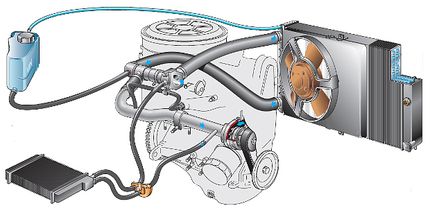
How to check the cooling system
Content
- Signs of a broken cooling system
- Causes of failure of the cooling system
- How to check the engine cooling system
- Maintenance of the internal combustion engine cooling system
Check cooling system There are various methods, and their choice depends on the reason for which it began to work worse. So, when white smoke appears from the exhaust, you need to look for an antifreeze leak, when the system is aired, you need to check the circulation of the coolant and its tightness. it is also worth inspecting the places of possible physical leakage of antifreeze, check the radiator cap and expansion tank, as well as the correct operation of the coolant sensor.
Often, after checking the internal combustion engine cooling system, car owners flush it using special or improvised means. In some cases, replacing antifreeze or antifreeze helps, because over time these process fluids lose their properties, or they were initially incorrectly selected, for example, by a previous car owner.
Signs of a broken cooling system
There are a number of typical signs that clearly indicate that the cooling system is partially or completely out of order and needs to be diagnosed. Among them:
- the appearance of white smoke (in copious amounts) from the exhaust pipe during the operation of the internal combustion engine;
- incorrect operation of the stove and / or air conditioner (insufficiently hot or cold air);
- overheating of the internal combustion engine, especially when driving uphill, including when the car is loaded;
- diagnostics of the ECU with a scanner with the detection of errors after the activation of the Check Engine signal light;
- decrease in the dynamic characteristics of the internal combustion engine, loss of its power;
- boiling antifreeze in the cooling system.
The appearance of at least one of the above signs indicates that the motorist is recommended to diagnose the internal combustion engine cooling system.
Causes of failure of the cooling system
When the first signs of a breakdown appear, you need to look for its cause and, accordingly, carry out repair work.
The reasons for the breakdown of the cooling system can be:
- ingress of coolant (antifreeze or antifreeze) into the combustion chamber of the air-fuel mixture;
- insufficient amount of coolant in the system (the reasons for this, in turn, may be a leak or significant evaporation);
- faulty thermostat;
- partial or complete failure of the pump;
- breakdown of the coolant temperature sensor;
- failure of the fan, its electrical circuit or control components;
- depressurization of the expansion tank cap or radiator cap;
- general depressurization of the system, pressure reduction, its airing.
Each of the listed causes is diagnosed in its own way, in accordance with its faulty elements.
How to check the engine cooling system
Checking a car's internal combustion engine cooling system requires an inspection of its seven components. The main task in this case is to find out if there are gases in the system, check the tightness and determine the leaks, determine the pressure in the system, the correctness of the circulation of the coolant, and also determine the temperature of the operation of the fans and the thermostat.
So, diagnostics of the following components of the cooling system is necessary:
- rubber pipes, joints on clamps;
- the integrity of the radiator housing and the expansion tank of the cooling system;
- mechanical (bearings) and electrical (electric circuit) components of the system fan;
- operation and correct installation of the system pump (pump);
- tightness of the cylinder head gasket;
- serviceability of the coolant temperature sensor;
- coolant level in the system;
- cover of the expansion tank of the system;
- coolant condition.
then we will briefly give information on how to diagnose the above elements and mechanisms.
How to check gases in the cooling system
An appropriate check is to determine the presence of moisture in the exhaust gases and their presence in the cooling system.
White exhaust fumes
Often, the unsatisfactory technical condition of the cooling system and the internal combustion engine as a whole is signaled by white exhaust gases. They are formed as a result of the fact that antifreeze (coolant) enters the combustion chamber from the cooling system, where it is diluted in the air-fuel mixture and burns with it. usually, this is due to a broken cylinder head gasket (cylinder head).

White smoke from the exhaust pipe
The main reasons why white smoke comes from the exhaust of a diesel or gasoline car: moisture, coolant in the cylinders, water in the fuel and a violation of the injection system.
