How Exhaust Systems Work
Content
It all starts in the engine
To understand how a car's exhaust works, it is necessary to have a basic understanding of the engine as a whole. An internal combustion engine in its simplest form is a large air pump. It collects in the air, mixes it with fuel, adds a spark, and ignites the air-fuel mixture. The key word here is "combustion". Because the process that makes a vehicle move involves combustion, there is waste, just as there is waste associated with any form of combustion. When a fire is lit in a fireplace, the waste products are smoke, soot and ashes. For an internal combustion system, the waste products are gases, carbon particles and tiny particles suspended in gases, collectively known as exhaust gases. The exhaust system filters these wastes and helps them get out of the car.
While modern exhaust systems are quite complex, this has not always been the case. It wasn't until the passage of the Clean Air Act of 1970 that the government had the ability to set the amount and type of exhaust gases produced by a vehicle. The Clean Air Act was amended in 1976 and again in 1990, forcing automakers to produce cars that meet stringent emission standards. These laws improved air quality in most major US metropolitan areas and led to the exhaust system as we know it today.
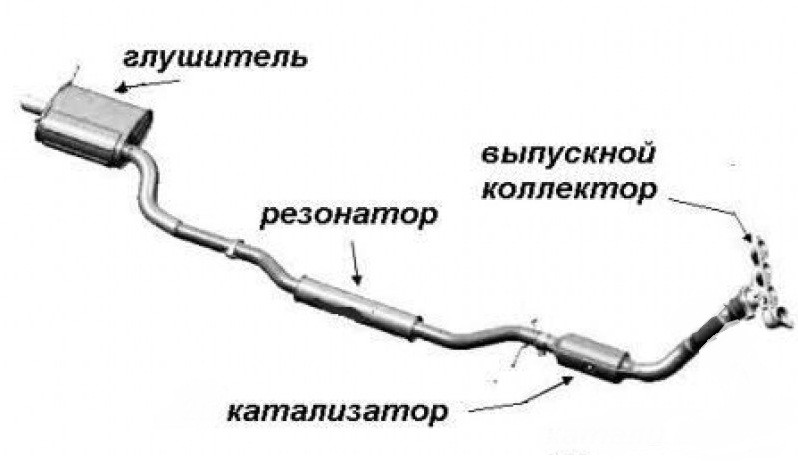
Exhaust system parts
Exhaust valve: The exhaust valve is located in the cylinder head and opens after the combustion stroke of the piston.
Piston: The piston pushes the combustion gases out of the combustion chamber and into the exhaust manifold.
Exhaust manifold: The exhaust manifold carries emissions from the piston to the catalytic converter.
Catalytic converter The catalytic converter reduces the amount of toxins in the gases for cleaner emissions.
Exhaust pipe The exhaust pipe carries emissions from the catalytic converter to the muffler.
Muffler The muffler reduces noise generated during combustion and exhaust emissions.
Essentially, the exhaust system works by collecting waste from the combustion process and then moving it through a series of pipes to different parts of the exhaust system. The exhaust exits the opening created by the movement of the exhaust valve and is directed to the exhaust manifold. In the manifold, the exhaust gases from each of the cylinders are collected together and then forced into the catalytic converter. In the catalytic converter, the exhaust is partially cleaned. Nitrogen oxides are broken down into their respective parts, nitrogen and oxygen, and oxygen is added to carbon monoxide, creating less toxic but still dangerous carbon dioxide. Finally, the tailpipe carries the cleaner emissions to the muffler, which reduces the accompanying noise when the exhaust gases are released into the air.
Diesel engines
There has been a longstanding belief that diesel exhaust is significantly dirtier than unleaded gasoline. That ugly black smoke coming out of the giant truck exhausts looks and smells a lot worse than what comes out of a car muffler. However, regulations on diesel emissions have become much stricter over the past twenty years, and in most cases, as ugly as it may seem, diesel exhaust is as clean as that of a gas-fuelled car. Diesel particulate filters remove 95% of diesel car smoke (source: http://phys.org/news/2011-06-myths-diesel.html), which means you see more soot than anything else. In fact, diesel engine exhaust contains less carbon dioxide than gas engine exhaust. Due to tighter control of diesel emissions as well as increased mileage, diesel engines are more commonly used in smaller vehicles, including Audi, BMW and Jeep models.
The most common symptoms and repair
Exhaust system repairs are commonplace. When there are so many moving parts in one constantly running system, general repairs are inevitable.
Cracked exhaust manifold The vehicle may have a cracked exhaust manifold which will sound like a loud ticking sound next to the engine which will sound like a giant clock.
Faulty Donut Pad: There will also be a loud ticking sound, but this can usually be heard from under the car when the passenger is sitting in the car with the door open.
Clogged catalytic converter: It will manifest itself as a sharp loss of power and a strong smell of something burned.
Rusty exhaust pipe or muffler: The sound of the exhaust coming out of the muffler will become noticeably louder.
Faulty O2 sensor: Check Engine light on dashboard
Modernization of the exhaust system of the car
There are several upgrades that can be made to the exhaust system to improve performance, enhance sound, and increase efficiency. Efficiency is important to the smooth running of a car and these upgrades can be done by certified mechanics who will order replacement exhaust system parts that match the original ones on the car. Speaking of performance, there are exhaust systems that can boost a car's power, and some can even help with fuel economy. This repair will require the installation of a completely new exhaust system. In terms of sound, the car's sound can go from a standard sound to a sound that can best be described as raucous, to the point where the car's sound is comparable to a roar. Don't forget that when you upgrade your exhaust, you need to upgrade your intake as well.