Classification of motor oils
Content
- API classification of engine oils
- Classification of engine oils according to ACEA
- SAE classification of engine oils
- Classification of motor oils according to ILSAC
- JASO classification for heavy duty diesel engines
- Engine Oil Specifications for Caterpillar Engines
- Engine oil specifications for Volvo engines
- Engine Oil Specifications for Cummins Engines
Standards and industry organizations such as the American Petroleum Institute (API), the Association of European Automobile Designers (ACEA), the Japan Automobile Standards Organization (JASO) and the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE) set specific standards for lubricants. Each standard defines specifications, physical properties (eg viscosity), engine test results and other criteria for formulating lubricants and oils. RIXX lubricants are fully compliant with API, SAE and ACEA requirements.
API classification of engine oils
The main purpose of the API engine oil classification system is to classify by quality. Based on the categories, a letter designation is assigned to the class. The first letter indicates the type of engine (S - petrol, C - diesel), the second - the performance level (the lower the level, the higher the letter of the alphabet).
API engine oil classification for gasoline engines
| API index | Applicability |
| SG | 1989-91 Engines |
| Ш | 1992-95 Engines |
| SJ | 1996-99 Engines |
| SL | 2000-2003 Engines |
| YOU | engines 2004 — 2011 year |
| Serial number | engines 2010-2018 |
| CH+ | modern direct injection engines |
| JV | modern direct injection engines |
Table "Classification of engine oils according to API for gasoline engines
API SL Standard
SL class oils are suitable for lean-burn, turbocharged and multi-valve internal combustion engines with increased requirements for environmental friendliness and energy saving.
API SM standard
The standard was approved in 2004. Compared to SL, the anti-oxidation, anti-wear and low-temperature properties are improved.
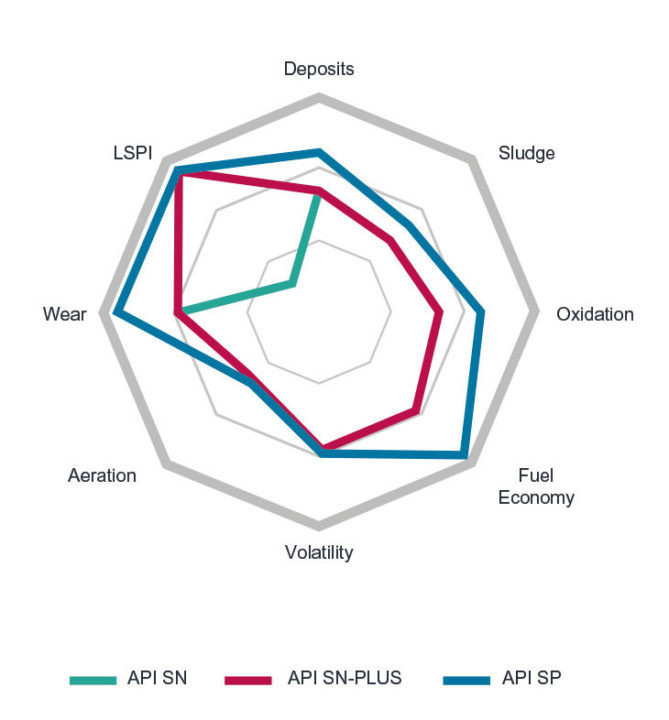
Standard API SN
Approved in 2010. Oils of the SN category have improved antioxidant, detergent and heat-resistant properties, provide high protection against corrosion and wear. Ideal for turbocharged engines. SN oils can qualify as energy efficient and meet the GF-5 standard.
API SN+ standard
The provisional standard was introduced in 2018. Designed for turbocharged engines equipped with direct fuel injection. SN+ oils prevent in-cylinder pre-ignition (LSPI) common to many modern engines (GDI, TSI, etc.)
