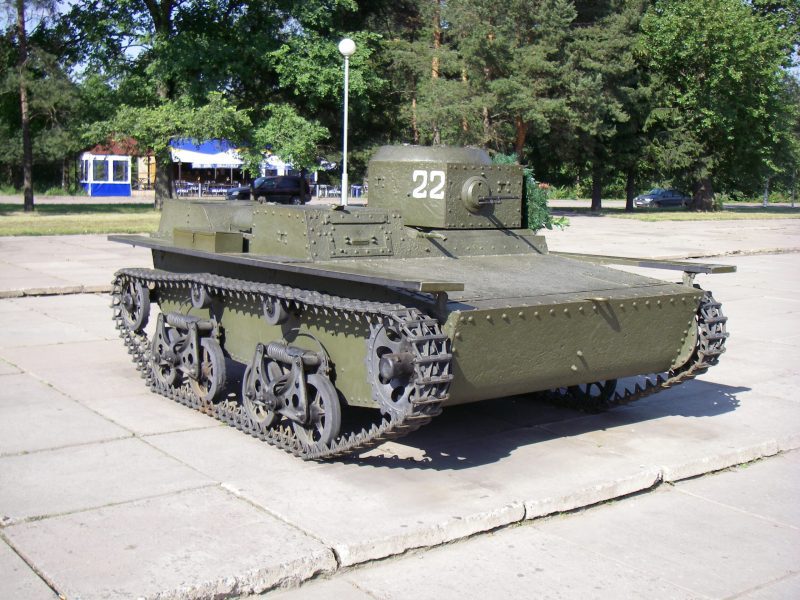
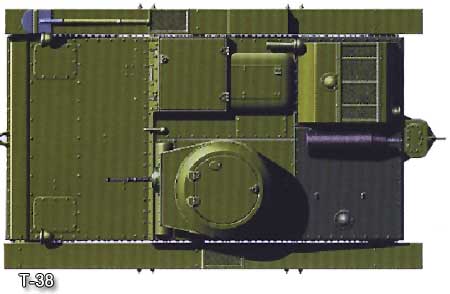
Small amphibious tank T-38
Small amphibious tank T-38
Welding was widely used in the production of the tank. The vehicle entered service with the Red Army in February 1936 and was in production until 1939. In total, the industry produced 1382 T-38 tanks. They were in service with tank and reconnaissance battalions of rifle divisions, reconnaissance companies of individual tank brigades. It should be noted that at that time none of the armies of the world had such tanks.
The operation of amphibious tanks in the troops revealed a large number of shortcomings and shortcomings in them. It turned out that the T-37A has an unreliable transmission and chassis, the tracks often fall off, the cruising range is low, and the buoyancy margin is insufficient. Therefore, the design bureau of plant # 37 was given an assignment to design a new amphibious tank based on the T-37A. Work began at the end of 1934 under the leadership of the new chief designer of the plant, N. Astrov. When creating a combat vehicle, which received the factory index 09A, it was supposed to eliminate the identified shortcomings of the T-37A, mainly to increase the reliability of the units of the new amphibious tank. In June 1935, a prototype of the tank, which received the army index T-38, went for testing. When designing a new tank, the designers tried, whenever possible, to use elements of the T-37A, by this time well mastered in production. The layout of the amphibious T-38 was similar to the T-37A tank, but the driver was placed on the right and the turret on the left. At the disposal of the driver there were inspection slits in the windshield and the right side of the hull.
The undercarriage was in many ways identical to the T-37A amphibious tank, from which the design of the suspension bogies and tracks was borrowed. The design of the drive wheel was slightly changed, and the guide wheel became identical in size to the track rollers (with the exception of the bearings).
The new car had a large number of shortcomings. For example, according to a report from factory No. 37 to the ABTU of the Red Army, from July 3 to July 17, 1935, the T-38 was tested only four times, the rest of the time the tank was under repair. Intermittently, tests of the new tank went on until the winter of 1935, and on February 29, 1936, by a decree of the Council of Labor and Defense of the USSR, the T-38 tank was adopted by the Red Army instead of the T-37A. In the spring of the same year, mass production of the new amphibian began, which until the summer went in parallel with the release of the T-37A.
The serial T-38 was somewhat different from the prototype - an additional road wheel was installed in the undercarriage, the design of the hull and the driver's hatch slightly changed. Armored hulls and turrets for T-38 tanks came only from the Ordzhonikidze Podolsky plant, which by 1936 managed to establish their production in the required quantity. In 1936, welded turrets manufactured by the Izhora plant were installed on a small number of T-38s, the backlog of which remained after the cessation of production of the T-37A.
