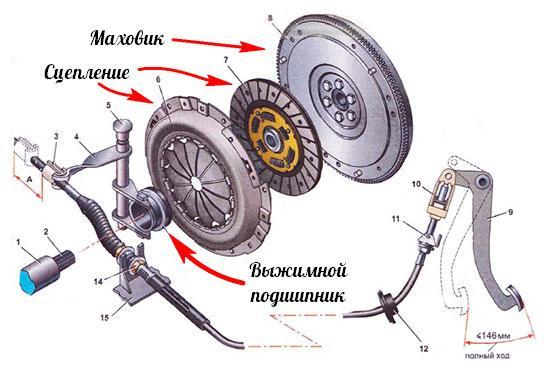
How does a throwout bearing work?
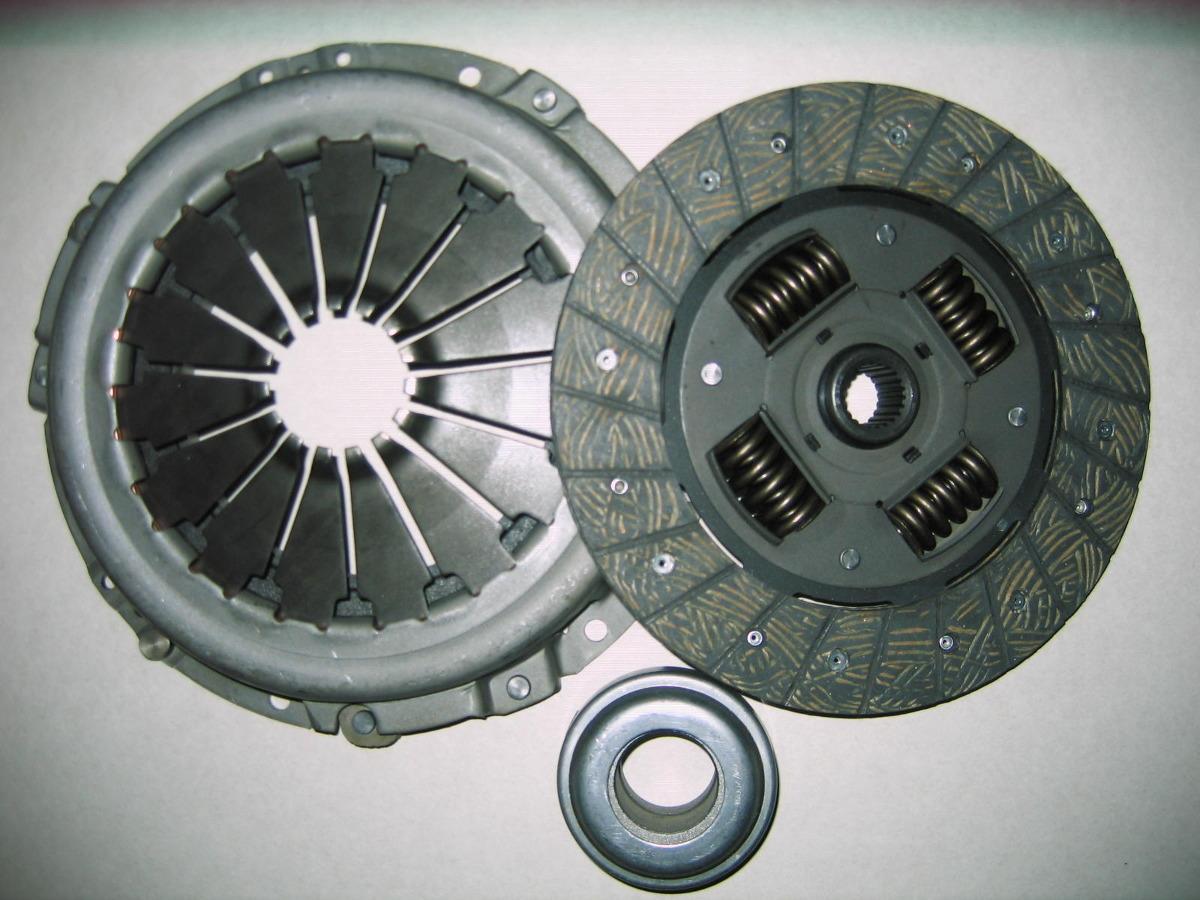 Its task is to transfer the pressure of the clutch pedal to the plates of the central pressure ring spring to engage or disengage the clutch.
Its task is to transfer the pressure of the clutch pedal to the plates of the central pressure ring spring to engage or disengage the clutch.
 The release bearing is usually in the form of a special angular contact ball bearing. Older solutions used self-aligning bearings (usually thrust ball bearings before). Currently, these are the so-called centrally controlled bearings. The self-aligning bearing must always have sufficient clearance, which means that in the absence of pressure on the clutch pedal, its end (working) surface should not come into contact with the spring sheets of the central pressure ring. The surface of the release bearing may be flat or convex. As for bearings with central control, they are either backlash or backlash without play. In the latter case, the initial load on the end is from 80 to 100 N.
The release bearing is usually in the form of a special angular contact ball bearing. Older solutions used self-aligning bearings (usually thrust ball bearings before). Currently, these are the so-called centrally controlled bearings. The self-aligning bearing must always have sufficient clearance, which means that in the absence of pressure on the clutch pedal, its end (working) surface should not come into contact with the spring sheets of the central pressure ring. The surface of the release bearing may be flat or convex. As for bearings with central control, they are either backlash or backlash without play. In the latter case, the initial load on the end is from 80 to 100 N.
In self-aligning bearings with central control, their front ring can move in the range of several millimeters and thus be located in the center of the so-called bearing surface.
A classic, characteristic sign of a release bearing problem, especially play, is the appearance of noise after pressing the clutch pedal. The loud release bearing does the trick for a while. However, if left in this state, it may become blurred or even completely destroyed. A stuck end raceway in contact with the center leaf springs is subject to accelerated wear. The central spring itself also suffers. This can be manifested by clutch jerks. However, if the release bearing is damaged, it will usually not be possible to disconnect the drive between the engine and the gearbox, i.e., turn off the clutches.
