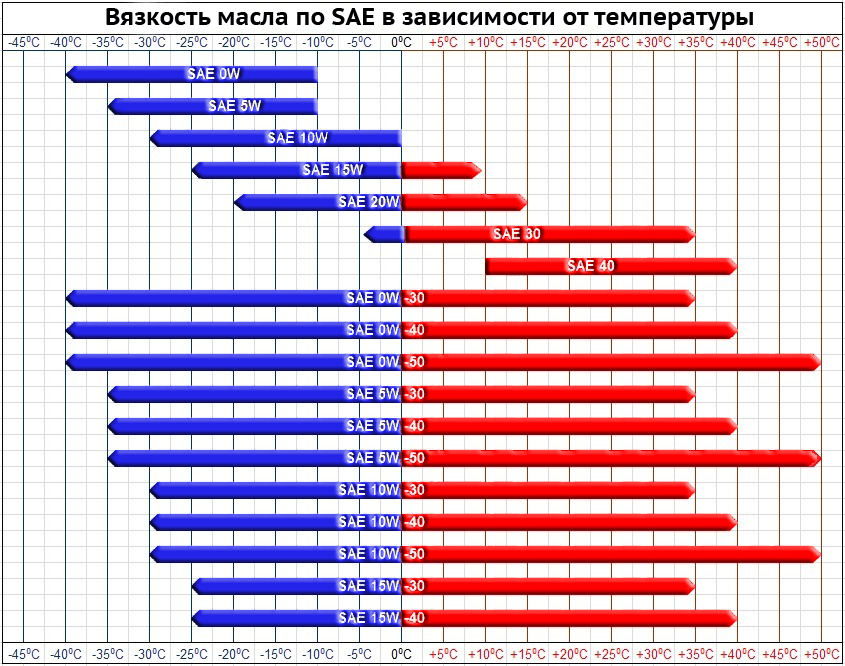
Car wheel rim marking
Content
Disc marking machine wheels are divided into two types - standard and additional. The standard includes information about the width of the rim, the type of its edge, the splitting of the rim, the mounting diameter, the annular protrusions, the offset, and so on.
As for the additional marking, it includes information on the maximum allowable load, the maximum allowable pressure in the tire, information on the methods of manufacturing the disc, information on the international certification of a particular disc. However, not every machine rim will have all of the information listed above. Most products only show some of the information listed.
Where are the markings on the discs
As for the location of the inscription on alloy wheels, usually the relevant information is indicated not like steel around the perimeter, but on the spokes or on the outside between them (in the place of the holes for mounting on the wheel). It all depends on the design of a particular disk. Typically, the inscriptions are located on the inside of the wheel spokes. Along the circumference of the hole for the hub nut, between the holes for the wheel bolts, some separate information is applied that relates to the size of the disk and its technical information.
On stamped discs, the marking is embossed on the surface from the inside or outside. There are two types of application. The first is when individual inscriptions are applied to the intermediate space between the mounting holes of the disks. In another version, the information is indicated simply along the perimeter of the rim closer to its outer edge. On cheap drives, the second option is more common.
Typical marking of rims

Marking discs for cars
When choosing new rims, many drivers face problems related to the fact that they do not know the decoding of rims, and, accordingly, do not know which ones are suitable for a particular car and which ones are not.
On the territory of the Russian Federation, the UNECE Rules apply, namely, the Technical Regulations of Russia "On the safety of wheeled vehicles" (GOST R 52390-2005 "Wheel disks. Technical requirements and test methods"). Accordingly, all the necessary information can be found in the specified official document. However, for most ordinary motorists, the information provided there will be redundant. Instead, when choosing, you need to know the basic requirements and parameters, and, accordingly, their decoding on the disk.
Alloy wheel marking
Most of the parameters listed below are relevant for alloy wheels. However, their difference from steel counterparts is that on the surface of cast disks there will additionally be an x-ray test mark, as well as a mark of the organization that carried out this test or has the appropriate permission to do so. Often they also contain additional information about the quality of the disc and its certification.
Marking of stamped discs
Labeling of disks, regardless of their types, is standardized. That is, the information itself on cast and stamped discs will be the same and simply reflect the technical information about a particular disc. Stamped discs usually contain technical information and often the manufacturer and the country where it is located.