LSPI (Low Speed This is a phenomenon that is typical for modern GDI, TSI engines, etc., in which at medium loads and medium speeds, the air-fuel mixture spontaneously ignites in the middle of the compression stroke.The effect is associated with the ingress of tiny oil particles into the combustion chamber.
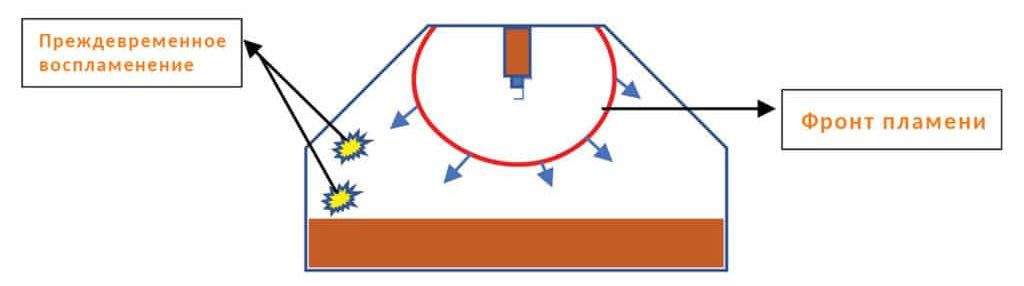
Standard API SP
5W-30SPGF-6A
Introduced May 1, 2020 API SP oils outperform API SN and API SN+ engine oils in the following ways:
- Protection against premature uncontrolled ignition of the air-fuel mixture (LSPI, Low Speed Pre Ignition);
- Protection against high temperature deposits in the turbocharger;
- Protection against high temperature deposits on the piston;
- Timing chain wear protection;
- Sludge and varnish formation;
API SP class engine oils can be resource-saving (preservative, RC), in which case they are assigned the ILSAC GF-6 class.
| Test | API SP-RC standard | API CH-RC |
|---|---|---|
| VIE sequence (ASTM D8114). Improvement in fuel economy in %, new oil / after 125 hours | ||
| xW-20a | 3,8% / 1,8% | 2,6% / 2,2% |
| xW-30a | 3,1% / 1,5% | 1,9% / 0,9% |
| 10W-30 and others | 2,8% / 1,3% | 1,5% / 0,6% |
| VIF sequence (ASTM D8226) | ||
| xW-16a | 4,1% / 1,9% | 2,8% / 1,3% |
| Sequence IIIHB (ASTM D8111), % phosphorus from original oil | Minimum 81% | Minimum 79% |
Table "Differences between API SP-RC and SN-RC standards"
API motor oil classification for diesel engines
| API index | Applicability |
| CF-4 | Four-stroke internal combustion engines since 1990 |
| CF-2 | Two-stroke internal combustion engines since 1994 |
| KG-4 | Four-stroke internal combustion engines since 1995 |
| H-4 | Four-stroke internal combustion engines since 1998 |
| KI-4 | Four-stroke internal combustion engines since 2002 |
| KI-4 plus | engines 2010-2018 |
| CJ-4 | introduced in 2006 |
| SK-4 | introduced in 2016 |
| FA-4 | clock cycle diesel engines that meet 2017 emissions requirements. |
Table "Classification of engine oils according to API for diesel engines
API CF-4 standard
API CF-4 oils provide protection against carbon deposits on pistons and reduce carbon monoxide consumption. Designed for use in four-stroke diesel internal combustion engines operating at high speeds.
API CF-2 standard
API CF-2 oils are designed for use in two-stroke diesel engines. Prevents cylinder and ring wear.
API Standard CG-4
Effectively removes deposits, wear, soot, foam and high temperature piston oxidation. The main disadvantage is the dependence of the oil resource on the quality of the fuel.
API CH-4 standard
API CH-4 oils meet growing demands for reduced valve wear and carbon deposits.
API CI-4 standard
The standard was introduced in 2002. CI-4 oils have improved detergent and dispersant properties, higher resistance to thermal oxidation, lower waste consumption and better cold pumpability compared to CH-4 oils.