Determining that white smoke is the result of antifreeze entering the internal combustion engine is quite simple. To do this, remove the dipstick from its seat in the cylinder block and check the oil. Moreover, both its level and condition. Usually, with a broken cylinder head gasket, the oil will also “leave”, respectively, its level will quickly decrease. The second thing you need to pay attention to is his condition. If antifreeze enters the oil environment, then the oil becomes white and looks like sour cream or cream (depending on the amount and duration of mixing of these two process fluids).
Also, one method to check the exhaust gases for the presence of evaporated coolant in them is to hold a clean white cloth to the exhaust pipe. If there is moisture in the exhaust gases, it means that it has got into the cylinders either from the fuel or from the cooling system (usually this happens when water is used as an antifreeze). If spots with a bluish or yellow tint remain on the napkin, these are traces of “flying away” antifreeze. Usually these stains have a sour smell. Accordingly, additional diagnostics are required.
Checking exhaust gases in the cooling system
With a broken cylinder head gasket, a situation often arises when exhaust gases enter the cooling system. Signs can be very different, but they coincide with those that appear when the system is aired. For example:
- Explicit seething in the expansion tank and / or radiator. This can be checked by removing the cover from one or the other device.
- The oven does not heat well. In the summer, the air conditioner may not work well, since the system works both for heating and for heating, only through different radiators (usually).
- The radiator is partially cold. Moreover, it can have different temperatures in its various parts, namely, above and below.
in order to determine if there are gases in the internal combustion engine cooling system, you can use the same method as when checking the integrity of the cylinder head gasket - use a condom or a balloon. The check is performed according to the following algorithm:
- unscrew the cap of the expansion tank or radiator, depending on which of them the steam and atmospheric valves are located;
- put a rubber ball on the neck of the expansion tank or radiator, respectively;
- start the internal combustion engine first at idle, and then a little more (the higher the speed, the more intense the gases will be released), up to approximately 3000 ... 5000 rpm;
- if during operation the condom or ball began to fill with exhaust gases, it means that the cylinder head gasket is broken.
It is not recommended to use a car with an airy (gassed) cooling system, at least in the long term, since this is fraught with serious overheating of the internal combustion engine and its partial or complete failure.
How to check for a leak
Also, one common problem with a car's internal combustion engine cooling system is its depressurization. Because of what, a fluid leak or airiness appears (although it can occur for other reasons). Depressurization can occur in a variety of places, but most often at the junction of pipes.

Why does antifreeze go
Why does the level of antifreeze in the system constantly decrease? How to find the cause and troubleshoot. Read more about this and more in this article.
Checking the tightness of the cooling system
The coolant leaves precisely because of the depressurization of the system. So, in order to check the tightness, you need to revise the following elements:
- housing and / or cover of the expansion tank of the internal combustion engine cooling system;
- thermostat seal;
- pipes, hoses, clamps and connections in the cooling system (depending on the specific vehicle and internal combustion engine);
- radiator housing;
- gland seal of the pump and its gasket;
- cylinder head gasket.
The presence of leaks is determined visually, by the presence of wet spots or by using an ultraviolet test. There is a special fluorescent composition on sale that can be added to antifreeze before pouring it into the system. also, for many modern antifreezes, such additives are initially included in their composition from the factory. The use of fluorescent additives will provide additional convenience in diagnosis, since in the event of a coolant leak, it will be enough to use an ultraviolet lamp to localize the damage site, which will significantly reduce the time and effort of the car owner or the master to localize the leak.
System pressure
The cooling system must always be pressurized. This is necessary in order to raise the boiling point of the coolant, since it is known from the laws of physics that the boiling point rises as its pressure rises. In most modern cars, the temperature of antifreeze at normal operating temperature of the internal combustion engine is about + 80 ° С ... + 90 ° С. Accordingly, if depressurization occurs, the pressure will drop, and with it the boiling point of the coolant will also decrease. By the way, the boiling point of old antifreeze is lower than freshly poured, so the coolant must be changed according to the regulations.
However, there is also the opposite problem, when the pressure in the cooling system increases significantly. Usually this situation occurs due to the fact that the air valve in the radiator cap or expansion tank is faulty (on different machines this valve can be installed on one or the other cap). How to check it and what it is for - read in the next section.
