How does the engine lubrication system work?
Content
Engine oil serves a vital purpose: It lubricates, cleans, and cools the many moving parts of an engine that go through thousands of cycles per minute. This reduces wear on engine components and ensures that all components operate efficiently at controlled temperatures. The constant movement of fresh oil through the lubrication system reduces the need for repairs and prolongs engine life.
Engines have dozens of moving parts and they all need to be well lubricated to ensure smooth and stable operation. As it passes through the engine, the oil travels between the following parts:
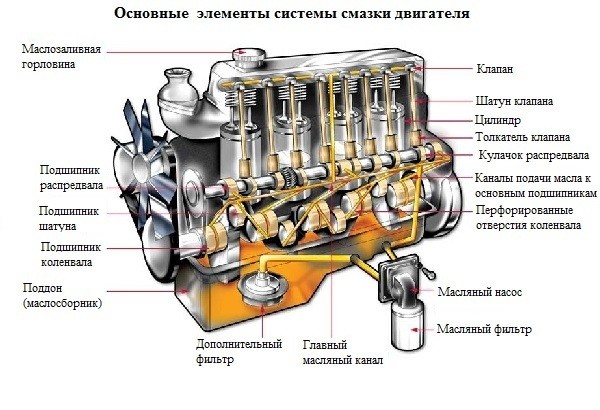
oil collector: The oil pan, also known as the sump, is usually located at the bottom of the engine. Serves as an oil reservoir. Oil accumulates there when the engine is turned off. Most cars have four to eight liters of oil in their sump.
Oil pump: The oil pump pumps oil, pushing it through the engine and providing constant lubrication to the components.
Pickup tube: Powered by the oil pump, this tube draws oil from the oil pan when the engine is turned on, directing it through the oil filter throughout the engine.
Pressure relief valve: Regulates oil pressure for constant flow as load and engine speed change.
The oil filter: Filters oil to trap debris, dirt, metal particles and other contaminants that can wear and damage engine components.
Spurt holes and galleries: Channels and holes drilled or cast in the cylinder block and its components to ensure even distribution of oil to all parts.
Settler types
There are two types of sedimentation tanks. The first is a wet sump, which is used in most cars. In this system, the oil pan is located at the bottom of the engine. This design is convenient for most vehicles because the sump is located close to the oil intake and is relatively inexpensive to manufacture and repair.
The second type of crankcase is the dry sump, which is most commonly seen on high performance vehicles. The oil pan is located elsewhere on the engine than at the bottom. This design allows the car to drop lower to the ground, which lowers the center of gravity and improves handling. It also helps prevent oil starvation if oil splashes out of the intake pipe during high cornering loads.
What does motor oil do
The oil is designed to clean, cool and lubricate engine components. The oil coats the moving parts in such a way that when they touch, they slide rather than scratch. Imagine two metal pieces moving against each other. Without oil, they will scratch, scuff, and cause other damage. With oil in between, the two pieces slide with very little friction.
The oil also cleans the moving parts of the engine. During the combustion process, contaminants are formed, and over time, tiny metal particles can accumulate when the components slide against each other. If the engine is leaking or leaking, water, dirt, and road debris can also get into the engine. The oil traps these contaminants, from where they are then removed by the oil filter as the oil passes through the engine.
The intake ports spray oil on the bottom of the pistons, which creates a tighter seal against the cylinder walls by creating a very thin liquid layer between the parts. This helps improve efficiency and power as the fuel in the combustion chamber can burn more completely.
Another important function of the oil is that it removes heat from the components, extending their life and preventing the engine from overheating. Without oil, the components will scratch each other as bare metal contacts metal, creating a lot of friction and heat.
Oil types
Oils are either petroleum or synthetic (non-petroleum) chemical compounds. They are typically a mixture of various chemicals that includes hydrocarbons, polyintrinsic olefins, and polyalphaolefins. Oil is measured by its viscosity or thickness. The oil must be thick enough to lubricate the components, yet thin enough to pass through galleries and between narrow gaps. Ambient temperature affects oil viscosity, so it must maintain efficient flow even in cold winters and hot summers.
Most vehicles use conventional petroleum-based oil, but many vehicles (especially performance-oriented ones) are designed to run with synthetic oil. Switching between them can cause problems if your engine isn't designed for one or the other. You may find that your engine begins to burn oil that enters the combustion chamber and burns off, often producing telltale blue smoke from the exhaust.
Synthetic Castrol oil offers certain benefits to your vehicle. Castrol EDGE is less sensitive to temperature fluctuations and can help improve fuel economy. It also reduces friction in engine parts compared to petroleum-based oils. Synthetic oil Castrol GTX Magnatec extends engine life and reduces the need for maintenance. Castrol EDGE High Mileage is specially formulated to protect older engines and improve their performance.
Rating oils
When you see a box of oil, you will notice a set of numbers on the label. This number indicates the grade of oil, which is important in determining which oil to use in your vehicle. The grading system is determined by the Society of Automotive Engineers, so sometimes you can see the SAE on the oil box.
SAE distinguishes two grades of oil. One for viscosity at low temperature and the second grade for viscosity at high temperature, usually the average operating temperature of the engine. For example, you will see an oil with the designation SAE 10W-40. 10W tells you that the oil has a viscosity of 10 at low temperatures and a viscosity of 40 at high temperatures.
The score starts at zero and increases in increments of five to ten. For example, you will see oil grades 0, 5, 10, 15, 20, 25, 30, 40, 50, or 60. After the numbers 0, 5, 10, 15, or 25, you will see the letter W, which means winter. The smaller the number in front of W, the better it flows at lower temperatures.
Today, multigrade oil is widely used in cars. This type of oil has special additives that allow the oil to function well at various temperatures. These additives are called viscosity index improvers. In practical terms, this means that vehicle owners no longer need to change their oil every spring and autumn to adapt to changing temperatures, as they used to.
Oil with additives
In addition to viscosity index improvers, some manufacturers include other additives to improve oil performance. For example, detergents may be added to clean the engine. Other additives may help prevent corrosion or neutralize acid by-products.
Molybdenum disulfide additives were used to reduce wear and friction and were popular until the 1970s. Many additives have not been proven to improve performance or reduce wear and are now less common in motor oils. Many older vehicles will have zinc added, which is essential for oil, given that the engine used to run on leaded fuel.
When the lubrication system is not working properly, serious engine damage can result. One of the most obvious problems is engine oil leakage. If the problem is not corrected, the vehicle can run out of oil, causing rapid engine damage and requiring costly repairs or replacements.
The first step is to locate the oil leak. The cause may be a damaged or leaking seal or gasket. If it's an oil pan gasket, it can be easily replaced on most vehicles. A head gasket leak can permanently damage a vehicle's engine, and in the event of a leak, the entire head gasket will need to be replaced. If your coolant is a light brown color, this indicates that the problem is with a blown cylinder head gasket and oil leaking into the coolant.
Another problem is the oil pressure light comes on. Low pressure can occur for various reasons. Filling the car with the wrong type of oil can result in low pressure in summer or winter. A clogged filter or a faulty oil pump will also reduce oil pressure.
Maintenance of your lubrication system
To keep the engine in good condition, it is necessary to service the lubrication system. This means changing the oil and filter as recommended in the owner's manual, which usually happens every 3,000-7,000 miles. You should also only use the grade of oil recommended by the manufacturer. If you notice any problems with the engine or an oil leak, you should immediately service the car with high-quality Castrol oil by an AvtoTachki field specialist.