API CI-4 Plus Standard
Standard for diesel engines with more stringent soot requirements.
Standard CJ-4
The standard was introduced in 2006. CJ-4 oils are designed for internal combustion engines equipped with particulate filters and other exhaust gas treatment systems. Use of fuel with sulfur content up to 500 ppm is allowed.
Standard CK-4
The new standard is based entirely on the previous CJ-4 with the addition of two new engine tests, aeration and oxidation, and more stringent laboratory tests. Use of fuel with sulfur content up to 500 ppm is allowed.
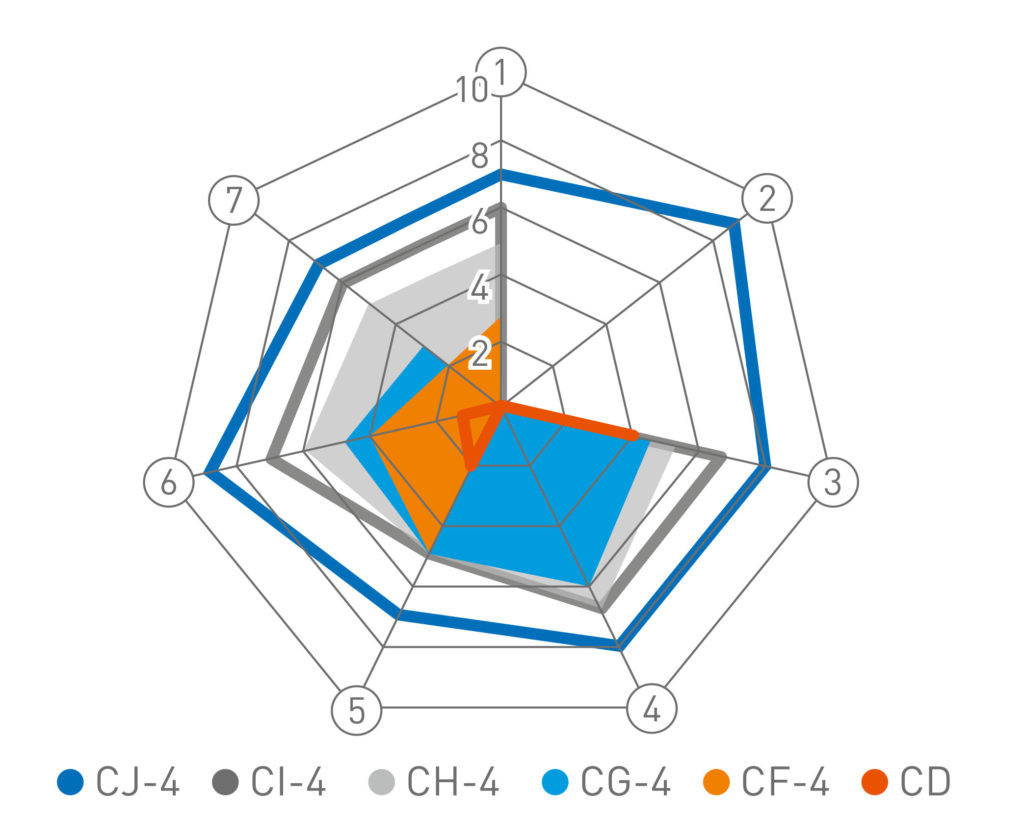
- Cylinder liner polishing protection
- Diesel Particulate Filter Compatibility
- Защита от коррозии
- Avoid oxidative thickening
- Protection against high temperature deposits
- Soot protection
- Antiwear properties
FA-4 API
Category FA-4 is designed for diesel engine oils with SAE xW-30 and HTHS viscosities from 2,9 to 3,2 cP. Such oils are specially designed for use in high-speed four-cylinder engines, have good compatibility with catalytic converters, particulate filters. Permissible sulfur content in the fuel is not more than 15 ppm. The standard is incompatible with previous specifications.