Excessive pressure is dangerous because even a new antifreeze, designed for a boiling point of about + 130 ° C, can boil under such conditions, with all the ensuing consequences. Therefore, if a similar situation is observed in the car, it is recommended to simply replace the radiator cap with a new one. As a last resort, you can try to clean and repair the old one, but this is not the best idea.
Radiator cover
As mentioned above, the pressure in the cooling system is not constant, and increases as the liquid heats up. Adding antifreeze is carried out through the radiator cap or through the expansion tank cap. The radiator cap has two valves in its design - bypass (another name is steam) and atmospheric (inlet). A bypass valve is needed to smoothly control the pressure inside the system. It is used to release excess pressure and maintain the pressure at that level. It is used during the operation of the internal combustion engine. The task of the atmospheric valve is the opposite, and is to ensure the gradual admission of air into the system through the cover in the process of cooling the coolant in the system. Usually, the minimum value is around 50 kPa (on old Soviet cars), and the maximum is about 130 kPa (on modern foreign cars).

How to check the radiator cap
If the engine cooling radiator cap breaks, not only can antifreeze leak, but the entire cooling system may not work correctly. in order to quickly check the cap for pressure you need... Read more
Checking the cooling system includes, among other things, an audit of the radiator cap and the mentioned valves included in its design. In addition to them, you need to check its general condition (thread wear, surface wear, cracks, corrosion). you also need to check the spring of the cover and its sealing connection. If the cover does not work correctly, then when the antifreeze is heated, the pipes and even the radiator will swell, and when cooled, they will shrink. Be that as it may, such a deformation will negatively affect both the state of the radiator itself and the operation of the system as a whole.
Cooling fan check
Before checking the cooling system fan, it must be borne in mind that there are three types of its drive - mechanical, hydromechanical and electric. The mechanical drive was used in older carbureted cars and was driven by a tension belt connected to the crankshaft.
Hydromechanical drive involves the use of a hydraulic drive, that is, a hydraulic system, which is quite rare. The fan is driven by a viscous coupling. It transmits torque from the crankshaft to the fan. The viscous coupling adjusts the fan speed by getting the fill fluid, silicone, into the oil. The hydraulic clutch regulates the fan speed due to the amount of fluid in it.
The most common cooling fan drive is electric. The control is carried out by the ECU based on information from several sensors, including the coolant temperature sensor.
The information listed above is necessary in order to understand what to check in a particular case. So, in the simplest mechanical drive, you can check the belt tension, the integrity of the fan bearings, its impeller, and its cleanliness.
For fans controlled by a viscous or hydraulic clutch, it is also necessary to check the rotation bearings, the condition of the impeller. However, the most important thing is the operation of the couplings. It is better not to do it yourself, but to seek help from a car service, since additional equipment is needed for checking and dismantling.
Diagnostics of the most common electric fan drive involves checking the following components:
- coolant temperature sensor;
- fan switch relay;
- fan electric motor;
- bearings and fan impeller;
- the presence of a signal and power from the computer.
To do this, you need to use a conventional electronic multimeter, included in the DC voltage measurement mode.
How to check the coolant circulation
A pump and a thermostat are responsible for circulation. Therefore, if its performance is impaired, then the pressure in the cooling system will change. So a mandatory check point is to check for pump malfunctions and check the thermostat. In addition, circulation is disturbed if the radiator is clogged with antifreeze decay products, so it is also subject to mandatory checks.
Thermostat
The thermostat allows the internal combustion engine to warm up faster and allow the coolant to reach operating temperature in the cold season, and prevent the engine from overheating in the warm season. Checking this one is quite simple, without even dismantling it from the car. However, before that, the thermostat must be found. usually, the thermostat is located behind the radiator, and is connected to it by a thick pipe, which should be guided by. The check is performed according to the following algorithm:
- start the internal combustion engine at idle and let it work in this mode for one or two minutes, so that the temperature of the antifreeze does not exceed + 70 ° C;
- open the hood and check to the touch the pipe from the radiator to the thermostat, it should be cold;
- when the set temperature of the coolant is exceeded (approximately + 80 ° С ... + 90 ° С), the thermostat should work and start the antifreeze in a large circle;
- while said pipe must be heated to the appropriate temperature.
