How modern airbags work
Content
Nowadays, you will not surprise anyone with the presence of an airbag in the car. Many reputable automakers already have it in the basic configuration of most models. Together with the seat belt, the airbags protect the occupants very reliably in the event of a collision and reduce the number of deaths by 30%.
From what it all began
The idea to use airbags in cars was implemented in the early 70s of the last century in the United States. The impetus was the invention by Allen Breed of a ball sensor - a mechanical sensor that determined a sharp decrease in speed at the moment of impact. And for the rapid injection of gas, the pyrotechnic method turned out to be optimal.
In 1971, the invention was tested in a Ford Taunus. And the first production model equipped with an airbag, a year later, was the Oldsmobile Toronado. Soon the innovation was picked up by other automakers.
The introduction of pillows was the reason for the massive abandonment of the use of seat belts, which in America were not popular anyway. However, it turned out that a gas cylinder firing at a speed of about 300 km / h can cause significant injury. In particular, cases of fractures of the cervical vertebrae and even a set of deaths were recorded.
The experience of the Americans was taken into account in Europe. Approximately 10 years later, Mercedes-Benz introduced a system in which the airbag did not replace, but complemented the seat belts. This approach has become generally accepted and is still used today - the airbag is triggered after the belt is tightened.
In the mechanical sensors used at first, the weight (ball) shifted at the moment of collision and closed the contacts that triggered the system. Such sensors were not accurate enough and relatively slow. Therefore, they were replaced by more advanced and faster electromechanical sensors.
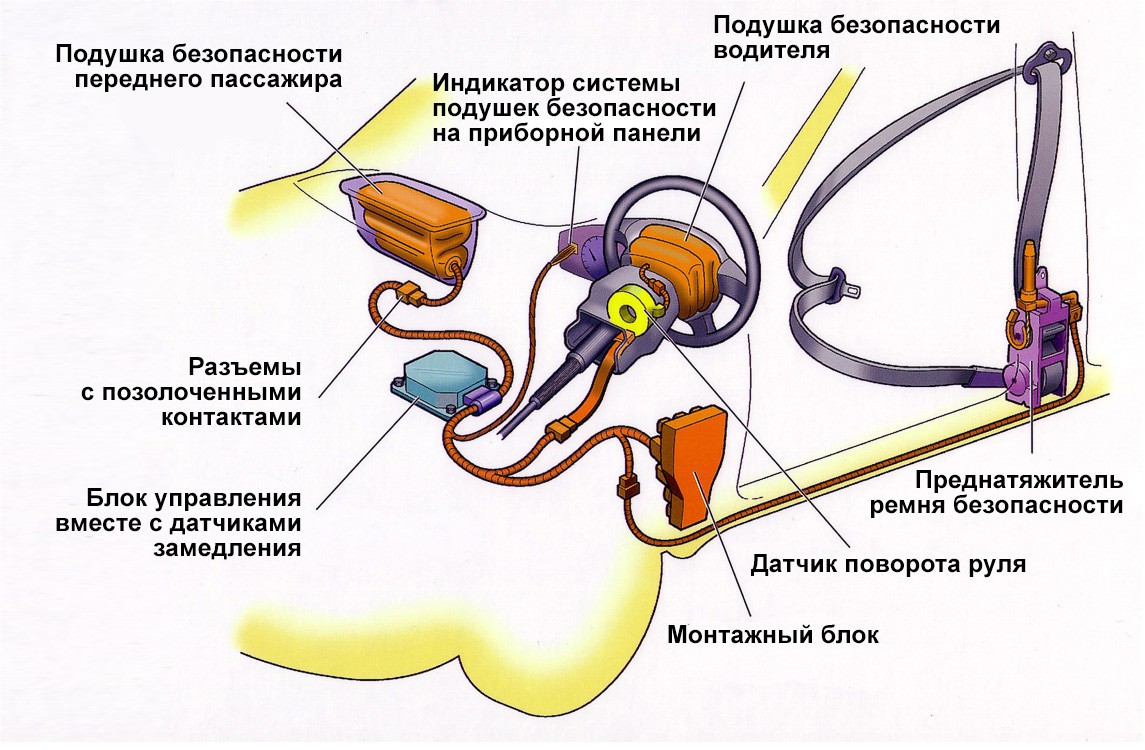
Modern air bags
The airbag is a bag made of durable synthetic material. When triggered, it almost instantly fills with gas. The material is coated with a talc-based lubricant, which promotes accelerated opening.