In the fall of 1936, at the NIBT proving ground, it was tested for the warranty mileage serial amphibious tank T-38 with carts of a new type. They were distinguished by the absence of a piston inside a horizontal spring, and in order for the guide rod not to come out of the tube in the event of a possible unloading of the rollers, a steel cable was attached to the cart brackets. During tests in September - December 1936, this tank covered 1300 kilometers on roads and rough terrain. The new bogies, as noted in the documents, "proved to work well, showing a number of advantages over the previous design."
The conclusions contained in the T-38 test report stated the following: “The T-38 tank is suitable for solving independent tactical tasks. However, to increase the dynamics, it is necessary to install the M-1 engine. In addition, deficiencies must be eliminated: the track falls off when driving over rough terrain, insufficient suspension damping, crew jobs are unsatisfactory, the driver has insufficient visibility to the left.” From the beginning of 1937, a number of changes were introduced into the design of the tank: an armored bar was installed on the viewing slot in the driver's frontal shield, which prevented lead splashes from entering the tank when firing a rifle and machine gun, a new model of bogies (with a steel cable) were used in the undercarriage. ... In addition, a radio version of the T-38, equipped with a 71-TK-1 radio station with a whip antenna, went into production. The antenna input was located on the upper front sheet of the hull between the driver's seat and the turret.
In the spring of 1937, the production of T-38 amphibious tanks was suspended - a large number of complaints were received from the troops for a new combat vehicle. After the summer maneuvers of 1937, given in the Moscow, Kiev and Belorussian military districts, the leadership of the Armored Directorate of the Red Army instructed the design bureau of the plant to modernize the T-38 tank. The modernization was supposed to be as follows:
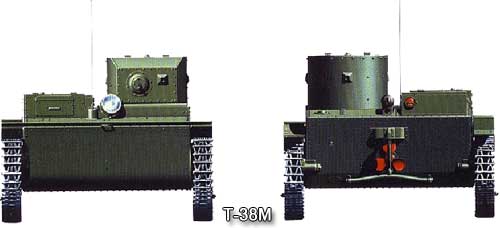
Work on the creation of new models of the T-38 was rather slow. In total, two prototypes were made, which received the designations T-38M1 and T-38M2. Both tanks had GAZ M-1 engines with a power of 50 hp. and carts from the Komsomolets tractor. Between themselves, the cars had minor differences.
The T-38M2 hull was increased by 75 mm, providing an increase in displacement of 450 kg, the sloth remained in the same place, there was no radio station on the car. In all other respects, the T-38M1 and T-38M2 were identical.
As part of the rifle and cavalry units of the Red Army (by that time there were no amphibious tanks in the tank brigades of the western military districts), the T-38 and T-37A took part in the “liberation campaign” in Western Ukraine and Belarus, in September 1939. By the beginning of hostilities with Finland. On November 30, 1939, in parts of the Leningrad Military District, there were 435 T-38s and T-37s, which actively participated in the battles. So, for example, on December 11, 18 squadrons consisting of 54 T-38 units arrived on the Karelian Isthmus. The battalion was attached to the 136th Rifle Division, the tanks were used as mobile firing points on the flanks and in the intervals between the combat formations of the attacking infantry units. In addition, the T-38 tanks were entrusted with the protection of the command post of the division, as well as the removal of the wounded from the battlefield and the delivery of ammunition.
On the eve of World War II, the airborne corps included a tank regiment, which was to be armed with 50 T-38 units. Soviet amphibious tanks received their baptism of fire during armed conflicts in the Far East. True, they were used there in very limited quantities. So, in the units and formations of the Red Army that participated in hostilities in the area of the Khalkhin-Gol River, T-38 tanks were only in the composition of the rifle and machine gun battalion of 11 tbr (8 units) and the tank battalion of 82 sd (14 units). Judging by the reports, they turned out to be of little use both in the offensive and in the defense. During the fighting from May to August 1939, 17 of them were lost.
The main modifications of the T-38:
Sources:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

 In 1935, the T-37A tank was modernized, aimed at improving its running characteristics. While maintaining the same layout, the new tank, designated T-38, became lower and wider, which increased its stability afloat, and an improved suspension system made it possible to increase speed and ride smoothness. Instead of an automobile differential on the T-38 tank, side clutches were used as a turning mechanism.
In 1935, the T-37A tank was modernized, aimed at improving its running characteristics. While maintaining the same layout, the new tank, designated T-38, became lower and wider, which increased its stability afloat, and an improved suspension system made it possible to increase speed and ride smoothness. Instead of an automobile differential on the T-38 tank, side clutches were used as a turning mechanism.