Decoding of disc marking
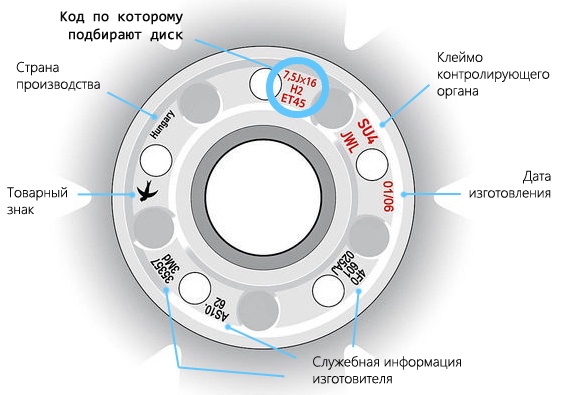
The standard marking of the wheel discs of a car is applied precisely to its surface. In order to understand what information is responsible for what, we will give a specific example. Let's say we have a machine disk with the designation 7,5 J x 16 H2 4 × 98 ET45 d54.1. We list its decoding in order.
Rim width
Rim width indicates the first number in the notation, in this case it is 7,5. This value specifies the distance between the inner edges of the rim. In practice, this means that tires that fit in width can be installed on this disc. The fact is that tires in a certain width range can be installed on any rim. That is, the so-called high-profile and low-profile. Accordingly, the width of the tires will also be different. The best option for choosing a disk for car wheels would be a tire width that is approximately in the middle of the tire value. This will allow you to install rubber with different widths and heights on the disk.
Rim Edge Type
The next marking of machine disks is the type of its edge. In accordance with European and international rules, the edge type can be designated by one of the following Latin letters - JJ, JK, K, B, D, P for passenger cars and E, F, G, H - for truck wheels. In practice, the description of each of these types is rather complicated. In each case it is about the shape or diameter of the contour of the disc, and in some cases rim angle. The specified parameter is service information, and it does not carry any useful information for a particular motorist. However, you may need this designation of the marking on the disk when you get acquainted with the requirements of the automaker and are interested in what type of edge should be on the disk for your car brand.
For example, wheels with the designation JJ are designed for SUVs. The disc with the letter P is suitable for Volkswagen cars, the disc with the letter K is for Jaguar cars. namely, the manual clearly indicates which wheels are suitable for a particular car and make a choice in accordance with the specified requirements.
Rim split
The next parameter of the rim is its detachability. In this case, there is a designation with the English letter X. This the symbol indicates that the design of the disk itself is one-piece, that is, it is a single product. If instead of the letter X, the symbol “-” is written, then this means that the rim is detachable, that is, it consists of several parts.
Most passenger car rims are one-piece. This allows you to install on them the so-called "soft" tires, that is, elastic. Split drives are usually installed on trucks or SUVs. This allows you to install hard tires on them, for which, in fact, a collapsible design was made.
Mounting diameter
After information about the splitness of the disk in the marking, there is a number indicating the diameter of the rim, in this case it is 16. It matches tire diameter. For passenger cars, the most popular diameters are 13 to 17 inches. Large discs, and accordingly, tires wider than 17'' (20-22'') are placed on cars with powerful internal combustion engines, including various SUVs, minibuses or trucks. In this case, when choosing, you need to take into account so that the diameter of the tire exactly matches the diameter of the rim.
Annular protrusions
Another name is ring rolls or humps. In this example, they have the designation H2. These are the most common discs. The information means that the design of the disk involves the use of protrusions for fixing tubeless tireslocated on both sides. This provides a more secure attachment to the disk.
If there is only one H symbol on the disc, this means that the protrusion is located on only one side of the disc. there are also several similar designations for the ledges. namely:
- FH - flat ledge (Flat Hump);
- AH - asymmetric tackle (Asymmetric Hump);
- CH - combined hump (Combi Hump);
- SL - there are no protrusions on the disc (in this case, the tire will hold on to the rim flanges).
Two humps increase the reliability of fixing the tire on the disk and reduce the likelihood of its depressurization. However, the disadvantage of the double hump is that it is more difficult to put on and take off the tire. But if you regularly use tire fitting services, this problem should not interest you.
Mounting parameters (PCD bolt pattern)
The next parameter, namely, 4×98 means that this disk has there are four mounting holes of a certain diameterthrough which it is attached to the hub. On imported rims, this parameter is referred to as PCD (Pitch Circle Diameter). In Russian, it also has the definition of "bolt pattern".