Classification of engine oils according to ACEA
ACEA is the European Automobile Manufacturers Association, which brings together the 15 largest European manufacturers of cars, trucks, vans and buses. It was founded in 1991 under the French name l'Association des Constructeurs Européens d'Automobiles. Initially, its founders were: BMW, DAF, Daimler-Benz, FIAT, Ford, General Motors Europe, MAN, Porsche, Renault, Rolls Royce, Rover, Saab-Scania, Volkswagen, Volvo Car and AB Volvo. Recently, the association opened its doors to non-European manufacturers, so now Honda, Toyota and Hyundai are also members of the organization.
The requirements of the European Association of European Automobile Manufacturers for lubricating oils far exceed those of the American Petroleum Institute. The ACEA oil classification was adopted in 1991. To obtain official approvals, the manufacturer must carry out the necessary tests in accordance with the requirements of EELQMS, a European organization responsible for the compliance of motor oils with ACEA standards and a member of ATIEL.
| Class | designation |
| Gasoline engine oils | Ax |
| Diesel engine oils up to 2,5 l | B x |
| Oils for gasoline and diesel engines equipped with exhaust gas converters | C x |
| Diesel engine oils over 2,5 liters (for heavy duty diesel trucks) | Former |
Table No. 1 "Classification of engine oils according to ACEA"
Within each class there are several categories, which are indicated by Arabic numerals (for example, A5, B4, C3, E7, etc.):
1 - energy-saving oils;
2 - widely consumed oils;
3 - high-quality oils with a long replacement period;
4 - the last category of oils with the highest performance properties.
The higher the number, the higher the requirements for oils (except for A1 and B1).
THAT 2021
The classification of ACEA engine oils in April 2021 has undergone some changes. The new specifications focus on evaluating the tendency of lubricants to leave deposits in turbocharged engines and resist LSPI pre-ignition.
ACEA A/B: full ash motor oils for gasoline and diesel engines
ACEA A1 / B1
Oils with extra low viscosity at high temperatures and high shear rates save fuel and do not lose their lubricating properties. They are used only where specifically recommended by the engine manufacturers. All motor oils, except for category A1 / B1, are resistant to degradation - destruction during operation in the engine of the polymer molecules of the thickener that is part of them.
ACEA A3 / B3
High performance oils. They are primarily used in high performance gasoline and indirect injection diesel engines in passenger cars and light trucks operating under severe conditions with long oil change intervals.
ACEA A3 / B4
High performance oils suitable for long oil change intervals. They are mainly used in high-speed gasoline engines and in diesel engines of cars and light trucks with direct fuel injection, if oils of this quality are recommended for them. By appointment, they correspond to engine oils of category A3 / B3.
ACEA A5 / B5
Oils with the highest performance properties, with an extra-long drain interval, with a fairly high degree of fuel efficiency. They are used in high-speed gasoline and diesel engines of cars and light trucks, specially designed for the use of low-viscosity, energy-saving oils at high temperatures. Formulated for use with extended engine oil drain intervals**. These oils may not be suitable for some engines. In some cases, it may not provide reliable engine lubrication, therefore, to determine the possibility of using one or another type of oil, one should be guided by the instruction manual or reference books.
ACEA A7 / B7
Stable engine oils that invariably retain their performance properties throughout their entire service life. Designed for use in engines of cars and light trucks equipped with direct fuel injection and turbocharging with extended service intervals. Like A5/B5 oils, they also provide protection against low speed premature ignition (LSPI), wear and deposits in the turbocharger. These oils are not suitable for use in some engines.
