PCV valve
Content
The crankcase ventilation valve (CVKG) or PCV (Positive Crankcase Ventilation) is used to effective use formed in the crankcase gas mixture. The part is installed on most modern models with an injection fuel supply system and takes a nominal part in regulating the composition of the air-fuel mixture. Incorrect operation of the VKG valve leads to to waste of fuel и unstable operation of the internal combustion engine.
We will describe in detail about the device, the principle of operation, breakdowns and methods for checking the PCV valve below.
Where is the PCV valve located and what is it for?
The location of the PCV valve directly depends on the vehicle modification. Typically, the part is built into the valve cover of the internal combustion engine, but can also be placed in a separate housing, combined with the oil separator, close to it. The latter option is actively used in the latest generations and models of BMW and Volkswagen.
You can find the crankcase ventilation valve by a thin flexible pipe extending from it, connected to the air duct in the area between the intake manifold and the throttle.
How the crankcase valve looks like can be seen in the photo with a good example.
Where is the crankcase ventilation valve on a VW Golf 4, click to enlarge
Where is the pcv valve located in the Audi A4 2.0, click to enlarge
Location of KVKG on Toyota Avensis 2.0, click to enlarge
What is the crankcase ventilation valve responsible for?
The main purpose of the PCV valve is crankcase gas volume controlsupplied to the throttle space in various modes of operation of the internal combustion engine. This achieves more precise air dosing to create the optimal ratio of the air-fuel mixture. Additionally KVKG prevents combustion of crankcase gases with a flashback in the intake.
The device and how the crankcase ventilation valve works

VKG valve device: video
Structurally, this part in crankcase ventilation is a bypass valve, consisting of a body with two branch pipes and a movable working element.
In built-in PCV valves, the inlet and outlet openings are blocked by a plunger, and in those located in a separate housing with an oil separator, by membranes. Springs prevent the locking element from moving freely without external influence.
How the VKG valve works
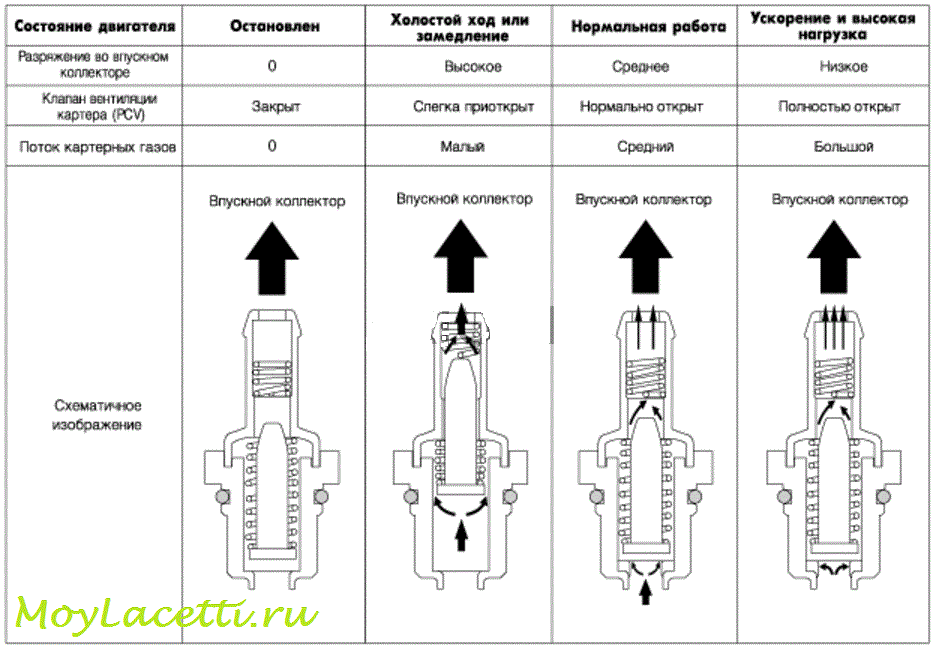
The principle of operation of the PCV valve is based on a change in inlet pressure. It is conditionally possible to distinguish 4 basic states of the KVKG according to the degree of opening and the amount of passing crankcase gases.