The system is complemented by shock sensors, a gas generator and a control unit.
Shock sensors do not determine the force of impact, as you might think, judging by the name, but acceleration. In a collision, it has a negative value - in other words, we are talking about the speed of deceleration.
Under the passenger seat there is a sensor that detects whether a person is sitting on it. In its absence, the corresponding pillow will not work.
The purpose of the gas generator is to instantly fill the air bag with gas. It can be solid fuel or hybrid.
In solid propellant, with the help of a squib, a charge of solid fuel is ignited, and combustion is accompanied by the release of gaseous nitrogen.
In a hybrid, a charge with a compressed gas is used - as a rule, it is nitrogen or argon.
After starting the internal combustion engine, the control unit checks the health of the system and issues a corresponding signal to the dashboard. At the time of the collision, it analyzes the signals from the sensors and, depending on the speed of movement, the rate of deceleration, the place and direction of the impact, triggers the activation of the necessary airbags. In some cases, everything can be limited only to the tension of the belts.
The control unit usually has a capacitor, the charge of which can set fire to the squib when the on-board network is completely turned off.
The air bag actuation process is explosive and occurs in less than 50 milliseconds. In modern adaptive variants, two-stage or multi-stage activation is possible, depending on the strength of the blow.
Varieties of modern airbags
At first, only frontal air bags were used. They remain the most popular to this day, protecting the driver and the passenger sitting next to him. The driver's airbag is built into the steering wheel, and the passenger airbag is located near the glove compartment.
The passenger's front airbag is often designed to be deactivated so that a child seat can be installed in the front seat. If it is not turned off, the blow of an opened balloon can cripple or even kill a child.
Side air bags protect the chest and lower torso. They are usually located in the back of the front seat. It happens that they are installed in the rear seats. In more advanced versions, it is possible to have two chambers - a more rigid lower one and a softer one to protect the chest.
In order to reduce the likelihood of chest defects, the pillow happens to be built directly into the seat belt.
In the late 90s, Toyota was the first to use head airbags or, as they are also called, “curtains”. They are mounted in the front and rear of the roof.
In the same years, knee air bags appeared. They are placed under the steering wheel and protect the driver's legs from defects. It is also possible to protect the legs of the front passenger.
Relatively recently, a central cushion has been used. In the event of a side impact or rollover of the vehicle, it prevents injury from people colliding with each other. It is placed in the armrest of the front or back of the rear seat.
The next step in the development of a road safety system will probably be the introduction of an airbag that deploys on impact with a pedestrian and protects his head from hitting the windshield. Such protection has already been developed and patented by Volvo.
The Swedish automaker is not going to stop at this and is already testing an external cushion that protects the entire car.
Air bag must be used correctly
When the bag suddenly fills with gas, hitting it can result in serious injury to a person and even cause death. The risk of breaking the spine from a collision with a pillow increases by 70% if a person is not seated.
Therefore, a fastened seat belt is a prerequisite for activating the air bag. Usually the system is adjusted so that if the driver or passenger is not seated, the corresponding airbag will not fire.
The minimum allowable distance between a person and the seat of the airbag is 25 cm.
If the car has an adjustable steering column, it is better not to get carried away and not push the steering wheel too high. Incorrect deployment of the airbag can cause serious injury to the driver.
Fans of non-standard taxiing during the firing of the pillow risk breaking their hands. With an incorrect position of the driver's hands, the air bag even increases the likelihood of a fracture compared to those cases where there is only a fastened seat belt.
If the seatbelt is fastened, the chance of injury when the air bag is deployed is small, but still possible.
In rare cases, airbag deployment can cause hearing loss or cause a heart attack. Impact on the glasses can break the lenses, and then there is a risk of damage to the eyes.
Common airbag myths
Hitting a parked car with a heavy object or, for example, a falling tree branch can cause the airbag to deploy.
In fact, there will be no operation, since in this case the speed sensor tells the control unit that the car is stationary. For the same reason, the system will not work if another car flies into a parked car.
A skid or sudden braking can cause the airbag to pop out.
This is absolutely out of the question. Operation is possible with an overload of 8g and above. For comparison, Formula 1 racers or fighter pilots do not exceed 5g. Therefore, neither emergency braking, nor pits, nor sudden lane changes will lead to the air bag shooting out. Collisions with animals or motorcycles also generally do not activate the airbags.