internet and find out what values are acceptable for your model.
How to find the leakage current
If the measurements turned out to be disappointing, you will have to look for the "culprit" of the high energy consumption. Let us first consider the malfunctions of standard components, which can lead to high leakage current.
- The diodes on the alternator rectifier should not pass current in the reverse direction, but this is only in theory. In practice, they have a small reverse current, on the order of 5-10 mA. Since there are four diodes in the rectifier bridge, from here we get up to 40 mA. However, over time, semiconductors tend to degrade, the insulation between the layers becomes thinner, and the reverse current can increase to 100-200 mA. In this case, only the replacement of the rectifier will help.
- The radio has a special mode in which it practically does not consume power. However, in order for it to enter this mode and not discharge the battery in the parking lot, it must be connected correctly. For this, the ACC signal input is used, which should be connected to the corresponding output from the ignition switch. The +12 V level appears at this output only when the key is inserted into the lock and turned slightly (ACC position - "accessories"). If there is an ACC signal, the radio is in standby mode and can consume quite a lot of current (up to 200 mA) while being turned off. When the driver pulls the key out of the car, the ACC signal disappears and the radio goes into sleep mode. If the ACC line on the radio is not connected or shorted to +12 V power, then the device is always in standby mode and consumes a lot of power.
- Alarms and immobilizers start to consume too much due to faulty sensors, for example, jammed door switches. Sometimes "appetites grow" due to a failure in the software (firmware) of the device. For example, the controller starts to constantly apply voltage to the relay coil. It depends on the specific device, but a complete shutdown and reset of the device, or a flashing, can help.
- Various switching elements such as relays or transistors can also create increased consumption. In a relay, these can be contacts “sticky” from dirt and time. Transistors have negligible reverse current, but when a semiconductor breaks down, its resistance becomes zero.
In 90% of cases, the problem lies not in the standard equipment of the car, but in non-standard devices connected by the driver himself:
- The “non-native” radio tape recorder is subject to the same rule for connecting the ACC line as for the standard one. Cheap low-quality radios can ignore this line altogether and remain in normal mode, consuming a lot of power.
- When connecting amplifiers, it is also necessary to follow the correct connection scheme, because they also have a power and energy saving control signal line, which is usually controlled by the radio.
- They just changed or added a security system, and the next morning the battery was discharged “to zero”? The problem is definitely in it.
- In some vehicles, the cigarette lighter socket does not turn off even when the ignition is turned off. And if any devices are powered through it (for example, the same DVR), then they continue to give a noticeable load on the battery. Don't underestimate the "little camera box", some of them have a consumption of 1A or more.
There are really a lot of devices in a modern car, but there is an effective way to search for an “enemy”. It consists in using a junction box with fuses, which is in every car. The +12 V bus from the battery comes to it, and the wiring to all kinds of consumers diverges from it. The process is as follows:
- We leave the multimeter in the same connected position as when measuring the leakage current.
- Find the location of the fuse box.
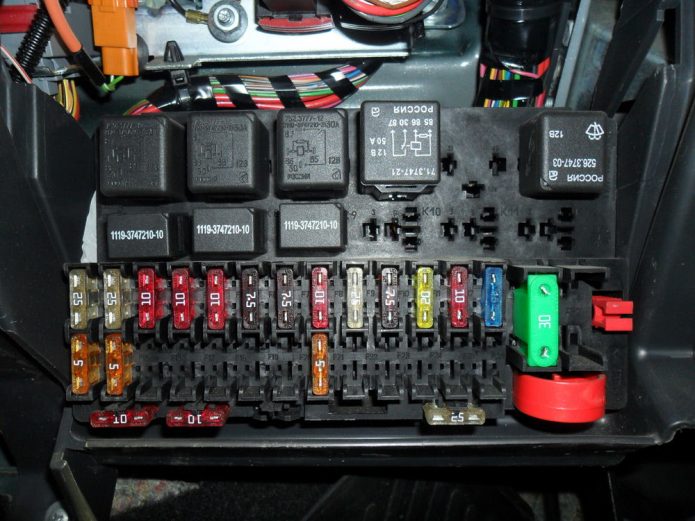

Fuse boxes are most often located in the engine compartment and in the cabin under the dashboard
- Now, one by one, we remove each of the fuses, following the readings of the multimeter. If the readings have not changed, put it back in the same place and move on to the next one. A noticeable drop in the readings of the device indicates that it is on this line that the problem consumer is located.
- The matter remains small: according to the electrical circuit of the car from the documentation, we find what this or that fuse is responsible for, and where the wiring goes from it. In the same place we find the end devices in which the problem was.
You went through all the fuses, but the current has not changed? Then it is worth looking for a problem in the power circuits of the car, to which the starter, generator and engine ignition system are connected. The point of their connection depends on the car. On some models, they are located right next to the battery, which is certainly convenient. It remains only to start turning them off one by one and do not forget to monitor the ammeter readings.
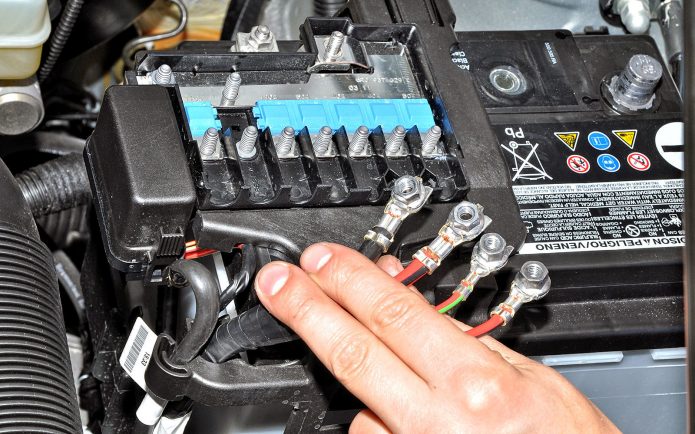

Power circuits are recommended to be checked as a last resort.
Another option is possible: they found a problematic line, but everything is in order with the connected consumers. Understand the wiring itself along this line. The most common situations are: the insulation of the wires has melted due to heat or heating of the engine, there is contact with the body of the car (which is the “mass”, i.e. minus the power supply), dirt or water has got into the connecting elements. You need to localize this place and fix the problem, for example, by replacing the wires or by cleaning and drying the blocks affected by pollution.
The problem of current leakage in a car cannot be ignored. Any electrical equipment is always a fire hazard, especially in a car, because there are combustible substances right there. Turning a blind eye to increased consumption, you will at least have to spend money on a new battery, and the worst that can happen is a fire or even an explosion in the car.
If the article seemed incomprehensible to you, or you do not have sufficient qualifications for working with electrical equipment, it is better to entrust the work to service station professionals.