How does an Electric Vehicle Engine work?
Content
No more cylinders, pistons and exhaust gases: an electric car's engine is built around a set of parts designed to convert electricity into mechanical energy by creating a magnetic field.
WHAT IS AN ELECTRIC MOTOR?
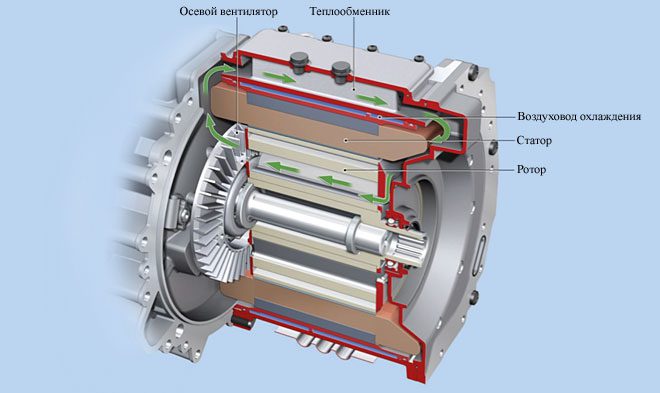
An electric car's engine is powered by a physical process developed in the late 19th century. This process consists in using current to create a magnetic field on a stationary part of the machine ("stator"), which, as it moves, sets the rotating part ("rotor") in motion. We'll spend more time on these two parts later in this article.
ELECTRIC MOTOR PRINCIPLE
What is the difference between a heat engine and an electric motor? The two terms are often used interchangeably. Therefore, it is important to distinguish between them from the very beginning. Although they are now used almost synonymously, in the automotive industry, the term "electric motor" refers to a machine that converts energy into mechanical (and therefore motion), and a heat engine performs the same task, but in particular using thermal energy. When we talk about converting thermal energy into mechanical energy, we are talking about combustion, not electricity.
Thus, the type of converted energy determines the type of motor: thermal or electric. With regard to electric vehicles, since mechanical energy is generated by electricity, the term "electric motor" is used to describe the system that drives an electric vehicle. This is called cravings.
HOW DOES AN ELECTRIC MOTOR WORK IN AN ELECTRIC VEHICLE?
Now that it is established that we are talking about electric motors here and not about thermal electric motors, let's take a look at how an electric motor works in an electric vehicle.
Today, electric motors are used in many household items. Those equipped with direct current (DC) motors have fairly basic functions. The motor is directly connected to a power source, so its rotation speed is directly dependent on the amperage. While these electric motors are easy to manufacture, they do not meet the power, reliability, or size requirements of an electric vehicle. However, they can be used to control wipers, windows and other small mechanisms inside the car.
STATOR AND ROTOR
To understand how an electric vehicle works, you need to become familiar with the physical components of its electric motor. It starts with a good understanding of how the two main parts work: the stator and the rotor. An easy way to remember the difference between the two is that the stator is "static" and the rotor is "spinning". In an electric motor, the stator uses energy to create a magnetic field, which then turns the rotor.
How, then, does an electric motor work on an electric car? ? This requires the use of alternating current (AC) motors, which require the use of a conversion circuit to convert the direct current (DC) supplied by the battery. Let's look at two types of current.
ELECTRIC VEHICLE: ALTERNATIVE CURRENT (AC) VERSUS DC (DC)
First of all, in order to understand how an electric car engine works, it is important to know the difference. between alternating current and direct current (electric currents).
There are two ways electricity travels through a conductor. Alternating current (AC) refers to an electrical current in which electrons periodically change direction. Direct current (DC), as the name suggests, only flows in one direction.
In car batteries, electric works with constant current. As for the main motor of an electric vehicle (which provides traction for the vehicle), this direct current, however, must be converted to alternating current using an inverter.
What happens after this energy reaches the motor? It all depends on the type of motor used: synchronous or asynchronous.