ACEA C: engine oils for gasoline and diesel engines equipped with particulate filters (GPF/DPF)
ACEA C1
Low-ash oils compatible with exhaust gas converters (including three-way) and diesel particulate filters. They belong to low-viscosity energy-saving oils. They have a low content of phosphorus, sulfur and a low content of sulphated ash. Extends the life of diesel particulate filters and catalytic converters, improves vehicle fuel efficiency**. With the release of the ACEA 2020 standard, it is not used.
ACEA C2
Medium ash oils (Mid Saps) for uprated gasoline and diesel engines of cars and light trucks, specially designed for the use of low-viscosity energy-saving oils. Compatible with exhaust gas converters (including three-component ones) and particulate filters, increases their service life, improves fuel efficiency of cars**.
ACEA C3
Stable medium ash oils compatible with exhaust gas converters (including three-component ones) and particulate filters; increase its useful life.
ACEA C4
Oils with low ash content (Low Saps) for gasoline and diesel engines designed for use with oils with HTHS>3,5 mPa*s
ACEA C5
Stable low ash oils (Low Saps) for improved fuel economy. Designed for modern gasoline and diesel engines designed for the use of low-viscosity oils with HTHS not more than 2,6 mPa*s.
ACEA C6
Oils are similar to C5. Provides additional protection against LSPI and turbocharger (TCCD) deposits.
| ACEA class | HTHS (KP) | Sulphate Ash (%) | Phosphorus content (%) | Sulfur content | Main number |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A1 / B1 | |||||
| A3 / B3 | > 3,5 | 0,9-1,5 | |||
| A3 / B4 | ≥3,5 | 1,0-1,6 | ≥10 | ||
| A5 / B5 | 2,9-3,5 | ⩽1,6 | ≥8 | ||
| A7 / B7 | ≥2,9 ≤3,5 | ⩽1,6 | ≥6 | ||
| С1 | 2,9 ≥ | ⩽0,5 | ⩽0,05 | ⩽0,2 | |
| С2 | 2,9 ≥ | ⩽0,8 | 0,07-0,09 | ⩽0,3 | |
| С3 | 3,5 ≥ | ⩽0,8 | 0,07-0,09 | ⩽0,3 | ≥6,0 |
| С4 | 3,5 ≥ | ⩽0,5 | ⩽0,09 | ⩽0,2 | ≥6,0 |
| С5 | 2,6 ≥ | ⩽0,8 | 0,07-0,09 | ⩽0,3 | ≥6,0 |
| С6 | ≥2,6 to ≤2,9 | ≤0,8 | ≥0,07 to ≤0,09 | ≤0,3 | ≥4,0 |
Table "Classification of motor oils according to ACEA for engines of passenger cars and light commercial vehicles"
ACEA E: heavy duty commercial vehicle diesel engine oils
THAT'S E2
Oils used in turbocharged and non-turbocharged diesel engines operating in medium to severe conditions with normal engine oil change intervals.
THAT'S E4
Oils for use in high-speed diesel engines that comply with Euro-1, Euro-2, Euro-3, Euro-4 environmental standards and operate under severe conditions with long engine oil change intervals. Also recommended for turbocharged diesel engines equipped with a nitrogen oxide reduction system*** and vehicles without diesel particulate filters. They provide low wear of engine parts, protection against carbon deposits and have stable properties.
THAT'S E6
Oils of this category are used in high-speed diesel engines that comply with Euro-1, Euro-2, Euro-3, Euro-4 environmental standards and operate in difficult conditions with long engine oil change intervals. Also recommended for turbocharged diesel engines with or without a diesel particulate filter when running on diesel fuel with a sulfur content of 0,005% or less***. They provide low wear of engine parts, protection against carbon deposits and have stable properties.
THAT'S E7
They are used in high-speed diesel engines that comply with Euro-1, Euro-2, Euro-3, Euro-4 environmental standards and operate in difficult conditions with long engine oil change intervals. Also recommended for turbocharged diesel engines without particulate filters, with an exhaust gas recirculation system, equipped with a nitrogen oxide emission reduction system***. They provide low wear of engine parts, protection against carbon deposits and have stable properties. Reduce the formation of carbon deposits in the turbocharger.