The number 4 means the number of mounting holes. In English, it has the designation LK. By the way, sometimes the mounting parameters may look like 4/98 in this example. The number 98 in this case means the value of the diameter of the circle along which the indicated holes are located.
Most modern passenger cars have four to six mounting holes. Less often you can find discs with the number of holes equal to three, eight or even ten. Typically, the diameter of the circle along which the mounting holes are located is from 98 to 139,7 mm.
Interestingly, for discs that have four mounting bolts, the PCD distance is equal to the distance between the centers of the diametrically spaced bolts or nuts. For discs equipped with five mounting bolts, the PCD value will be equal to the distance between any adjacent bolts multiplied by a factor of 1,051.
Some manufacturers produce universal rims that can be installed on various hubs. For example, 5x100/120. Accordingly, such disks are suitable for various machines. However, in practice, it is better not to use such discs, since their mechanical characteristics are less than those of ordinary ones.
Departure marking on rims
In a specific example, the symbols in the ET45 (Einpress Tief) disc marking mean the so-called departure (in English, you can also find the definition of OFFSET or DEPORT). This is a very important parameter when choosing. namely, disk departure et is distance between vertical plane, which conditionally passes in the middle of the rim and plane corresponding to the point of contact between the disk and the machine hub. There are three types of wheel offsets:
- Positive. In this case, the central vertical plane (plane of symmetry) is located farther from the center of the car body in relation to the plane of contact between the disk and the hub. In other words, the disc is the least protruding from the car body. The number 45 means the distance in millimeters between the two indicated planes.
- Negative. In this case, on the contrary, the plane of contact between the disk and the hub is further from the central plane of symmetry of the disk. In this case, the disc offset designation will have a negative value. For example, ET-45.
- Null. In this case, the plane of contact between the disk and the hub and the plane of symmetry of the disk coincide with each other. In this case, the disk contains the designation ET0.
When choosing a disc, it is very important to know the information about which discs the automaker allows to install. In some cases, it is allowed to install discs with only positive or zero overhang. Otherwise, the machine will lose stability and driving problems may begin, especially at speed. The admissible error of a departure of wheel disks makes ±2 millimeters.
Bore diameter
When choosing a disc, you will need to know what dia means in the disc label. As the name implies, the corresponding number indicates the diameter of the mounting hole on the hub in millimeters. In this case, it has the designation d54,1. Such disc insertion data is encoded in the DIA notation.
For most passenger cars, the corresponding value is usually between 50 and 70 millimeters. It must be clarified before choosing a particular disk, otherwise the disk simply cannot be installed on the machine.
On many large-diameter alloy wheels (that is, with a large DIA value), manufacturers provide for the use of adapter rings or washers (also called "arch supports") for centering on the hub. They are made of plastic and aluminum. Plastic washers are less durable, but for Russian realities they have a huge advantage. namely, they do not oxidize and do not allow the disc to stick to the hub, especially in severe frosts.
Please note that for stamped (steel) wheels, the diameter of the hole for the hub must necessarily match the recommended value prescribed by the vehicle manufacturer. This is due to the fact that steel discs do not use adapter rings.
If a cast or forged wheel is used on the car, then the diameter of the hole for the hub is determined by the size of the plastic bushing. Accordingly, it must be selected additionally for a specific car, namely, after selecting a specific disk for the car. Usually, the automaker does not install adapter rings on original machine disks, since the disks are initially made with a hole of the desired diameter.
Additional marking of disks and decoding of their designations
The parameters listed above are fundamental when choosing a disc for a car. However, on some of them you can find additional inscriptions and markings. For example:
- MAX LOAD. This abbreviation means what maximum allowable load is allowed for a particular rim. usually, the number is expressed in pounds (LB). in order to convert the value in pounds to the value in kilograms, it is enough to divide by a factor of 2,2. For example, MAX LOAD = 2000 LB = 2000 / 2,2 = 908 kilograms. That is, disks, like tires, have a load index.
- MAX PSI 50 COLD. In a specific example, the inscription means that the maximum allowable air pressure in a tire mounted on a disc must not exceed 50 pounds per square inch (PSI). For reference, a pressure equal to one kilogram-force is approximately 14 PSI. Use a calculator to convert the pressure value. That is, in this particular example, the maximum allowable pressure in the tire should not exceed 3,5 atmospheres in the metric coordinate system. And the inscription COLD, it means that the pressure must be measured in a cold tire (before the car starts moving, including not under the scorching sun).