The degree of opening of the PCV valve depending on the mode of operation of the internal combustion engine
| Modes | ICE is not running | Idling/Deceleration | Uniform movement, medium speed | Acceleration, high revs |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vacuum in the intake manifold | 0 | high | Secondary | poor |
| PCV valve condition | Closed | ajar | normally open | Fully open |
| Quantity of passing crankcase gases | 0 | Small | Secondary | Large |
From the inlet side, the pressure created by crankcase gases acts on the valve. When it exceeds the spring force, the element blocking the hole (membrane or plunger) moves inward, opening the access of the gas mixture to the filter housing.
VKG valve device in VW Polo
Filling KVKG in Chevrolet Lacetti
At the same time, from the side of the outlet, the valve is affected by a vacuum (pressure below atmospheric), which is created in the intake manifold. Restricting the flow area of the valve allows you to redirect part of the gases from the crankcase, collected under the valve cover, into the space between the air filter and the throttle valve. In the event of a flashback and a sharp drop in vacuum in the intake manifold, the outlet of the KVKG is completely blocked, thereby preventing the ignition of a combustible gas mixture.
What does the PCV valve do?
PCV valve modes
The PCV valve directly affects the operation of the internal combustion engine, optimizing the mixture formation process. By changing the flow area of the channel, it corrects the supply of crankcase gases containing combustible particles into the air channel before and after the throttle. This allows you to use the crankcase ventilation system as efficiently as possible and at the same time prevent the entry of an unaccounted for combustible-air mixture into the intake manifold.
If the crankcase ventilation valve fails, they are fed into the intake in excess, or do not work at all. Moreover, in the first case, this is usually not fixed by any sensors, and in the second case, it leads to attempts at unjustified correction of the air-fuel mixture.
Due to the excess air entering the combustion chamber, the internal combustion engine starts worse, failures are possible during acceleration or in other cases when it is necessary to increase traction. Valve jamming can lead to an increase in fuel consumption and over-enrichment of fuel assemblies, resulting in erratic operation and vibration of the motor at idle.
Valve in the crankcase ventilation system
Signs and Causes of a Broken PCV Valve

ICE speed hang due to PCV valve and troubleshooting: video
Although the crankcase ventilation valve has a simple device, from time to time it still fails or does not work correctly. What are the signs of a broken VKG valve? Most often it is:
- vibration of the internal combustion engine, different from tripling;
- hissing in the intake manifold after progazovka;
- failure in traction from 3000 to 5000 rpm;
- RPM fluctuation.
With concomitant problems in crankcase ventilation, an increase in oil consumption, oiling of the throttle valve and ventilation hoses leading from the crankcase is possible.
What breakdowns of the crankcase gas valve can be?
Usually there is a violation of the tightness of the housing due to mechanical damage (for example, during installation after cleaning) or untimely operation, incomplete opening and closing of the dampers due to their wedging.
So, the main causes of PCV valve failure are destruction or jamming locking elements or external influences.
breakdowns of the crankcase gas valve and their symptoms are indicated in the table.
| breaking | Why appears | Symptoms | What is happening |
|---|---|---|---|
| Depressurization / air leakage |
|
| Unaccounted for DMRV air is sucked into the manifold, crankcase gases completely or partially go outside. |
| Stuck Open/Improved Performance |
|
| Excess crankcase gases with fuel particles enter the intake. During warm-up and load, this mode is optimal, in other internal combustion engines it does not work correctly. |
| Stuck closed/reduced performance |
| The calculated flow of air into the intake is violated. The entire flow of crankcase gases is supplied in front of the throttle valve. |
The CVCG may not work correctly due to malfunctions in the crankcase ventilation system or problems with the CPG. In this case, sharp the volume of crankcase gases increasespassing through the valve, and the likelihood of its rapid oiling. Therefore, before checking the PCV valve, you should make sure that there are no problems that lead to the release of oil through the breather or its extrusion through gaskets and seals.
Check the PCV valve
Diagnostic autoscanner Rokodil ScanX
You can check the PCV valves physical and software method. In the second case, you will need an assistant, a diagnostic scanner or OBD II adapter and a special application for a PC or mobile device. One of the best options is the autoscanner Rokodil ScanX, since it is compatible with all car brands, view the performance of all sensors and systems, gives error tips.