THAT'S E9
Low-ash oils for diesel engines of high power, meeting environmental standards up to Euro-6 inclusive and compatible with diesel particulate filters (DPF). Application at standard drain intervals.
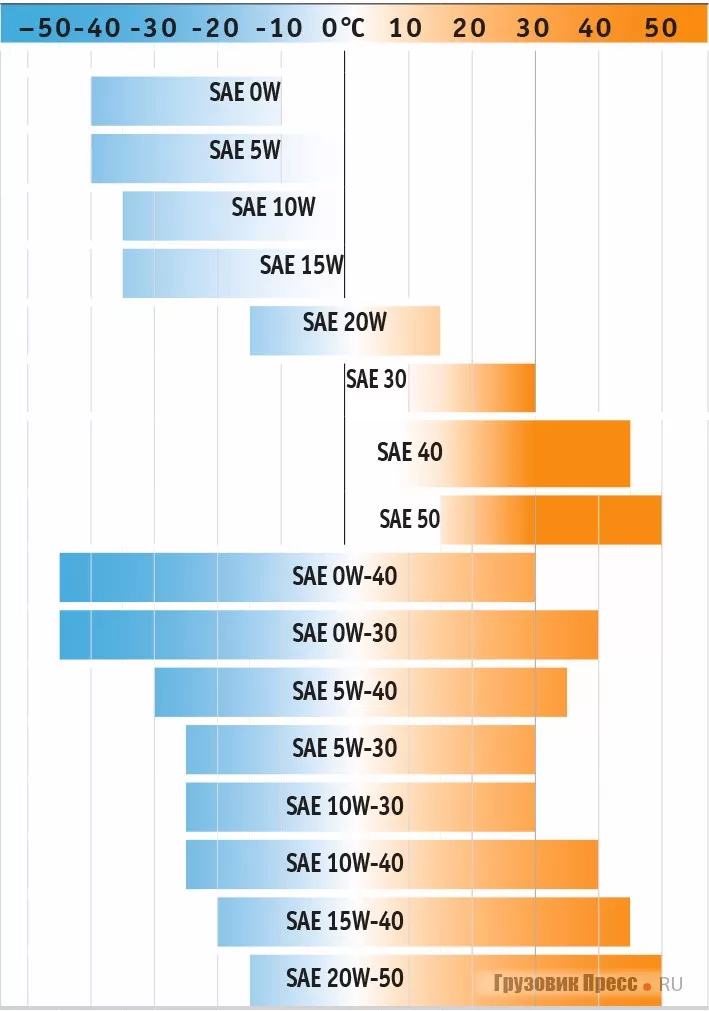
SAE classification of engine oils
The classification of motor oils by viscosity, established by the American Society of Automotive Engineers, is generally accepted in most countries of the world.
The classification contains 11 classes:
6 winter: 0 W, 5 W, 10 W, 15 W, 20 W, 25 W;
8 years: 8, 12, 16, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60.
All-weather oils have a double meaning and are written with a hyphen, denoting first the winter class, then the summer one (for example, 10W-40, 5W-30, etc.).

