How car headlights work
Content
Lighthouse history
When cars were first made, the headlight was more like a lamp with an enclosed acetylene flame that the driver had to manually light. These first headlights were introduced in the 1880s and gave drivers the ability to drive more safely at night. The first electric headlights were made in Hartford, Connecticut and introduced in 1898, although they were not mandatory on new car purchases. They had a short lifespan due to the incredible amount of energy needed to produce enough light to light up a roadway. When Cadillac integrated a modern electrical system into cars in 1912, headlights became standard equipment on most cars. Modern cars have brighter headlights, last longer, and have many facets; e.g. daytime running lights, dipped beam and high beam.
headlight types
There are three types of headlights. Incandescent lamps use a filament inside the glass that emits light when heated with electricity. It takes a surprising amount of energy to produce such a small amount of light; as anyone who has drained their battery by accidentally leaving their headlights on can attest. Incandescent lamps are being replaced by more energy efficient halogen lamps. Halogen headlights the most common headlights in use today. Halogens have replaced incandescent bulbs because in an incandescent bulb, more energy is converted into heat than into light, resulting in wasted energy. Halogen headlights use much less energy. Today, some car brands, including Hyundai, Honda and Audi, use High Intensity Discharge Headlights (HID).
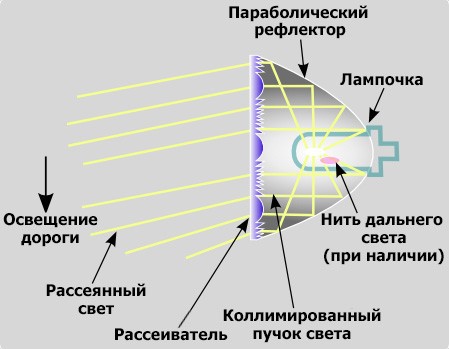
Components of a halogen headlight or incandescent lamp
There are three types of headlight housings that use halogen or incandescent bulbs.
First, lens optics headlight, is designed so that the filament in the light bulb is at or near the focus of the reflector. In them, prismatic optics molded into the lens refract light, which spreads it upward and forward to provide the desired light.
Slot machine reflector headlight optics also has a filament in the bulb at the base of the light, but uses multiple mirrors to properly distribute the light. In these headlights, the lens is used simply as a protective cover for the bulb and mirrors.
Projector lamps are similar to the other two types, but may also have a solenoid that, when activated, turns to turn on the low beam. In these headlights, the filament is located as an image plane between the lens and the reflector.
HID Headlight Components
In these headlights, a mixture of rare metals and gases is heated to produce a bright white light. These headlights are about two to three times brighter than halogen headlights and can be very annoying to other drivers. They are distinguished by a bright white glow and a blue tint of the contour. These headlights are much more energy efficient and produce brighter light while consuming less energy. HID headlights use about 35W, while halogen bulbs and older incandescent bulbs use about 55W. However, HID headlights are more expensive to manufacture, so they are mostly seen on high-end vehicles.
Export
Like any other part of the car, headlights begin to lose their effectiveness after a certain time. Xenon headlights last longer than halogen headlights, although both will exhibit a distinct lack of brightness when overused, or longer than their recommended lifespan, which is about a year for halogen and twice that for HID. Some headlights in the past were fairly simple repairs for a home mechanic. He or she can simply buy a light bulb from a parts store and then follow the instructions in the owner's manual. However, new car models are much more complex and can be harder to get to. In these cases, it is best to contact a licensed headlight repair mechanic.
Common Headlight Problems
There are a few common problems with today's headlights. They can lose brightness due to too much use, dirty or cloudy lens caps, and sometimes a dim headlight can be a sign of an alternator problem. It could also be a cracked or broken light bulb or a bad filament. A quick inspection by a licensed mechanic for diagnostics will light the way.
How high beams work and when to use them
The difference between low and high beam headlights lies in the distribution of light. When the dipped beam is on, the light is directed forward and downward to illuminate the roadway without disturbing drivers traveling in the opposite direction. However, high beam headlights are not limited in direction of light. That is why the light goes both upwards and forwards; High beam is designed to view the entire environment, including possible dangers on the road. With high beams providing XNUMX feet more visibility, the driver can see better and be safer. However, this will affect the visibility of those driving in front of the vehicle and should only be used in low traffic areas.
Headlight position
The headlights of the vehicle must be positioned in such a way as to provide the driver with optimum visibility without interfering with those traveling in the opposite direction. In older cars, the lens is adjusted with a screwdriver; on newer vehicles, adjustments must be made from inside the engine compartment. These adjustments allow you to tilt the lenses in different ways to create optimal lighting conditions. While technically not a headlight repair, it is not always easy to get the correct headlight angle and position. A licensed mechanic has the experience to make this adjustment and ensure safer night driving.