For physical diagnostics, carried out by checking the response of the CVCG to external influences from the instruments, only an open-end wrench is required to remove the valve.
In some cars, namely, new BMW models, the PCV valve is non-removable and non-separable. Check it out physically impossible without destroying the hull. In this case, you can check either using computer diagnostics, or by replacing it with a known-good node.
To check the operation of the crankcase valve, follow this order:

Do-it-yourself VKG valve check Toyota Vitz: video
- Remove the valve from the hole in the valve cover, having previously removed the hose from the outlet pipe.
- Inspect the inlet for dirt, remove if necessary.
- Blow out the valve with your mouth from the outlet side: air should not pass through a working KVKG.
- Reattach the ventilation hose to the outlet.
- Start and warm up the engine.
- Close the valve inlet tightly with your finger. In a serviceable part, this action is accompanied by a click and a vacuum is felt - the finger will “stick” to the hole.
Checking the crankcase ventilation valve is carried out programmatically by the position of the throttle valve at idle.
Checking the PCV valve using computer diagnostics on the example of a Chevrolet Lacetti car:

Professional check of the PCV valve on a Chevrolet Lacetti with computer diagnostics: video
- Unscrew the valve with a 24-mm open-end wrench, after removing the hose from the outlet pipe.
- Attach the hose to the outlet.
- Connect the scanner or OBD II adapter to the diagnostic socket in the passenger compartment.
- Run the program for diagnostics and display the throttle position readings (the actual position of the remote control).
- Start and warm up the engine. In this case, the value of the real position of the remote sensing should be within 35–40 steps.
- Plug the valve inlet with duct tape or have an assistant plug it with your finger. The parameter should increase by about five 5 steps.
- Remove the ventilation hose from the PCV valve outlet. If the CVCG is OK, the actual throttle position will drop to 5 steps. This indicates that the valve was restricting the passage of gases into the intake at idle.
Servicing the crankcase ventilation valve
One of the basic reasons for the incorrect operation of the CVKG is the contamination of the working surfaces. This can be avoided by cleaning the crankcase ventilation valve. every 20–000 km.
Slight oiling of the surface of the KVKG is a natural process. However, if it becomes in oil faster than 10 km, this is a reason for diagnosing the crankcase ventilation system. It is possible that the oil separator or vent hose is clogged.
How and how to clean the PCV valve
Cleaning the PCV valve with WD-40 spray
The following products are best suited for cleaning the PCV valve:
- carburetor or injector cleaner;
- brake cleaner;
- WD-40;
- kerosene or diesel fuel.
When using the agent in the form of an aerosol with a tube, it should be injected through the inlet pipe into the KVKG. Kerosene and diesel fuel can be injected with a syringe or syringe. The flushing procedure must be repeated until all deposits are removed.
After cleaning, you need to check the performance of the PCV valve using one of the methods described above. If flushing does not help, the part need to replace.
Frequently asked questions about the crankcase valve
What is a crankcase ventilation valve?
KVKG - an element of the crankcase ventilation system, structurally representing a membrane or plunger bypass valve.
Where is the crankcase ventilation valve located?
In most models, the KVKG is located in the valve cover of the internal combustion engine (rear or top) or in close proximity to it in a separate housing along with an oil separator.
What is a PCV valve for?
The PCV valve controls the flow of crankcase gases into the intake manifold, directing them in front of the throttle valve. It allows you to optimize the composition of the air-fuel mixture under various operating modes of the internal combustion engine.
How to check the operation of the PCV valve?
The working KVKG is not blown from the outlet side, but passes air from the inlet side. When the inlet of the removed valve is closed on the running and warmed-up internal combustion engine, a click is heard and it is felt how the blocking object (finger) is attracted. If the valve does not pass any of these checks, it can be concluded that the VKG valve is inoperable.
How to determine the breakdown of the crankcase ventilation valve?
A CVCG jammed in the open position leads to excessive enrichment of the air-fuel mixture and unstable operation of the internal combustion engine (revs and troit float) at idle after warming up. If the valve does not open in time or its capacity decreases, the mixture will be lean, and there will be problems with starting and acceleration dynamics will deteriorate.