| SAE viscosity grade | Starting power (CCS), mPas-s | Pump performance (MRV), mPa-s | Kinematic viscosity at 100°C, not less than | Kinematic viscosity at 100°С, not higher | Viscosity HTHS, mPa-s |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 W | 6200 at -35°C | 60000 at -40°C | 3,8 | - | - |
| 5 W | 6600 at -30°C | 60000 at -35°C | 3,8 | - | - |
| 10 W | 7000 at -25°C | 60000 at -30°C | 4.1 | - | - |
| 15 W | 7000 at -20°C | 60000 at -25°C | 5.6 | — | - |
| 20 W | 9500 at -15°C | 60000 at -20°C | 5.6 | - | - |
| 25 W | 13000 at -10°C | 60000 at -15°C | 9.3 | - | - |
| 8 | - | - | 4.0 | 6.1 | 1,7 |
| 12 | - | - | 5,0 | 7.1 | 2.0 |
| sixteen | - | - | 6.1 | 8.2 | 23 |
| twenty | - | - | 6,9 | 9.3 | 2,6 |
| thirty | - | - | 9.3 | 12,5 | 2,9 |
| 40 | - | - | 12,5 | 16,3 | 2,9* |
| 40 | - | - | 12,5 | 16,3 | 3,7** |
| fifty | - | - | 16,3 | 21,9 | 3,7 |
| 60 | - | - | 21,9 | 26.1 | 3,7 |
Classification of motor oils according to ILSAC
The Japan Automobile Manufacturers Association (JAMA) and the American Automobile Manufacturers Association (AAMA) have jointly established the International Lubricant Standardization and Approval Committee (ILSAC). The purpose of the creation of ILSAC was to tighten the requirements for manufacturers of motor oils for gasoline engines.
Oils that meet ILSAC requirements have the following characteristics:
- reduced oil viscosity;
- reduced tendency to foam (ASTM D892/D6082, sequence I-IV);
- reduced phosphorus content (to extend the life of the catalytic converter);
- improved filterability at low temperatures (GM test);
- increased shear stability (oil performs its functions even at high pressure);
- improved fuel economy (ASTM test, Sequence VIA);
- low volatility (according to NOACK or ASTM);
| Category | Description |
| GF-1 | Introduced in 1996. Meets API SH requirements. |
| GF-2 | Introduced in 1997. Meets API SJ requirements. |
| GF-3 | Introduced in 2001. API SL compliant. |
| GF-4 | Introduced in 2004. Conforms to the API SM standard with mandatory energy saving properties. SAE viscosity grades 0W-20, 5W-20, 5W-30 and 10W-30. Compatible with catalysts. Possesses the increased resistance to oxidation, the general improved properties. |
| GF-5 | Introduced October 1, 2010 Conforms to API SN. Energy saving increase by 0,5%, improvement of anti-wear properties, reduction of sludge formation in the turbine, reduction of carbon deposits in the engine. Can be used in internal combustion engines running on biofuels. |
| GF-6A | Introduced May 1, 2020. It belongs to the API SP resource saving category, provides the consumer with all its benefits, but refers to multigrade oils in SAE viscosity classes: 0W-20, 0W-30, 5W-20, 5W-30 and 10W-30. Back Compatibility |
| GF-6B | Introduced May 1, 2020. Applies to SAE 0W-16 engine oils only and is not backward compatible with API and ILSAC categories. |
Classification of motor oils according to ILSAC
ILSAC GF-6 standard
The standard was introduced on May 1, 2020. Based on API SP requirements and includes the following enhancements:
- fuel economy;
- support fuel economy;
- preservation of motor resource;
- LSPI protection.
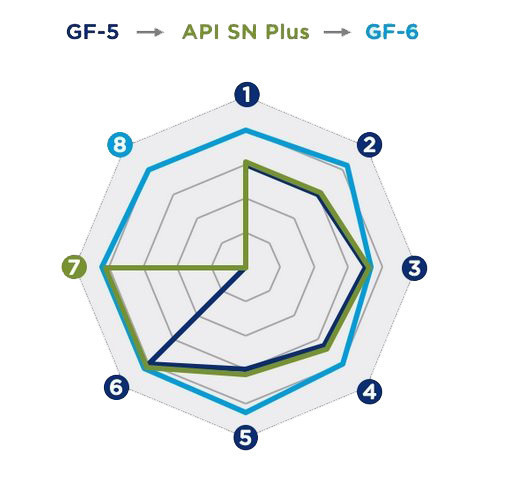
- Piston Cleaning (Seq III)
- Oxidation control (Seq III)
- Export protection cap (Seq IV)
- Engine deposit protection (Seq V)
- Fuel economy (Se VI)
- Corrosive wear protection (Seq VIII)
- Low speed pre-ignition (Seq IX)
- Timing Chain Wear Protection (Seq X)
Class ILSAC GF-6A
It belongs to the API SP resource saving category, provides the consumer with all its benefits, but refers to multigrade oils in SAE viscosity classes: 0W-20, 0W-30, 5W-20, 5W-30 and 10W-30. Back Compatibility
ILSAC class GF-6B
Applies to SAE 0W-16 viscosity grade motor oils only and is not backward compatible with API and ILSAC categories. For this category, a special certification mark has been introduced - "Shield".