If during the test the thermostat does not open or it is open from the very beginning, it is necessary to carry out additional diagnostics after it has been dismantled. Do this in a pot of hot water and a thermometer.
The thermostat may fail completely (which happens not so often), or it may simply be jammed due to debris. In this case, it can simply be cleaned and reinstalled, but it is better to change it to a new one.
Radiator
Checking the radiator is to find out if there is a leak or a plug in its body and whether it effectively cools the antifreeze. Accordingly, for verification, you need to carefully examine the radiator housing (when it is cold), as well as its connections with the corresponding pipes. If there are microcracks, the coolant will seep through them, since the antifreeze is very fluid. For example, you can find drops of it on the pavement (or other surface) after a long car park.
The efficiency of the radiator can also be checked by the fact that if all other elements of the cooling system are operating normally, then most likely the radiator is simply clogged from the inside and is unable to properly perform its functions. In this case, you can clean either the entire cooling system as a whole (Whatever it is, it will not hurt), or dismantle the radiator (if possible) and clean it separately from the outside and from the inside.
Checking the coolant temperature sensor
In all modern cars, the engines of which are controlled by an electronic unit (ECU), there is a coolant temperature sensor. It is necessary in order to transmit the relevant information to the ECU, which in turn corrects other work-related signals.

Checking the coolant temperature sensor
Checking the vehicle's internal combustion engine coolant temperature sensor is done using a multimeter. Depending on the method, additional resources will also be required, but the presence of tabular and nominal data on resistance is mandatory Read more
The coolant temperature sensor (abbreviated as DTOZH) is a thermistor, that is, a resistor that changes its internal electrical resistance depending on how the temperature of its sensing element changes. The last one is also in the coolant line to perform the corresponding functions. Checking the sensor is performed using an electronic multimeter switched to ohmmeter mode, that is, to the mode of measuring electrical resistance.
Coolant condition
First of all, you need to remember that any automaker recommends a certain type of antifreeze for the cars it produces. And some of them can be mixed with each other, and some are absolutely impossible! Accordingly, you need to use the recommended class of antifreeze. In addition, there is a list of routine maintenance, which includes the periodic replacement of the coolant. On average, it is recommended to do this once every two years.
When checking the cooling system, you need to pay attention to the level and condition of antifreeze. The level can be controlled by the corresponding MIN and MAX marks on the walls of the expansion tank. Moreover, it is equally harmful when there is very little liquid and when it is in excess. However, usually it gradually disappears, so antifreeze or antifreeze must be added periodically.
Also, when monitoring the coolant, it is important to pay attention to its condition. namely, it should be as clean and transparent as possible. If there are a lot of impurities and / or debris in the antifreeze, then it will lose some of its performance characteristics, namely, its boiling point will decrease with all the ensuing consequences. You also need to pay attention to the presence of an oil film on the surface of the liquid in the expansion tank. If it takes place, then the fluid should be replaced, and the system should be additionally diagnosed in order to localize the place from where the oil seeps into the antifreeze.
The last check in this vein is the smell. Usually, new antifreeze has a sweet smell. If, instead, the coolant gives off a burning smell and has a burnt smell, then this means that it is partially out of order and it is better to replace it.
Maintenance of the internal combustion engine cooling system
usually, cooling system problems are associated with untimely or poor-quality maintenance of its individual elements or the use of inappropriate antifreeze. Accordingly, in order for the cooling system to work properly and perform its functions in the long term, it is necessary to periodically perform its maintenance and diagnostics. These procedures include:
- use of antifreeze, the type of which is prescribed by the vehicle manufacturer;
- timely replacement of the coolant;
- checking the tightness of the system, the pressure in it;
- the correct operation of individual components, such as a pump, radiator, expansion tank, pipes, clamps;
- periodic flushing of the system with appropriate means;
- diagnostics of the coolant temperature sensor.
Remember that preventive measures are always less laborious and take less time to complete. In addition, a good cooling system increases the overall resource of the car's internal combustion engine.