Renault FT-17 light tank
Renault FT-17 light tank
The history of the creation of the Renault FT tankThe idea of creating a light tank during the First World War had important production, economic and operational justifications. The adoption of light vehicles of a simplified design, with an automobile engine and a small number of crews, was to quickly establish the mass production of a new combat weapon. In July 1916, Colonel J.-B. Etienne returned from England, where he got acquainted with the work of British tank builders, and once again met with Louis Renault. And he managed to convince Renault to take on the design of a light tank. Etienne believed that such vehicles would be needed as an addition to medium tanks and would be used as command vehicles, as well as for direct escort of attacking infantry. Etienne promised Renault an order for 150 cars, and he set to work.
The first wooden model of the char mitrailleur (“machine-gun machine”) was ready by October. The commander's model of the Schneider CA2 tank was taken as a basis, and Renault quickly produced a prototype weighing 6 tons with a crew of 2 people. The armament consisted of a machine gun, and the maximum speed was 9,6 km / h.
December 20 in the presence of members Advisory Committee on Special Forces Artillery the designer himself tested the tank, which he did not like because he had only machine-gun armament. Although Etienne, counting on the tanks to act against manpower, offered precisely machine-gun weapons. The low weight and dimensions were criticized, because of which the tank, allegedly, could not overcome trenches and ditches. However, Renault and Etienne were able to convince the committee members of the advisability of continuing the work. In March 1917, Renault received an order for 150 light combat vehicles.
Demonstration November 30, 1917 On April 9, official tests were carried out, which ended in complete success, and the order was increased to 1000 tanks. But the Minister of Armaments demanded to place two people in the tower and increase the internal volume of the tank, so he suspended the order. However, there was no time, the front needed a large number of light and cheap combat vehicles. The commander-in-chief was in a hurry with the construction of light tanks, and it was too late to change the project. And it was decided to put a 37-mm cannon on some of the tanks instead of a machine gun.
Etienne proposed to include in the order a third version of the tank - a radio tank (because he believed that every tenth Renault tank should be made as command and communication vehicles between tanks, infantry and artillery) - and increase production to 2500 vehicles. The commander-in-chief not only supported Etienne, but also increased the number of ordered tanks to 3500. This was a very large order that Renault alone could not handle - therefore, Schneider, Berliet and Delaunay-Belleville were involved .
It was planned to release:
The ratio of order and production of tanks as of October 1, 1918
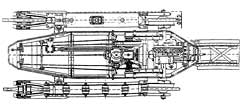
The first tanks were produced with an octagonal riveted turret, the armor of which did not exceed 16 mm. it was impossible to establish the production of a cast turret with an armor thickness of 22 mm; the development of the gun mounting system also took quite a long time. By July 1917, the prototype of the Renault cannon tank was ready, and on December 10, 1917, the first “radio tank” was built. From March 1918, new tanks began to enter the French army until the end The First World War she received 3187 cars. Undoubtedly, the design of the Renault tank is one of the most outstanding in the history of tank building. Renault's layout: engine, transmission, drive wheel at the rear, control compartment at the front, fighting compartment with a rotating turret in the center - is still a classic; for 15 years, this French tank served as a model for the creators of light tanks. Its hull, unlike the tanks of France of the First World War "Saint-Chamond" and "Schneider", was a structural element (chassis) and was a frame of corners and shaped parts, to which armor plates and chassis parts were attached with rivets. Back – Forward >> | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||


 The tank, hastily developed and put into production at the height of the First World War, for more than a quarter of a century performing combat missions from Western France to the Far East and from Finland to Morocco, is a very impressive characteristic of the Renault FT-17. The classic layout scheme and the first very successful (for its time) implementation of the “tank formula”, the combination of optimal operational, combat and production indicators put the Renault FT tank among the most outstanding designs in the history of technology. Light tank received an official name "Char leger Renault FT models 1917"abbreviated
The tank, hastily developed and put into production at the height of the First World War, for more than a quarter of a century performing combat missions from Western France to the Far East and from Finland to Morocco, is a very impressive characteristic of the Renault FT-17. The classic layout scheme and the first very successful (for its time) implementation of the “tank formula”, the combination of optimal operational, combat and production indicators put the Renault FT tank among the most outstanding designs in the history of technology. Light tank received an official name "Char leger Renault FT models 1917"abbreviated