JASO classification for heavy duty diesel engines
| JASO DH-1 | Class of oils for diesel engines of trucks, providing prevention wear resistance, corrosion protection, resistance to oxidation and the negative effects of oil soot recommended for engines not equipped with a diesel particulate filter (DPF) permissible operation on an engine running on fuel with a sulfur content of more than 0,05%. |
| JASO DH-2 | A class of oils for diesel engines of trucks equipped with aftertreatment systems such as diesel particulate filters (DPF) and catalysts. Oils belong to the class JASO DH-1 to protect the engine against wear, deposits, corrosion and soot. |
Table "JASO Classification for Heavy Duty Diesel Engines"
Engine Oil Specifications for Caterpillar Engines
| EKF-3 | Low ash engine oils for the latest Caterpillar engines. Compatible with diesel particulate filters (DPF). Based on API CJ-4 requirements plus additional testing by Caterpillar. Meets requirements for Tier 4 engines. |
| EKF-2 | Engine oil grade for Caterpillar equipment, including engines equipped with ACERT and HEUI systems. Based on API CI-4 requirements plus additional engine testing Caterpillar. |
| ECF-1а | Engine oil grade for Caterpillar equipment, including engines equipped with ACERT and HEUI. Based on API CH-4 requirements plus additional Caterpillar testing. |
Table "Engine oil specifications for Volvo engines"
Engine oil specifications for Volvo engines
| VDS-4 | Low ash engine oils for the latest Volvo engines, including Tier III. Compatible with diesel particulate filters (DPF). Complies with API CJ-4 performance level. |
| VDS-3 | Engine oils for Volvo engines. The specification is based on the ACEA E7 requirements, but has additional requirements for high temperature deposit formation and protection of cylinders from polishing. In addition, the specification implies passing additional tests of Volvo engines. |
| VDS-2 | Engine oils for Volvo engines. The specification confirms that Volvo engines have successfully passed field tests under more severe conditions. |
| YOU | Engine oils for Volvo engines. Includes API CD/CE specifications as well as field testing of Volvo engines. |
Table "Engine oil specifications for Volvo engines" 
- Cylinder liner polishing protection
- Diesel Particulate Filter Compatibility
- Защита от коррозии
- Avoid oxidative thickening
- Protection against high temperature deposits
- Soot protection
- Antiwear properties
Engine Oil Specifications for Cummins Engines
| KES 20081 | Oil standard for heavy duty diesel engines equipped with EGR exhaust gas recirculation systems. Compatible with diesel particulate filters (DPF). Based on API CJ-4 requirements plus additional Cummins testing. |
| KES 20078 | Oil standard for high power diesel engines equipped with an EGR exhaust gas recirculation system. Based on API CI-4 requirements plus additional Cummins testing. |
| KES 20077 | Oil standard for heavy duty diesel engines not equipped with EGR, operating under severe conditions outside North America. Based on ACEA E7 requirements plus additional Cummins testing. |
| KES 20076 | Oil standard for high power diesel engines not equipped with an EGR exhaust gas recirculation system. Based on API CH-4 requirements plus additional Cummins testing. |
Table "Characteristics of engine oils for Cummins engines"