- FORGET. This inscription means that a particular disk is made by forging (that is, forged).
- BEADLOCK. Means that the disc is equipped with the so-called tire locking system. Currently, such discs are not allowed to be used for security reasons, so they are no longer available for sale.
- BEADLOCK SIMULATOR. A similar inscription indicates that the disk contains a simulator of the tire fixation system. In this case, such disks can be used everywhere. In practice, this means that these disks are no different from ordinary ones.
- SAE/ISO/TUV. These abbreviations refer to the standards and regulatory bodies under which the discs were manufactured. On domestic tires, you can sometimes find the value of GOST or the manufacturer's specifications.
- Date of manufacture. The manufacturer indicates the corresponding date of manufacture in encrypted form. Usually it is four digits. The first two of them mean a week in a row, starting from the beginning of the year, and the second two - exactly the year of manufacture. For example, the designation 1217 indicates that the disc was made in the 12th week of 2017.
- Country of manufacture. On some discs you can find the name of the country in which the product was manufactured. Sometimes manufacturers only leave their logo on the disc or simply write the name.
Japanese wheel markings
On some discs produced in Japan, you can find the so-called JWL marking. Translated from English, the abbreviation means Japanese alloy wheels. This marking is applied only to those discs that are sold in Japan. Other manufacturers may apply the appropriate abbreviation as desired. However, if it is on the disk, it means that the disk meets the requirements of the Ministry of Land Resources, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism of Japan. By the way, for trucks and buses, a similar abbreviation will be slightly different - JWL-T.
There is also one non-standard marking − VIA. It is applied to the disc only if the product has been successfully tested in the laboratory of the Transport Inspection of Japan. The abbreviation VIA is a registered trademark. Therefore, its application to discs that have not passed the appropriate tests is punishable. Therefore, the disks on which the indicated abbreviation is applied will initially be of very high quality and durable.
How to choose a wheel rim
When choosing a particular disc, car owners often have a problem - how to choose the right disc in accordance with the available rubber. Let's take a specific example of tires marked 185/60 R14. The width of the rim, in accordance with the requirements, must be 25% less than the width of the tire profile. Accordingly, one quarter must be subtracted from the value of 185 and the resulting value converted to inches. The result is five and a half inches.
So, after the above calculations, it can be argued that for a 185/60 R14 tire, a disc with a diameter of 14 inches and a width of 5,5 ... 6,0 inches is suitable. The remaining parameters listed above must be specified in the technical documentation for the car.
Below is a table that summarizes information about standard (factory) installed disks acceptable by their manufacturers. Accordingly, for cars, you need to select wheels with suitable parameters.
| Car model | Sizes and factory rim data |
|---|---|
| Toyota Corolla 2010 release | 6Jx15 5 / 114,3 ET39 d60,1 |
| Ford Focus 2 | 5JR16 5 × 108 ET52,5 DIA 63,3 |
| Lada Grant | 13 / 5.0J PCD 4×98 ET 40 CH 58.5 or 14 / 5.5J PCD 4×98 ET 37 CH 58.5 |
| Lada Vesta 2019 release | 6Jx15 4 / 100 ET50 d60.1 |
| Hyundai Solaris 2019 release | 6Jx15 4 / 100 ET46 d54.1 |
| Kia Sportage 2015 release | 6.5Jx16 5 / 114.3 ET31.5 d67.1 |
| Kia Rio | PCD 4×100 diameter 13 to 15, width 5J to 6J, offset 34 to 48 |
| Nyva | Razboltovka - 5 × 139.7, departure - ET 40, width - 6.5 J, centering hole - CO 98.6 |
| Renault Duster 2011 | Size — 16x6,5, ET45, bolting — 5x114,3 |
| Renault Logan 2019 | 6Jx15 4 / 100 ET40 d60.1 |
| VAZ 2109 2006 | 5Jx13 4 / 98 ET35 d58.6 |
Hack and predictor Aviator
The choice of rim should be based on the technical information that the car manufacturer provides in the car's manual. namely, the dimensions of the disks allowed for installation, their types, the values of the overhangs, the diameters of the holes, and so on. On most vehicles, discs of different diameters can be installed. However, their key parameters must necessarily comply with the technical documentation.